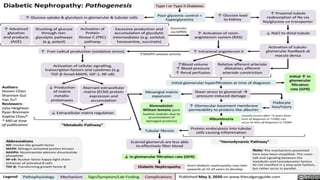
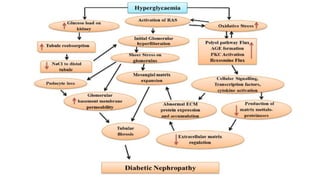
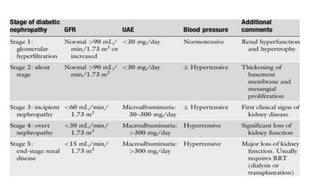
Diabetic nephropathy is characterized by persistent albuminuria, declining glomerular filtration rate, and hypertension, affecting about 20-50% of diabetes patients. It progresses through stages defined by the estimated glomerular filtration rate, with treatment focusing on glycemic and blood pressure control, along with dietary adjustments. Prevention measures include optimal blood glucose management, controlling hypertension, and avoiding nephrotoxic substances.







![Treatment and Management:
Several issues are key in the medical care of patients with diabetic nephropathy.
These include glycemic control, management of hypertension, and reducing dietary salt intake and
phosphorus and potassium restriction in advanced cases.
A meta-analysis from the Cochrane Database shows a large fall in blood pressure with salt
restriction, similar to that of single-drug therapy. [Suckling RJ, He FJ, MacGregor GA. Altered
dietary salt intake for preventing and treating diabetic kidney disease. Cochrane Database of
Systematic Reviews. 2010(12).]
Glycemic Control:
a) Dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitors: The DPP–4 inhibitors (ie, gliptins) include sitagliptin,
saxagliptin, linagliptin, and alogliptin, and they decrease the breakdown of the incretin hormones
such as glucagonlike peptide 1 (GLP-1).
Sitagliptin was the first available DPP-4 inhibitor. Approximately 80% of sitagliptin is cleared by the
kidney; therefore, the standard dose of 100 mg daily should be reduced in patients with reduced GFRs.
With an eGFRof 30 or greater to less than 50 mL/min/1.73 m2, the recommended dose is 50 mg once
daily, and with an eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2, a dose of 25 mg once daily is advised.
[Bergman AJ, Cote J, Yi B, Marbury T, Swan SK, Smith W, Gottesdiener K, Wagner J, Herman GA.
Effect of renal insufficiency on the pharmacokinetics of sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor.
Diabetes care. 2007 Jul 1;30(7):1862-4.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diabeticnephropathy-240127142214-1939e61b/85/Diabetic-Nephropathy-pptx-11-320.jpg)
![Treatment and Management:
b) Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors:
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors (acarbose, miglitol) decrease the breakdown of oligosaccharides and
disaccharides in the small intestine, slowing the absorption of glucose after a meal. The major adverse
effects are bloating, flatulence, and abdominal cramping.
c) Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: Canagliflozin , dapagliflozin
d) Glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists / incretin mimetics: semaglutide, liraglutide
Management of Hypertension
a) ACE inhibitors: Captopril, Enalapril
b) ARB: Losartan, Ibresartan
The choice between an ARB and an ACE inhibitor is made more difficult by the results of the
Microalbuminuria-Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (MICRO-HOPE) Trial, in which ramipril reduced
the risk for myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular death by 26% after 2 years. Perhaps the more
interesting question is whether the combination of an ACE inhibitor and an ARB is more effective than
either drug alone. One meta-analysis showed that ACEI + ARB reduced 24-hour proteinuria to a greater
extent than ACEI alone. However, this benefit was associated with small effects on GFR, serum creatinine,
potassium, and blood pressure. [Jennings DL, Kalus JS, Coleman CI, Manierski C, Yee J. Combination
therapy with an ACE inhibitor and an angiotensin receptor blocker for diabetic nephropathy-a meta-
analysis. Clinical Diabetology. 2007;8(6):219-28.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diabeticnephropathy-240127142214-1939e61b/85/Diabetic-Nephropathy-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![Treatment and Management:
c) Direct renin inhibitors:
In a small double-blind, randomized, crossover trial, Persson et al observed the combination of
aliskiren and irbesartan to be more antiproteinuric in type 2 diabetes mellitus than was monotherapy
with either drug. This study assessed the effect of aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor, on proteinuria in
patients with type 2 DM (n = 26) and compared the effect with that of placebo, irbesartan (an ARB),
and the combination of aliskiren and irbesartan. [Persson F, Rossing P, Reinhard H, Juhl T,
Stehouwer CD, Schalkwijk C, Danser AJ, Boomsma F, Frandsen E, Parving HH. Renal effects of
aliskiren compared with and in combination with irbesartan in patients with type 2 diabetes,
hypertension, and albuminuria. Diabetes care. 2009 Oct 1;32(10):1873-9.]
Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonist Therapy:
o In July 2021, the FDA approved Finerenone ,to lower the chances of sustained eGFR decline, end-
stage kidney disease, cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, and hospitalization for
heart failure in adults with CKD associated with type 2 DM. [Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Anker SD, Pitt B,
Ruilope LM, Rossing P, Kolkhof P, Nowack C, Schloemer P, Joseph A, Filippatos G. Effect of
finerenone on chronic kidney disease outcomes in type 2 diabetes. New England Journal of
Medicine. 2020 Dec 3;383(23):2219-29.]
Endothelin Antagonist Therapy
o Endothelin antagonists (Avosentan) have demonstrated antifibrotic, anti-inflammatory, and
antiproteinuric effects in experimental studies.[https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2008050482]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diabeticnephropathy-240127142214-1939e61b/85/Diabetic-Nephropathy-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![Treatment and Management:
Renal Replacement Therapy:
In principle, diabetic patients who require renal replacement therapy have the following 4 options:
- Refusal of further treatment for uremia, leading to a progressive decline in general health and
ultimately leading to death
- Peritoneal dialysis
- Hemodialysis
- Renal transplantation
Measures for Prevention of Diabetic Nephropathy :
Efforts should be made to modify or treat associated risk factors such as hyperlipidemia, smoking, and
hypertension.
Specific goals for prevention include the following:
Optimal blood glucose control (hemoglobin A1c [HbA1c] < 7%)
Control of hypertension (BP < 120/70 Hg)
Avoidance of potentially nephrotoxic substances such as NSAIDs and aminoglycosides
Early detection and optimal management of diabetes, especially in family history of diabetes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/diabeticnephropathy-240127142214-1939e61b/85/Diabetic-Nephropathy-pptx-14-320.jpg)




