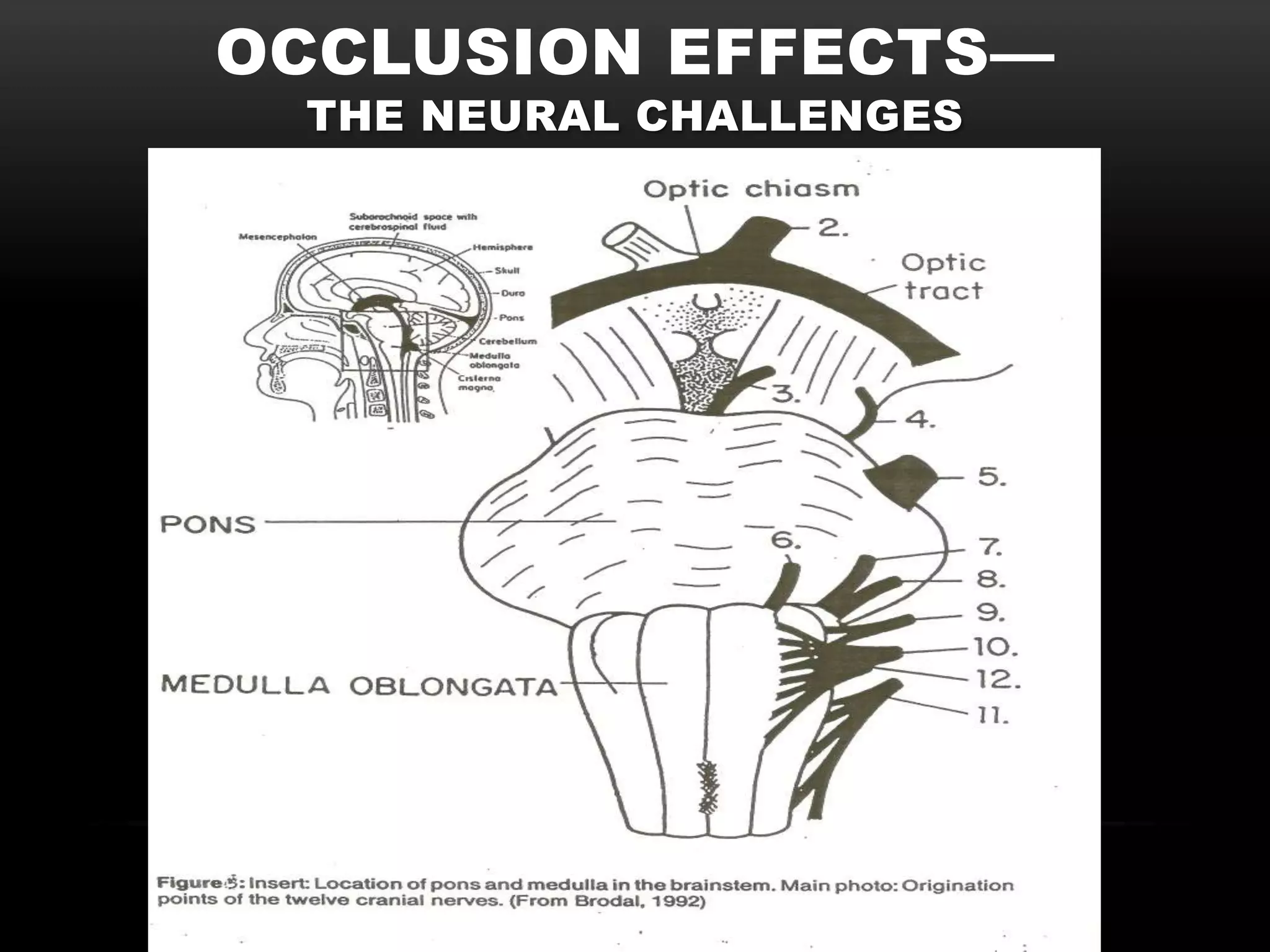
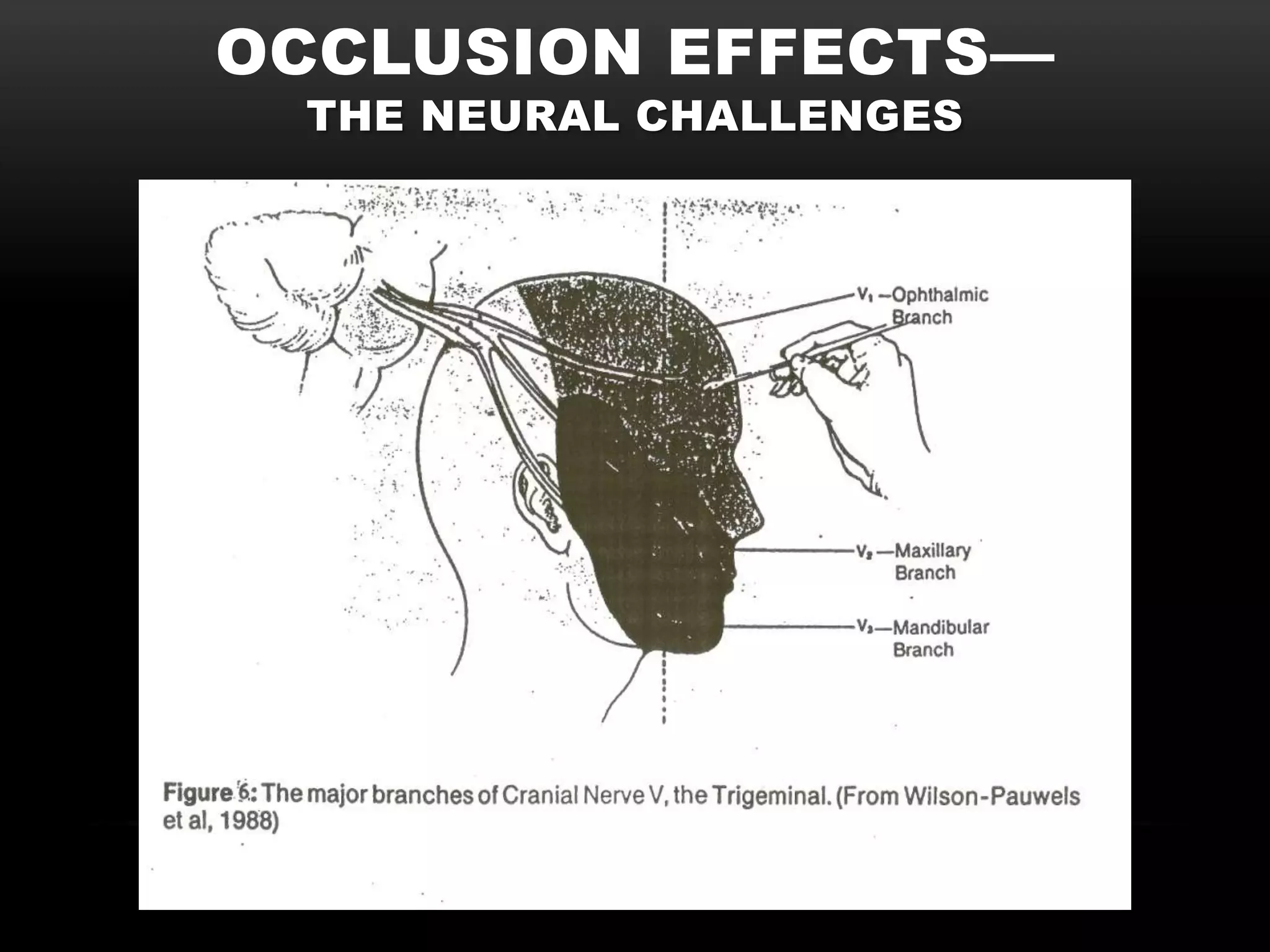
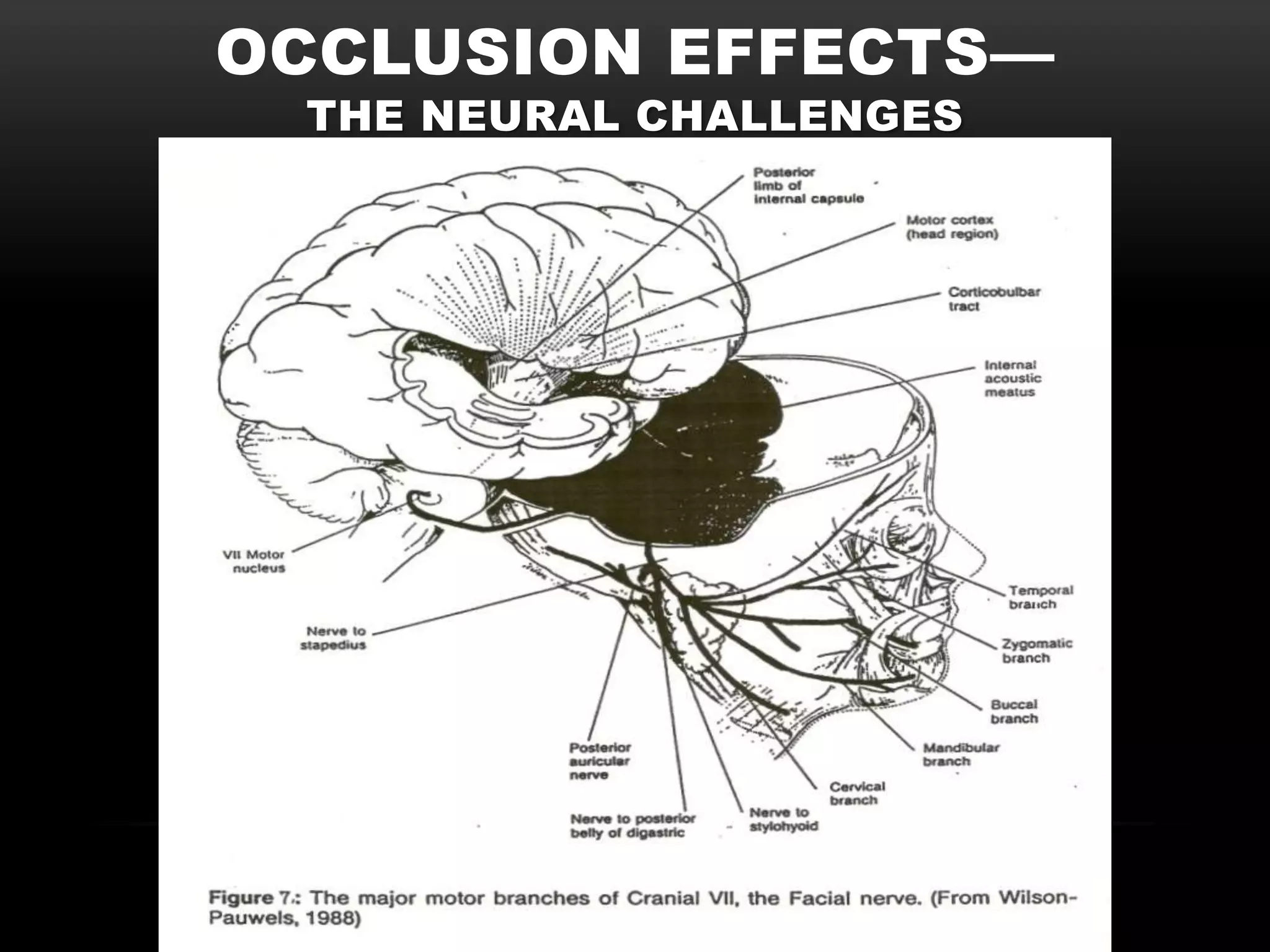
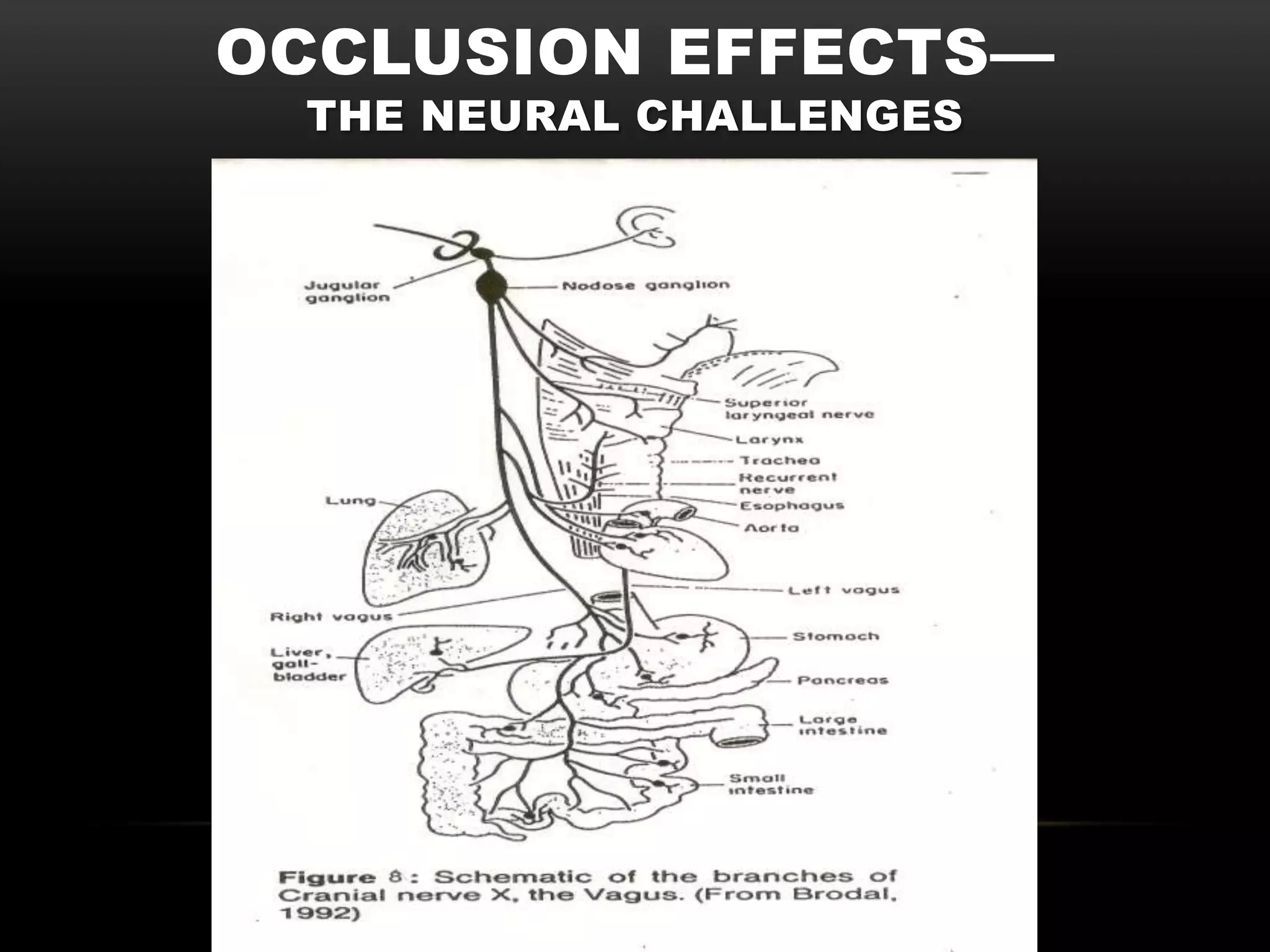
The document discusses the neural challenges associated with occlusion effects when wearing hearing aids. It defines non-acoustic/neural occlusion as sensations in the body from hearing aids whether they are on or off. This is believed to be caused by pressure on the nerves of the outer ear. It involves four cranial nerves and two cervical nerves that innervate the outer ear and may cause symptoms away from the ears like headaches or neck tension. Individual variability in nerve pathways means occlusion effects will vary between people.