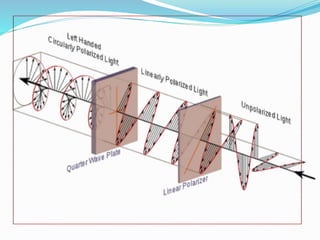
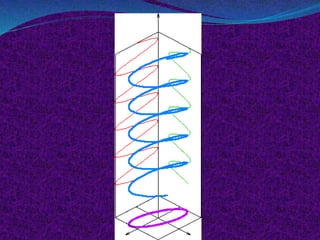
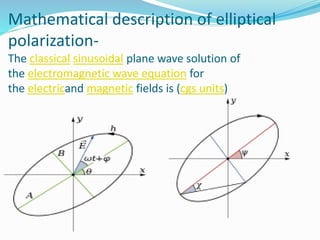
This document provides information about circular and elliptical polarizers. It discusses that circular polarizers can create or selectively pass circularly polarized light and are used in photography and 3D glasses. It then explains how a quarter-wave plate placed after a linear polarizer can transform linearly polarized light into circularly polarized light. The document also defines elliptical polarization as having an electric field that traces out an ellipse, and notes it can be considered a general case of both circular and linear polarization.