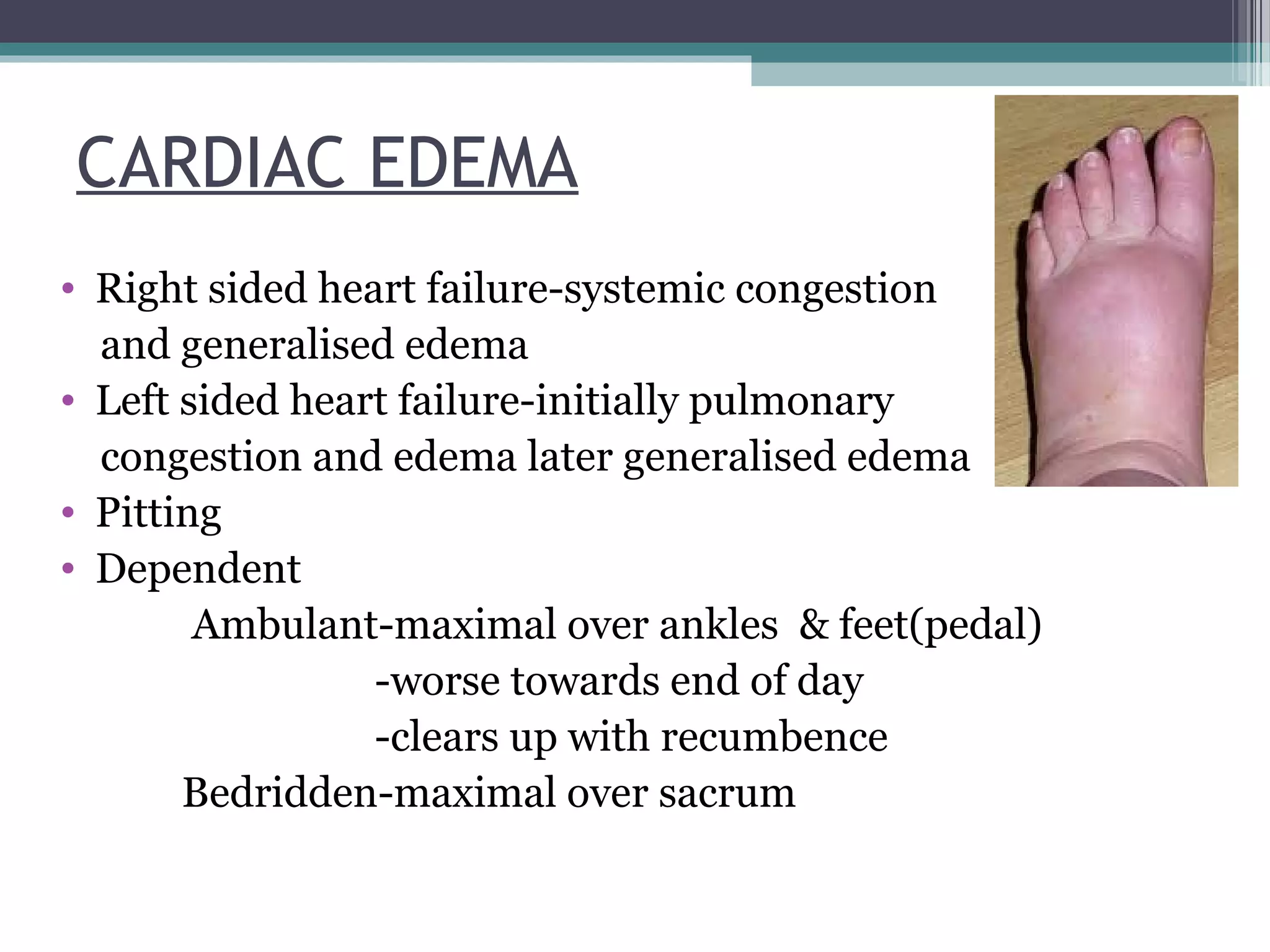
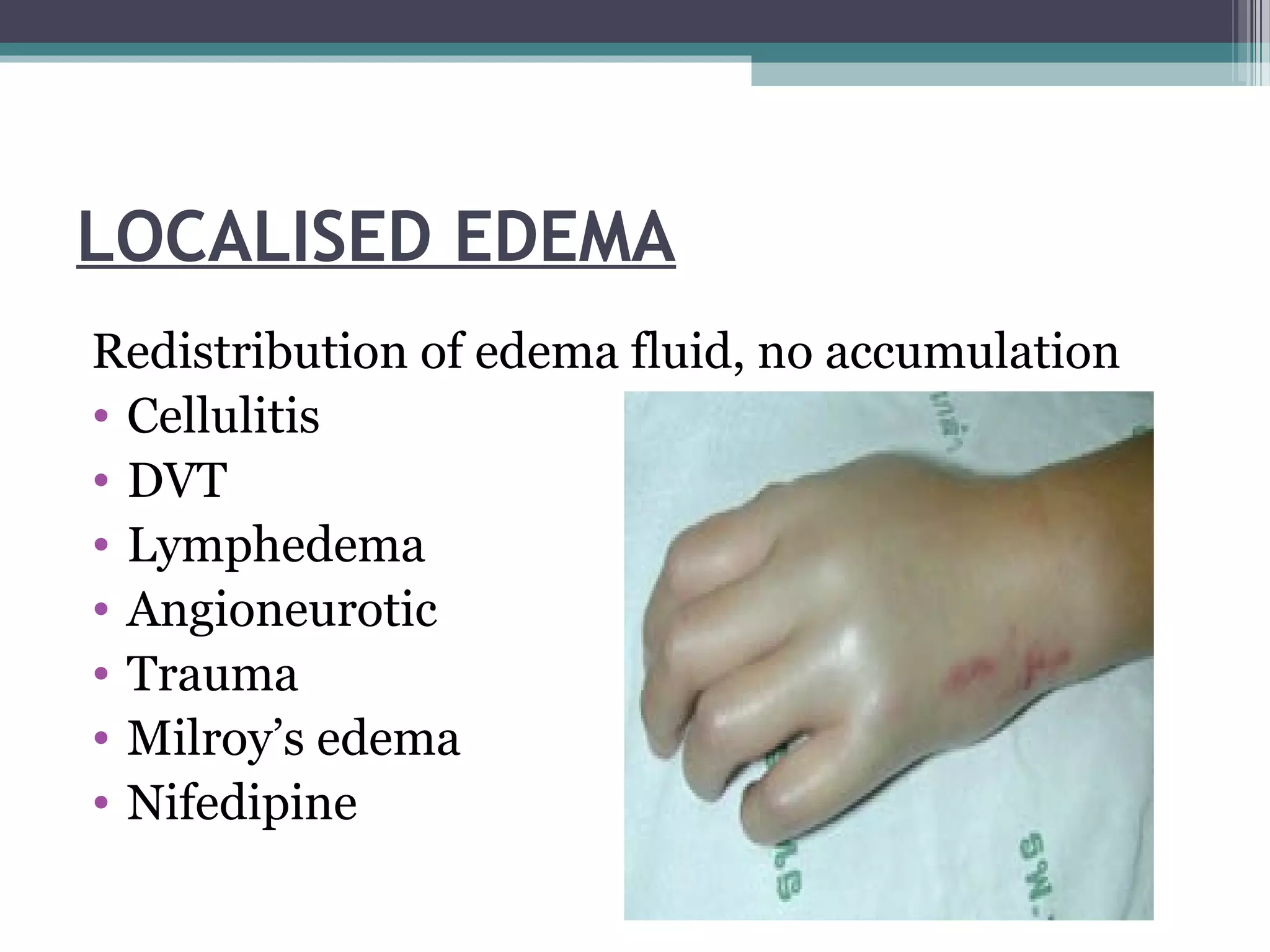
Cardiac, renal, liver disease and hypoproteinemia can cause generalized edema. Cardiac edema presents as pitting edema in the legs, ankles and feet that worsens at the end of the day. Renal edema in nephrotic syndrome causes severe generalized edema involving the face, legs and ascites with massive proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia. Liver cirrhosis causes edema in the legs and face due to decreased protein synthesis. Localized edemas include cellulitis, DVT, lymphedema and angioneurotic edema. Certain endocrine conditions like hypothyroidism and Cushing's disease can also cause edema.