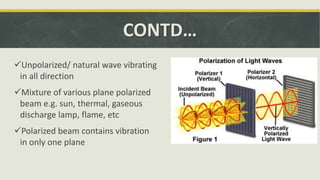
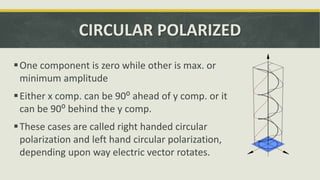
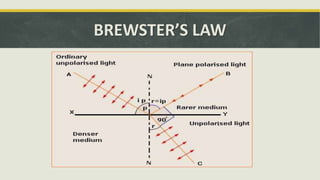
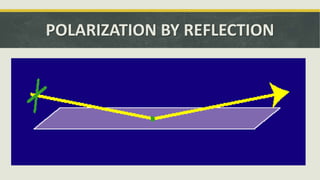
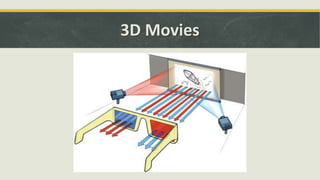
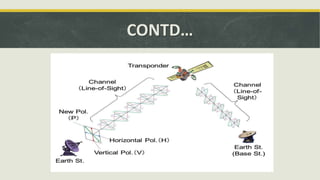
The document discusses the concept of polarization in light, explaining its definitions, types, and related terms. It covers the laws of polarization, such as Brewster's law, and outlines applications in fields like astronomy, 3D movies, and communication. Additionally, it details instruments involved in polarization, including polarizers and analyzers.