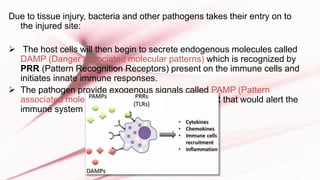
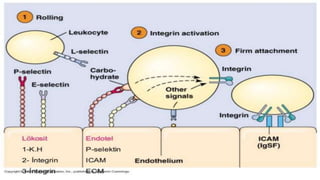
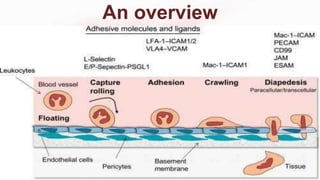
The document discusses leukocyte extravasation, the process by which leukocytes exit the bloodstream to reach sites of tissue injury or infection. It details the multistep mechanisms involved, including tethering, rolling, activation, firm adhesion, and transendothelial migration facilitated by various adhesion molecules and chemokines. The document highlights the role of selectins, integrins, and endothelial cell interactions in regulating the movement of leukocytes during inflammation.