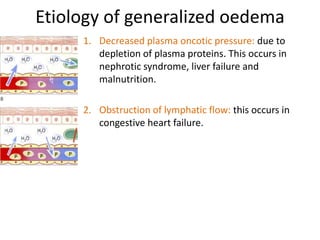
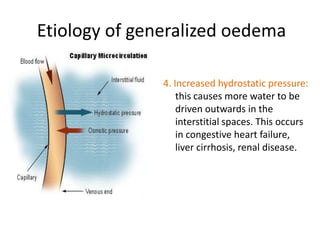
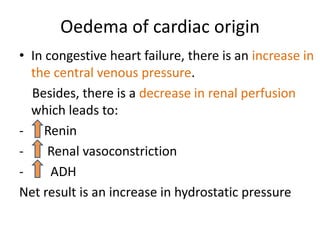
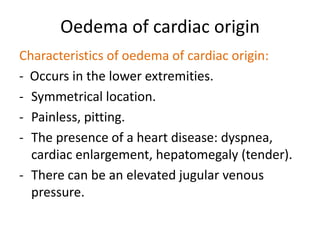
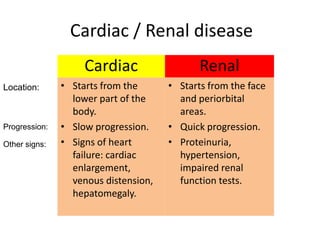
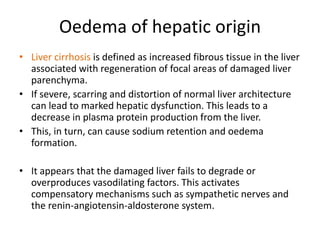
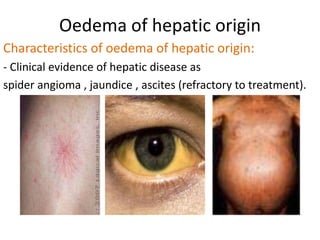
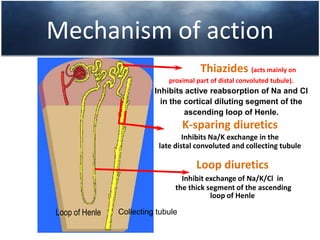
This document discusses the clinical approach to a patient presenting with generalized edema. It defines edema and discusses mechanisms that can cause fluid accumulation. The main causes of generalized edema are cardiac (congestive heart failure), renal (nephrotic syndrome), hepatic (liver cirrhosis), nutritional (malnutrition), allergic reactions, and drugs. Investigations and treatment focus on identifying the underlying cause and using diuretics and fluid restriction to increase excretion of sodium and water. Diuretic classes - thiazides, loops, and potassium-sparing - are described along with their mechanisms, indications, side effects and contraindications. Diuretic resistance and its management are also covered.



![Mechanisms maintaining Interstitial Fluid Volume[Oncotic pressure = osmotic pressure created by plasma protein molecules (P) that are impermeable across the capillary membrane].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/generalizedoedema-110421164627-phpapp02/85/Generalized-oedema-4-320.jpg)