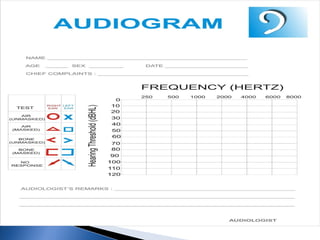
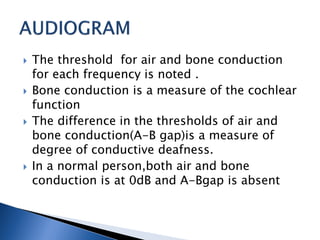
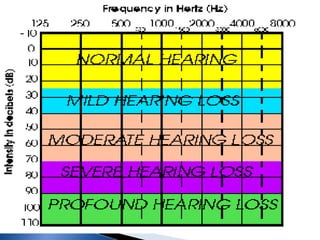
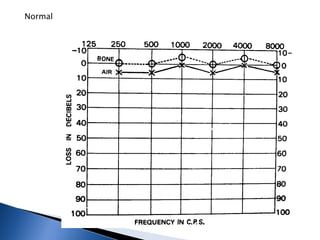
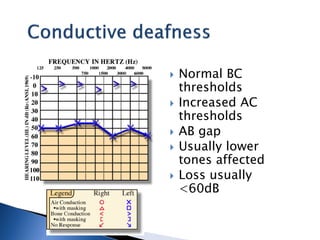
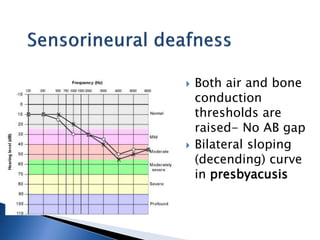
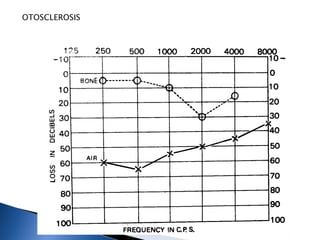
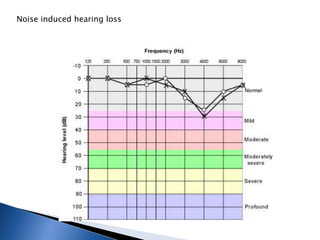
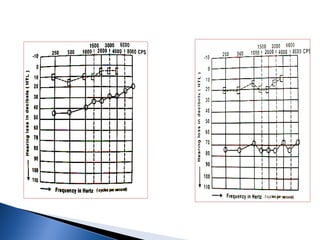
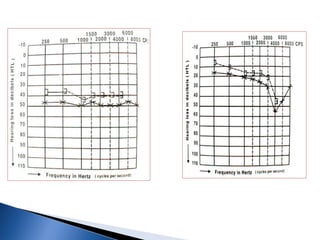
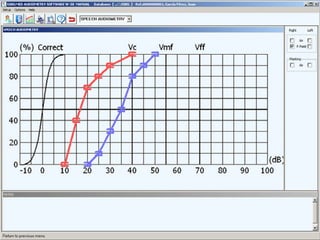
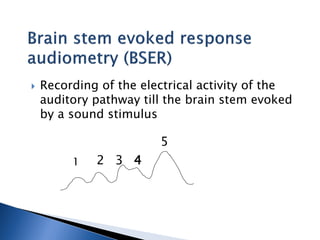
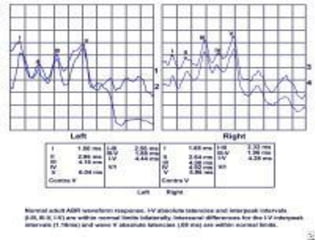
1. Pure tone audiometry is an objective test that measures air and bone conduction thresholds to evaluate the type and severity of hearing loss. It is helpful for documentation and diagnosis.
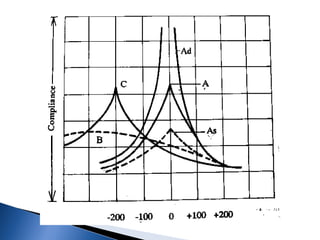
2. Impedance audiometry objectively measures middle ear function through tympanometry and acoustic reflex testing. It can detect middle ear pathologies and is a fast screening test.
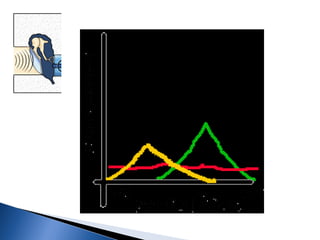
3. Otoacoustic emissions are sounds originating from the cochlea that can help diagnose cochlear hearing loss through an objective, noninvasive test done in both children and adults.