1) The document discusses examples of calculating the Jacobian of transformations. It defines the Jacobian as the determinant of the partial derivatives of the transformed coordinates.
2) It then discusses Möbius transformations, which are fractional linear transformations of the form (az+b)/(cz+d). The Jacobian of a Möbius transformation depends only on z.
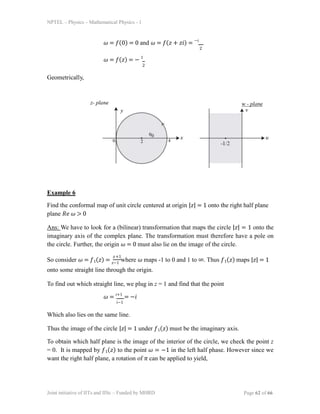
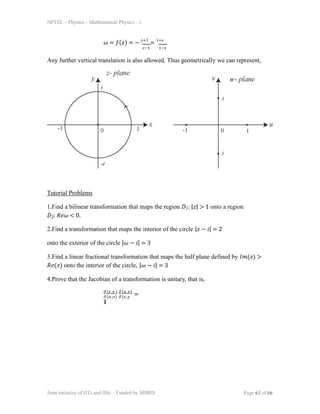
3) Several examples are given of using Möbius transformations to map one geometric region to another, such as mapping a circle to a line.