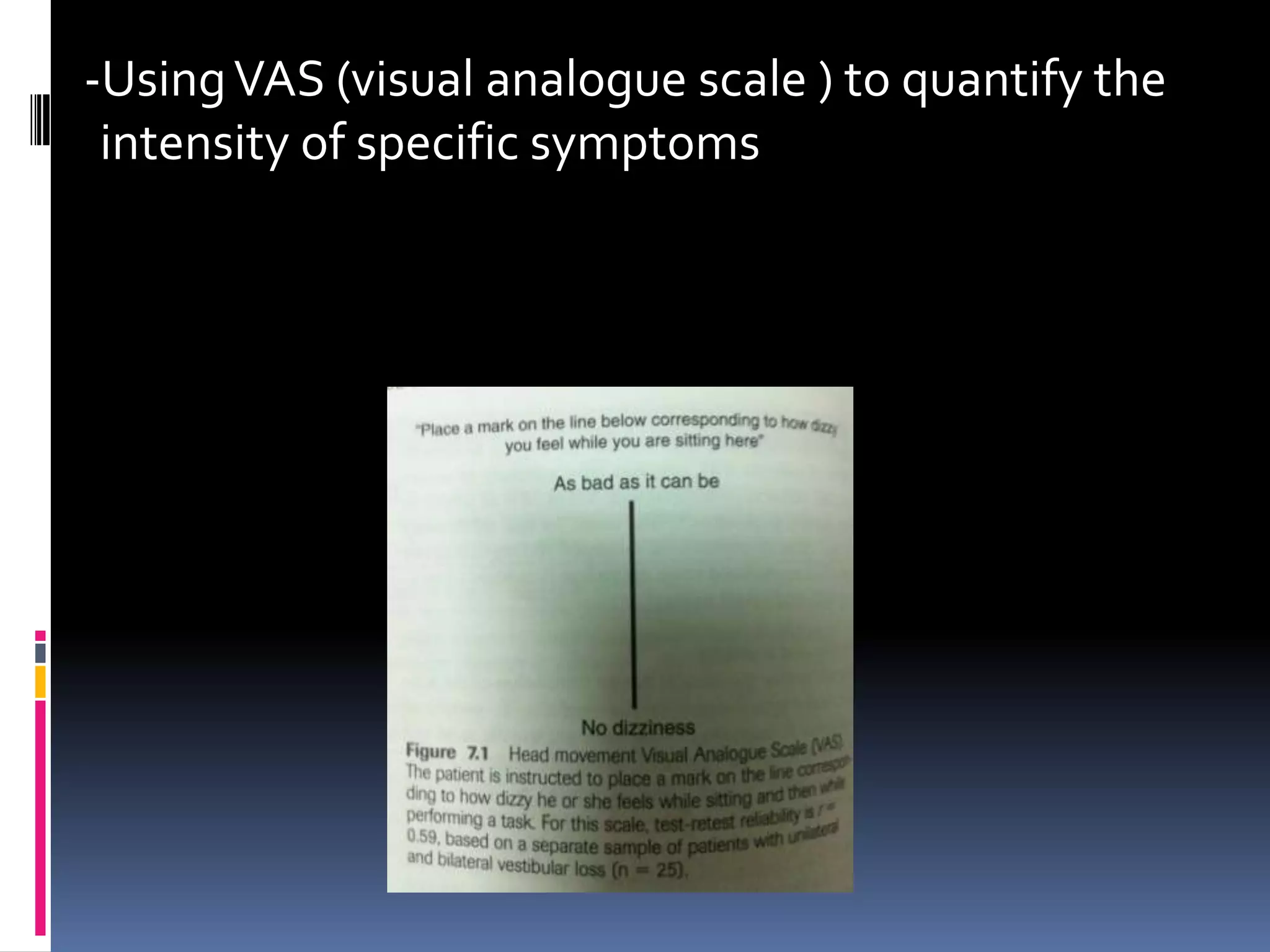
The document discusses vestibular function tests and clinical examinations, highlighting the high incidence of dizziness, particularly in older adults. It outlines the anatomy, physiology, and various examination methods including history taking, physical examinations, and laboratory tests that assist in diagnosing vestibular disorders. The importance of accurate diagnosis and management strategies aimed at minimizing functional limitations and preventing disability is emphasized.