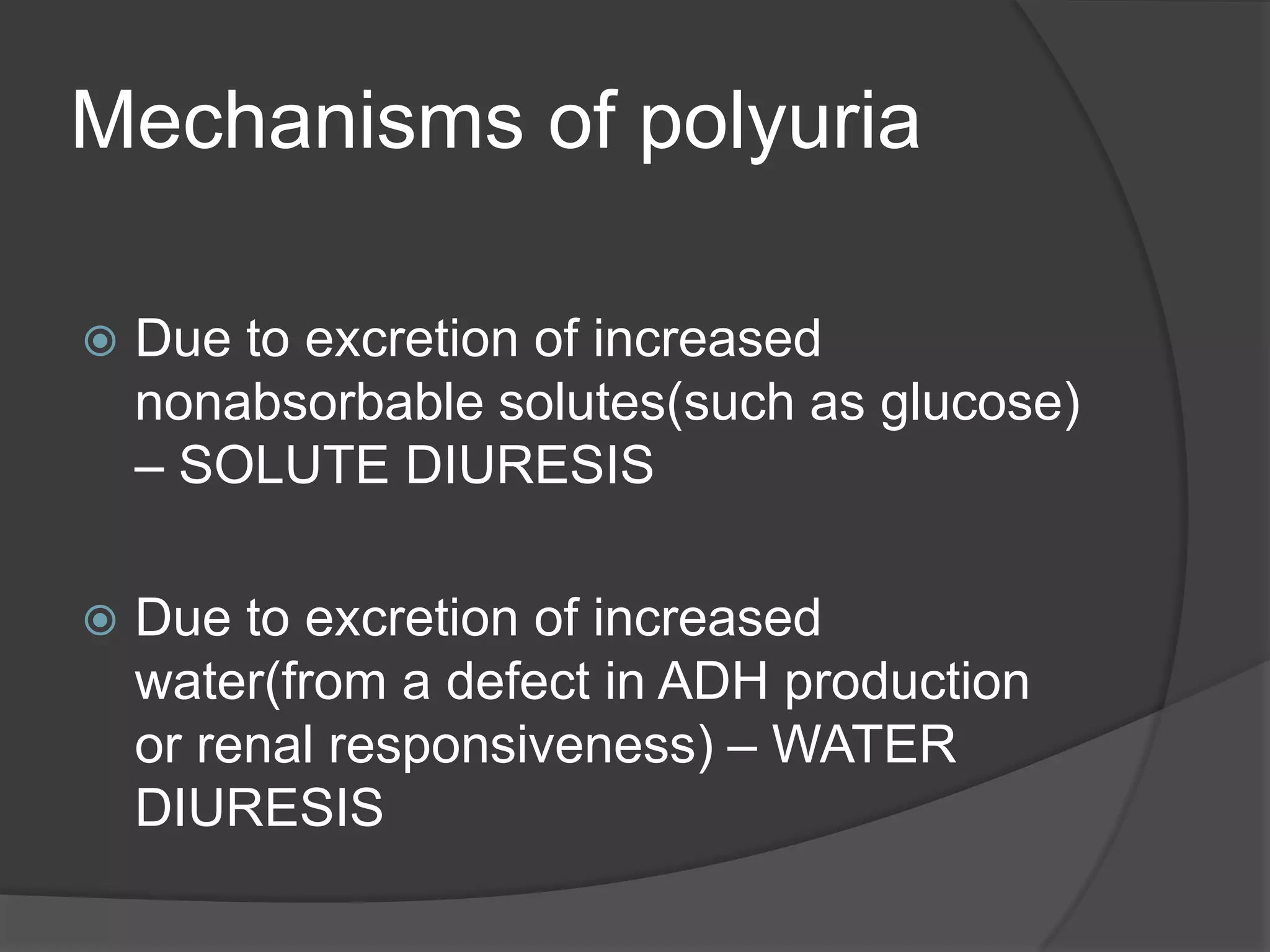
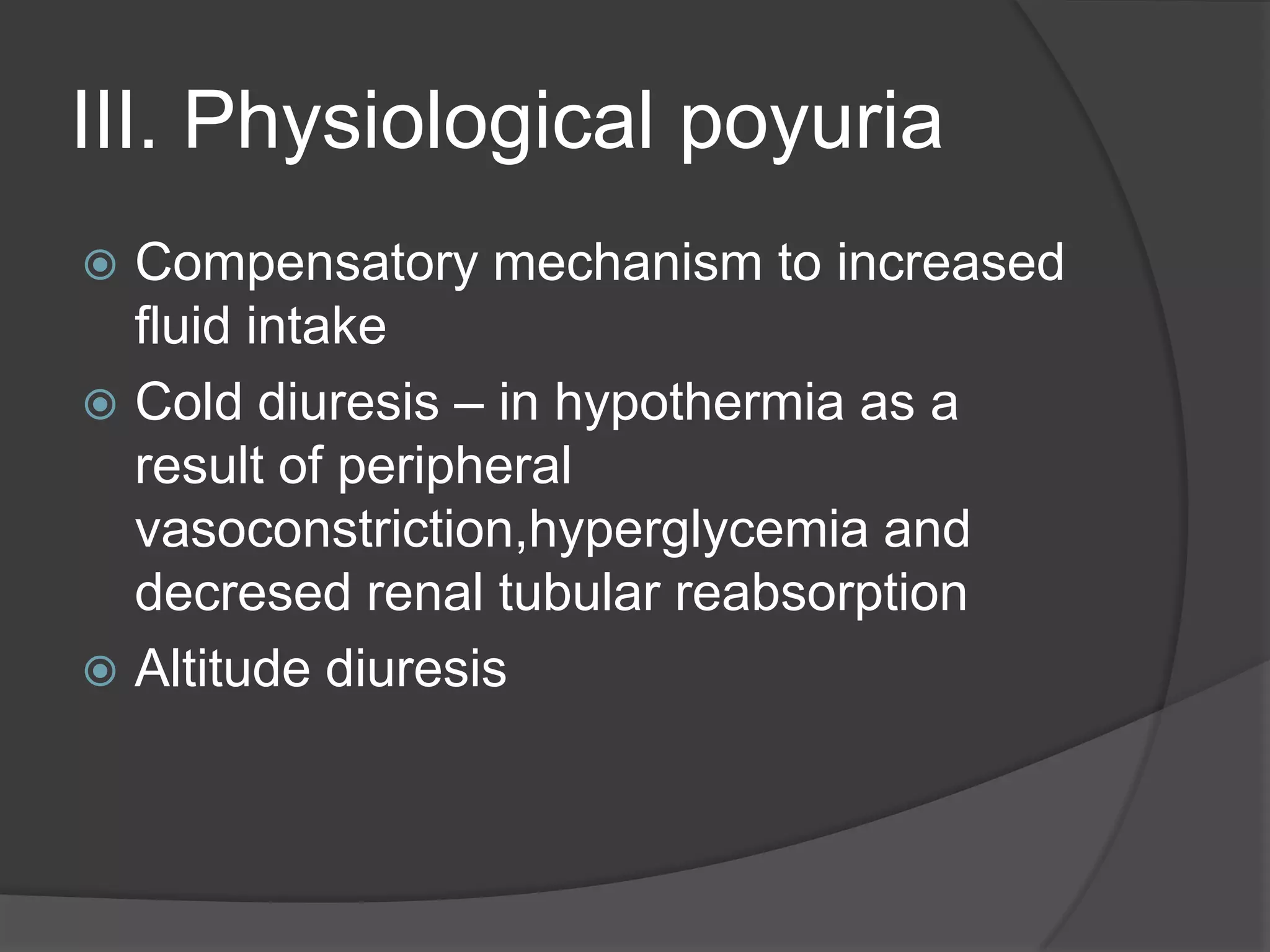
Polyuria is defined as excessive urine production of more than 3 liters per day in adults. It can be caused by either water diuresis or solute diuresis. Water diuresis is characterized by dilute urine of less than 250 mosmol/L and is caused by problems with antidiuretic hormone production or kidney response. Solute diuresis produces urine of more than 300 mosmol/L and is caused by increased glucose, urea, or other solutes. Polyuria can be pathological due to diseases like diabetes, pharmacological due to medications or fluids, or physiological for compensatory reasons.