The document provides an overview of the physiology of hearing. It discusses:
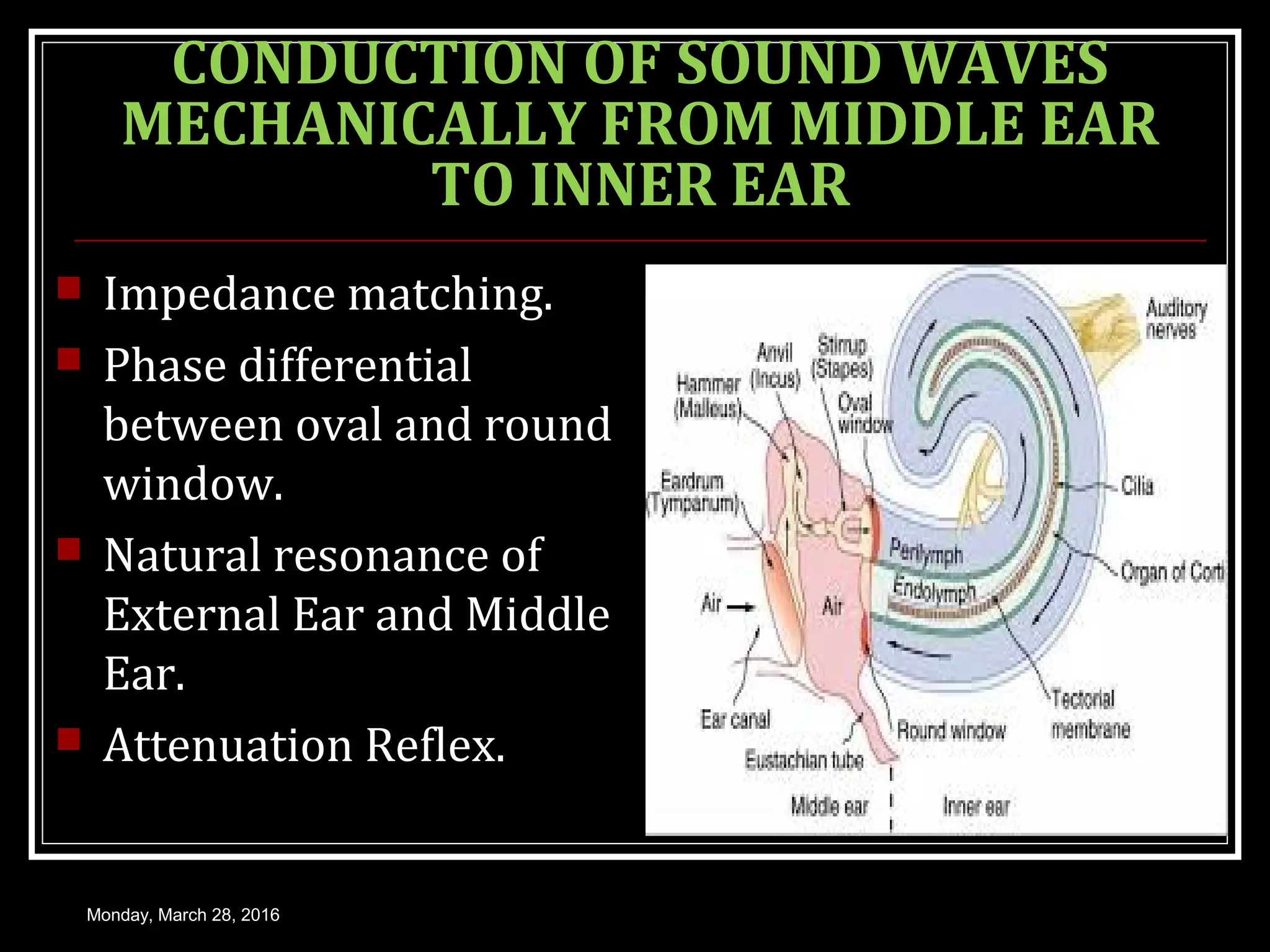
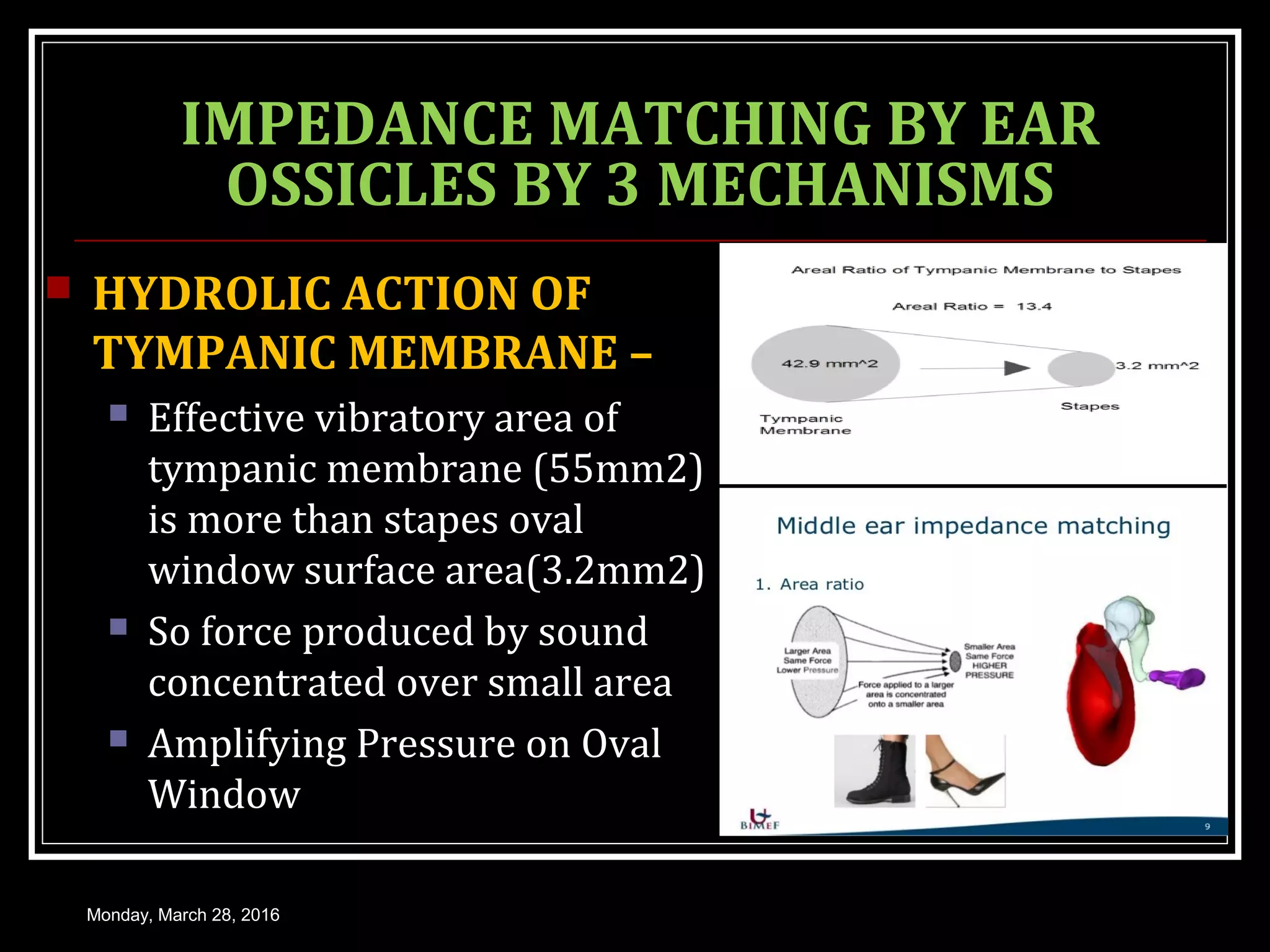
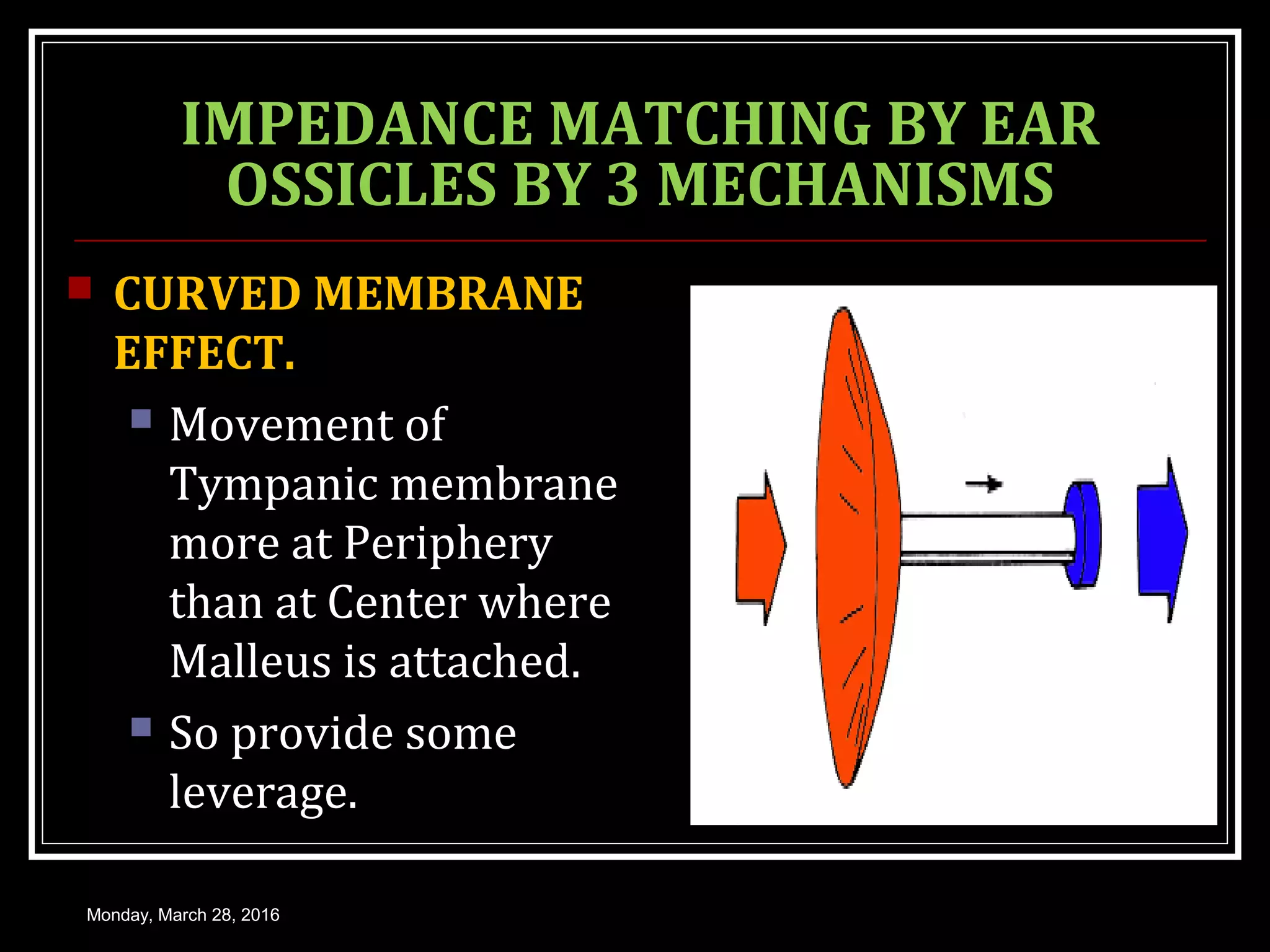
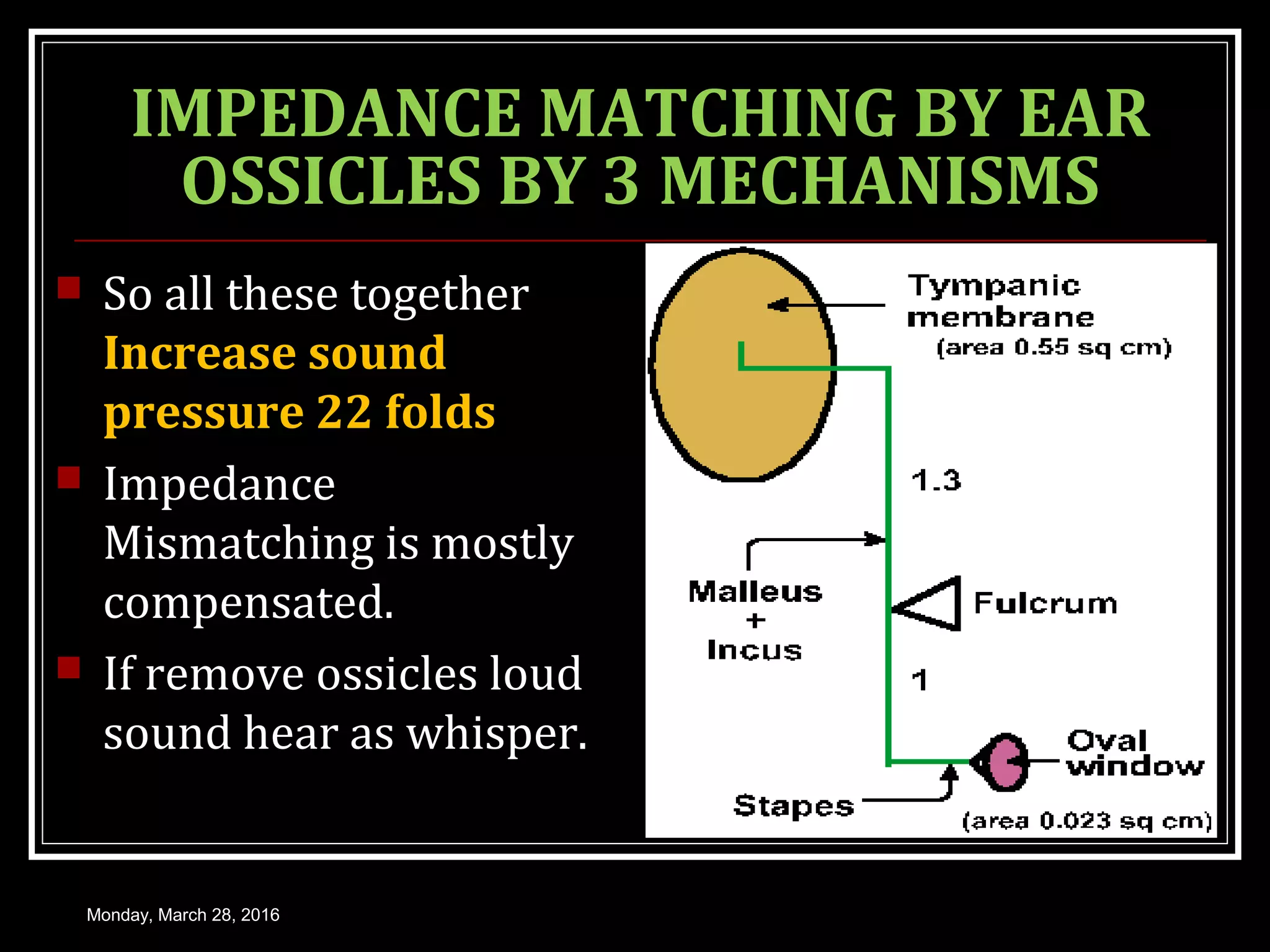
1) How sound waves are conducted through the external ear, middle ear bones, and inner ear fluid. The middle ear bones provide impedance matching to transmit sounds to the inner ear.
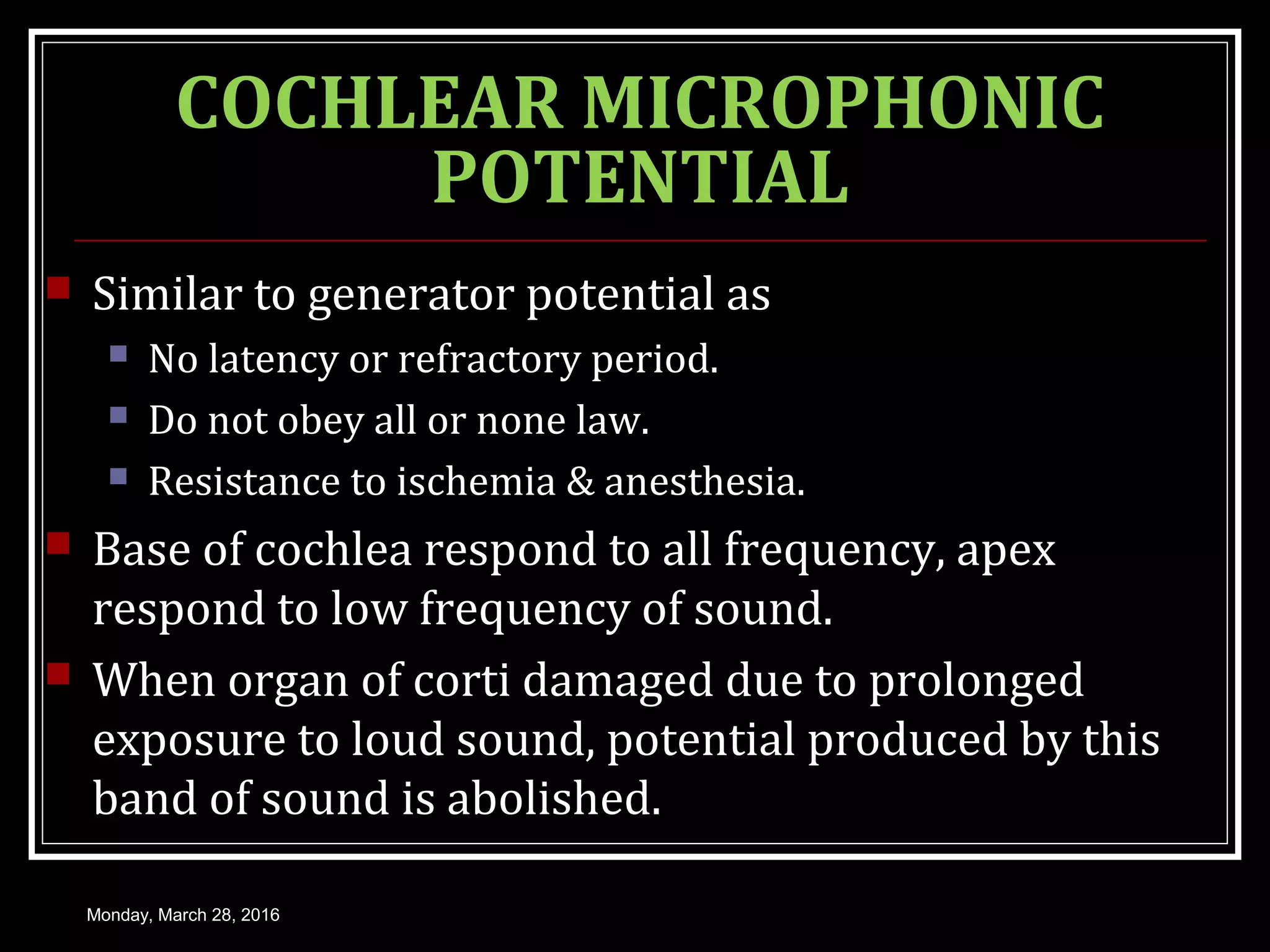
2) In the inner ear, sound causes the basilar membrane to vibrate, stimulating hair cells. This leads to a change in the hair cell membrane potential and the generation of action potentials in the auditory nerve.
3) Neural signals are transmitted from the cochlear nuclei to the auditory cortex through several structures in the brainstem and thalamus. The auditory pathway shows tonotopic organization and hemispheric specialization for