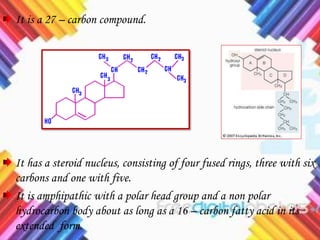
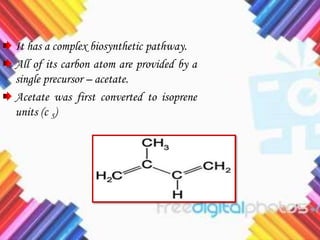
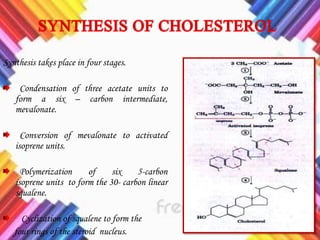
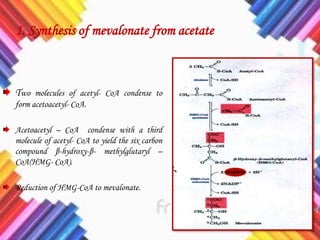
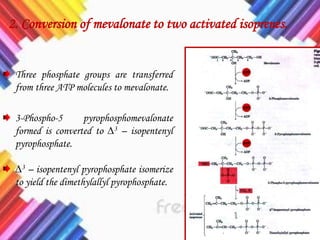
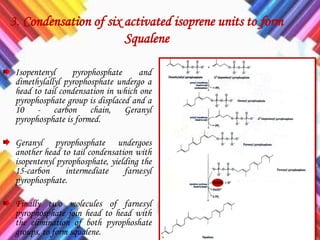
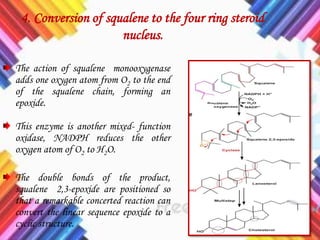
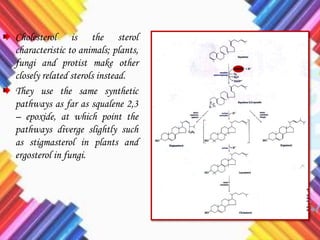
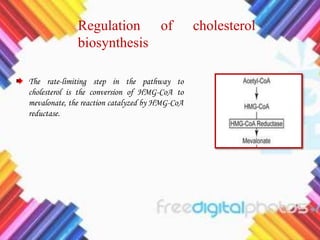
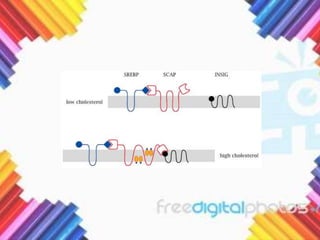
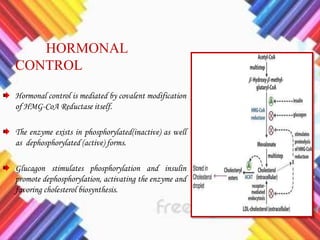
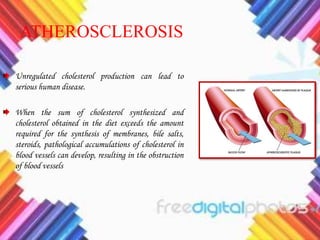
Cholesterol is a crucial molecule in animal physiology, synthesized by all cells, and plays significant roles in cell membrane structure and hormone production. Its regulation is vital, as imbalances can lead to cardiovascular diseases; low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is often termed 'bad cholesterol', while high-density lipoprotein (HDL) is considered 'good cholesterol'. The complex biosynthesis of cholesterol involves several biochemical pathways and is tightly regulated through transcriptional mechanisms and hormonal control.