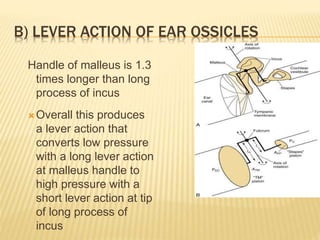
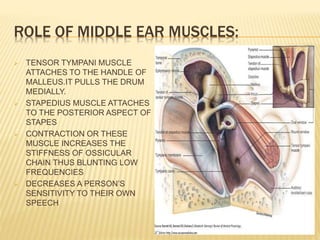
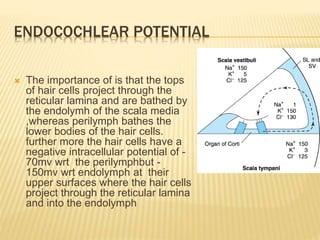
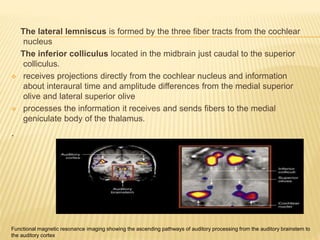
The document discusses the physiology of hearing. It covers the key components required for normal hearing including sound conduction through the ear canal, middle ear, and inner ear. The middle ear acts as an impedance matcher and sound intensity transducer. The cochlea contains hair cells that transduce sound waves into neural signals. The basilar membrane varies in width and stiffness along its length to allow different frequencies to stimulate separate regions of the cochlea.