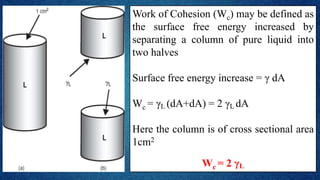
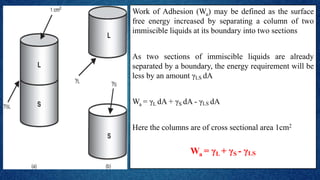
The document discusses the concept of the spreading coefficient, which determines whether a liquid, such as oleic acid, will spread on the surface of another liquid, like water. It defines key terms including work of cohesion and work of adhesion, outlining how the spreading coefficient is calculated and the conditions under which spreading occurs or does not occur. Additionally, it covers factors that affect the spreading coefficient, such as the chain length of fatty acids and alcohols, and mentions practical applications in fields like medicine and emulsification.