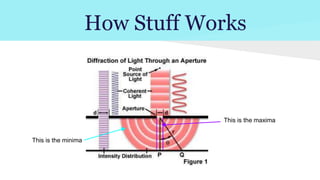
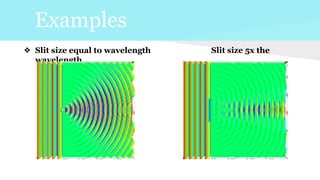
Diffraction is the bending of light waves as they pass from one medium to another. When light passes through an aperture or slit, it produces a diffraction pattern of alternating light and dark fringes. The size of the aperture determines the extent to which light bends and the ability of an optical instrument like a camera to resolve fine image details, with smaller apertures resulting in more diffraction and less resolution. Diffraction limits the resolving power of lenses and explains why images may appear blurred if the aperture is too large compared to the wavelength of light.