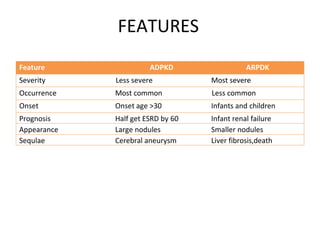
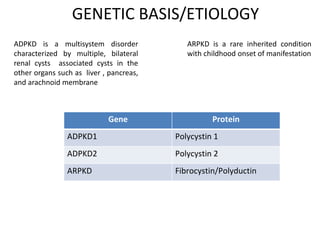
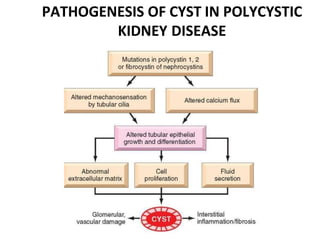
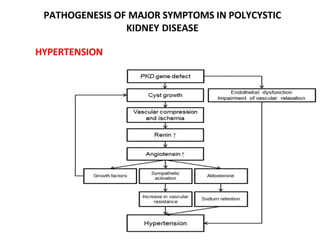
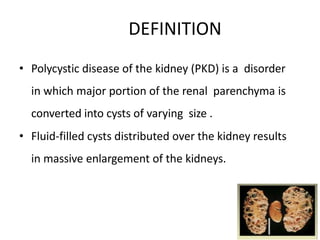
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the formation of cysts in the kidneys, leading to enlargement and potential renal failure. There are two main types: autosomal dominant (ADPKD), which affects adults, and autosomal recessive (ARPKD), which typically manifests in infants. Management includes blood pressure control, treatment of complications, and possible surgical interventions, with severe cases possibly necessitating dialysis or transplantation.

![TYPES
• 1. Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease(ADPKD)
• Inherited as a Autosomal Dominant Disease…
most common in Adult
• 2. Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPKD)
• Inherited as a Autosomal Recessive
Disease….most common in infants
[ADPKD(50:50 Chance) and ARPKD(1:4 Chance)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pkdupload-191113134410/85/Polycystic-Kidney-Disease-PKD-5-320.jpg)