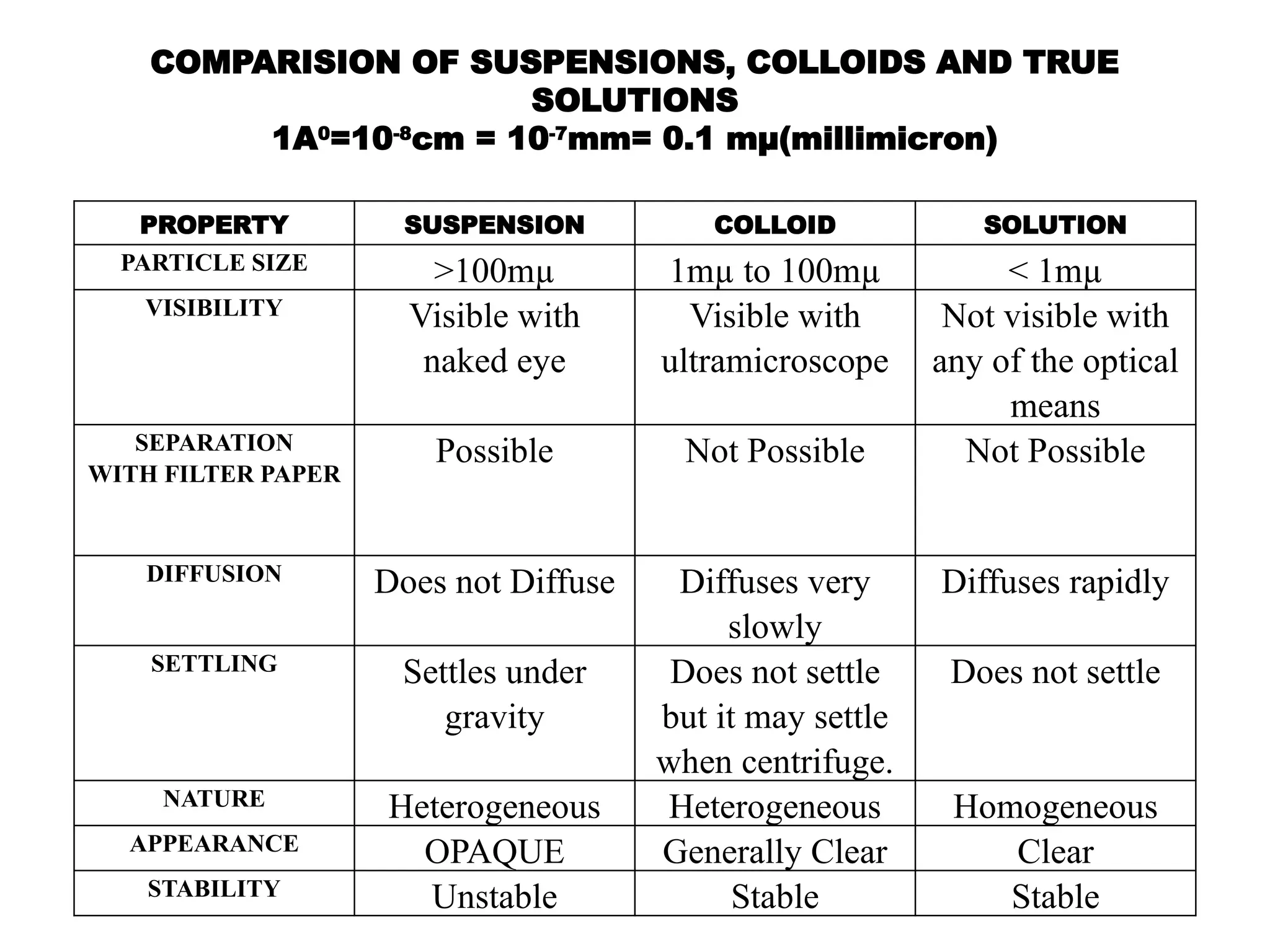
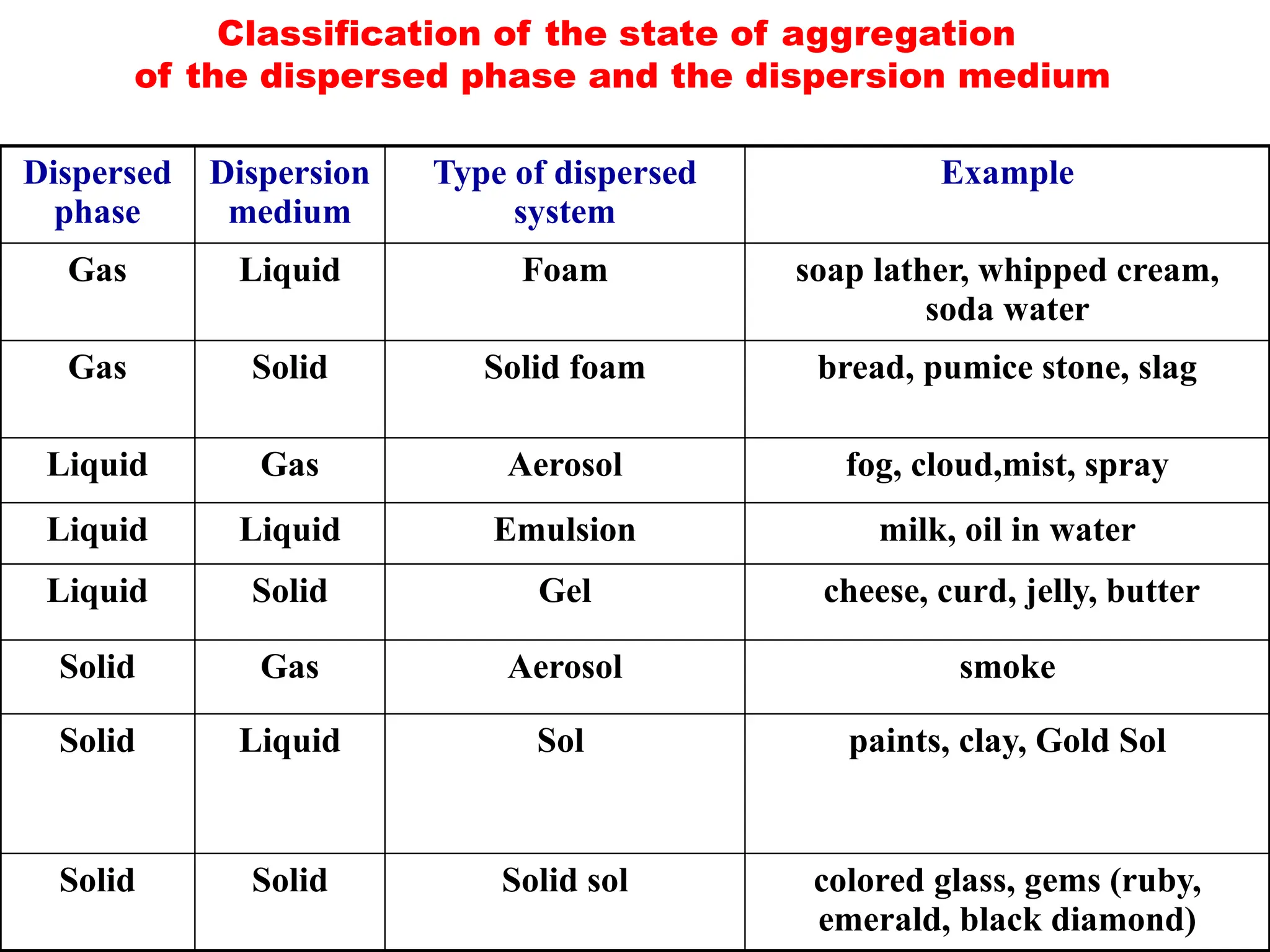
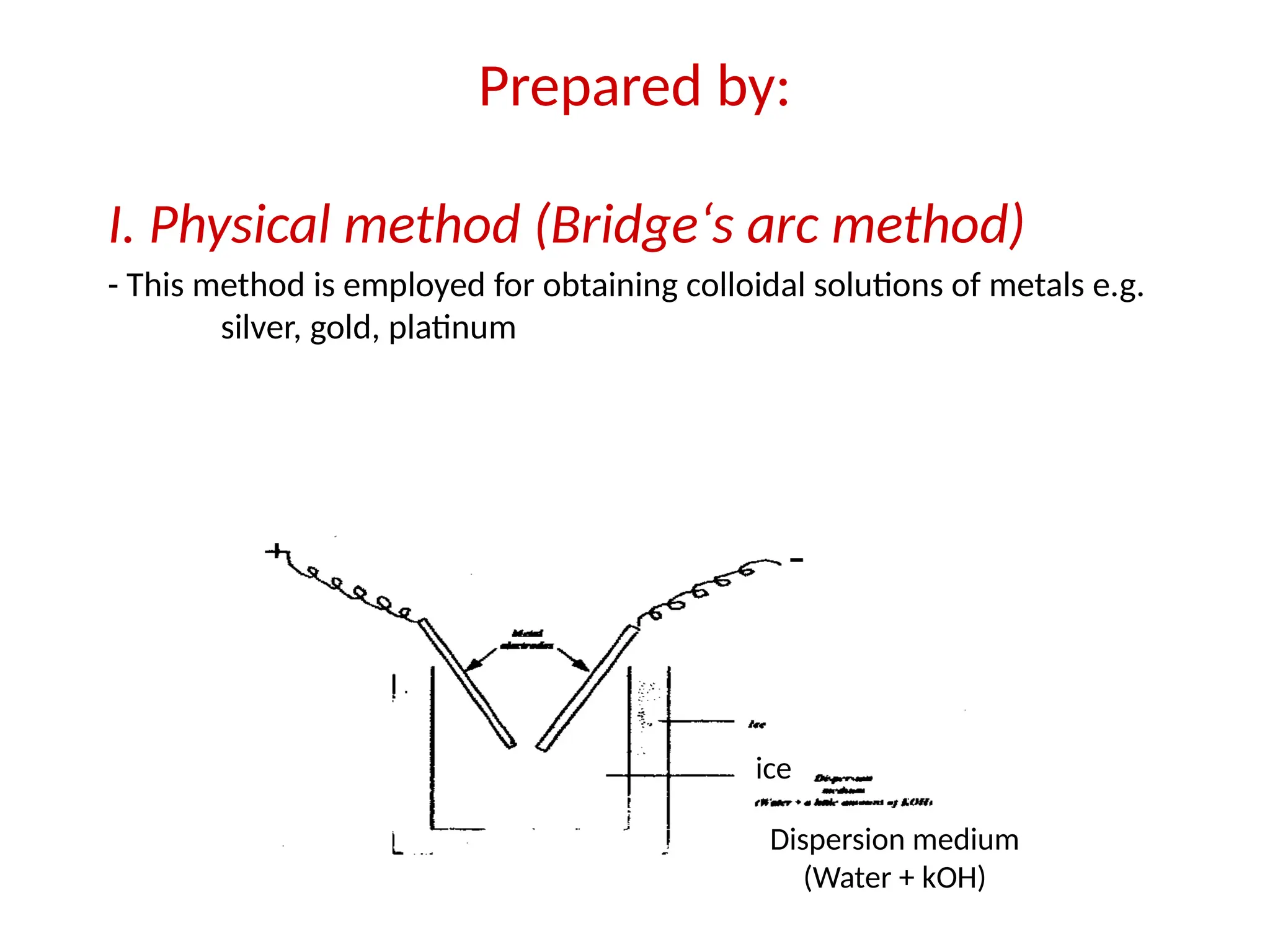
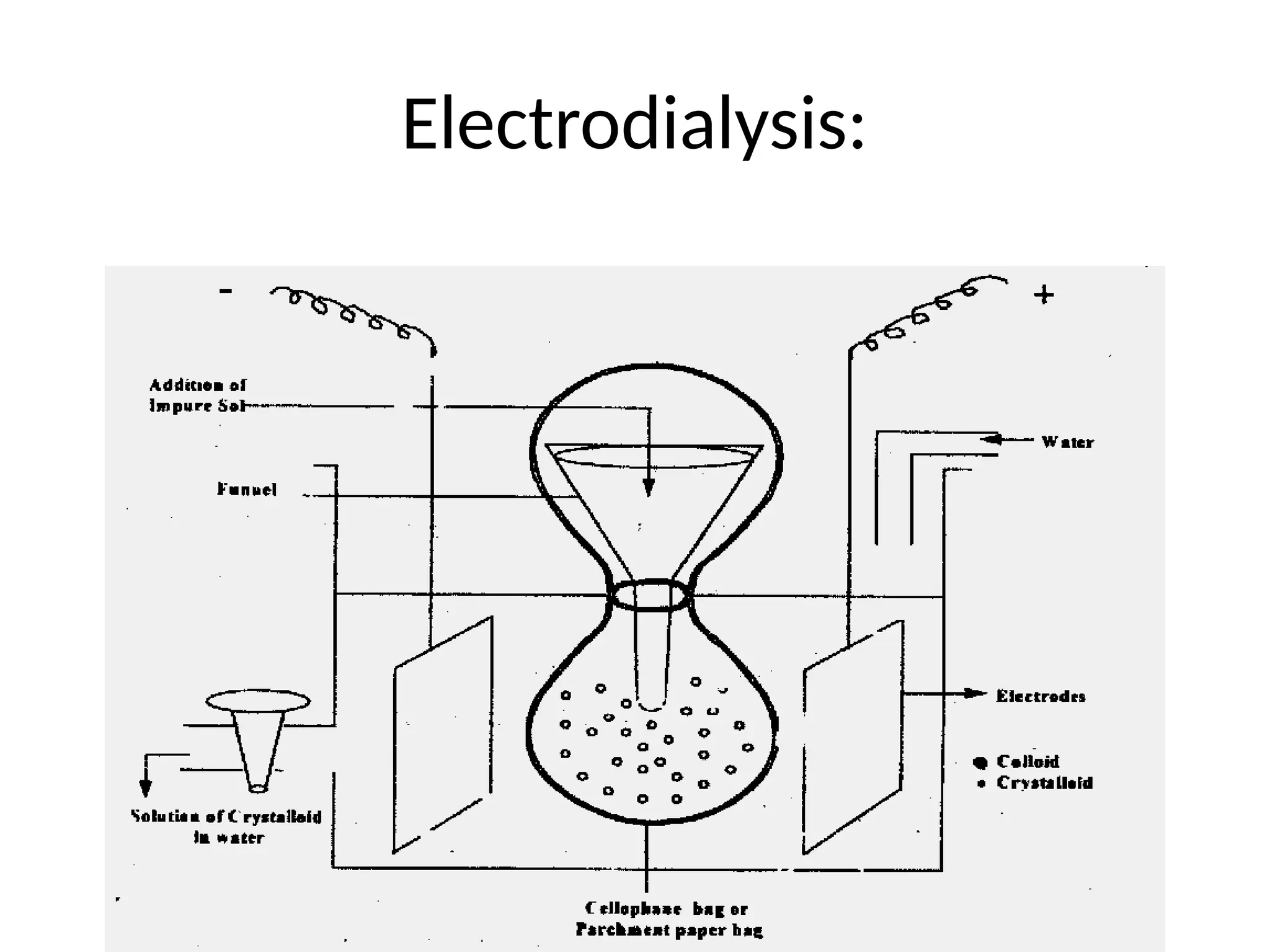
The document compares suspensions, colloids, and true solutions, highlighting their properties such as particle size, visibility, diffusion, and stability. It discusses the classification of colloids into lyophilic and lyophobic types, along with examples and applications found in nature and technology. Additionally, it describes methods for preparing and purifying colloidal solutions.