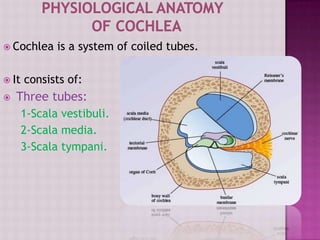
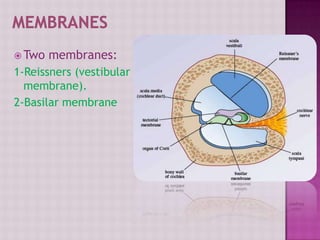
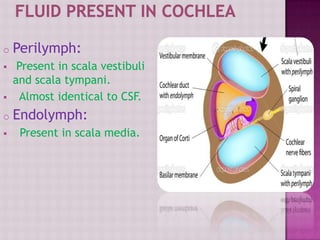
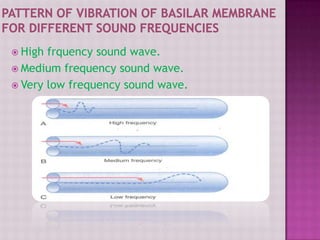
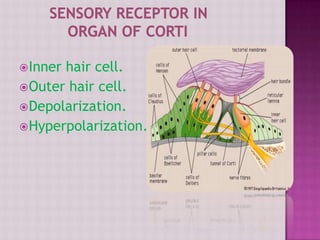
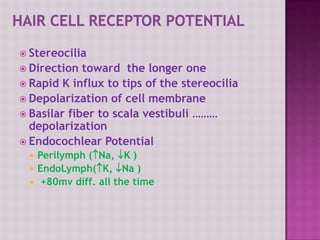
The cochlea contains three fluid-filled tubes called scalae that are separated by two membranes. It houses thousands of basilar fibers along the basilar membrane that vary in length, diameter, and stiffness from the base to the apex. When sound waves enter the cochlea, they cause traveling waves along the basilar membrane that peak at different locations depending on the sound frequency. Resting on the basilar membrane are hair cells that detect these waves and transmit neural signals in response to different sound frequencies.