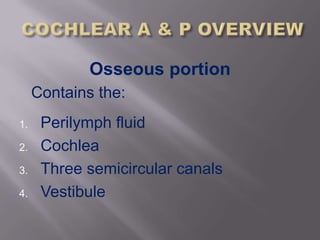
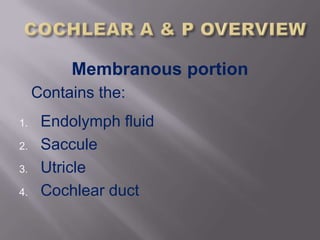
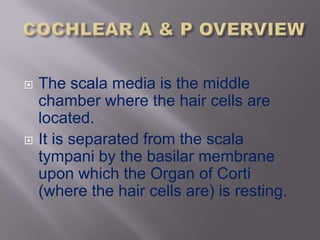
The inner ear is composed of an osseous portion containing fluid and structures like the cochlea and semicircular canals, and a membranous portion containing additional fluid and structures such as the saccule and utricle. The inner ear consists of the vestibular portion for balance and the cochlear portion for hearing, with the cochlea being a spiral shaped structure that converts sound into electrical signals through hair cells. The cochlea contains three fluid filled canals and uses traveling waves that vary in amplitude at different points along the basilar membrane to detect different frequencies of sound.