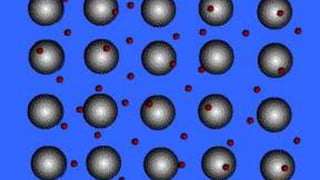
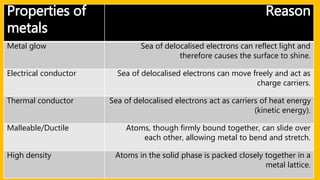
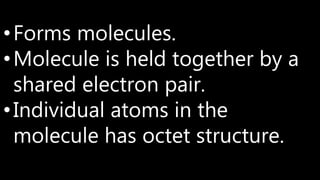
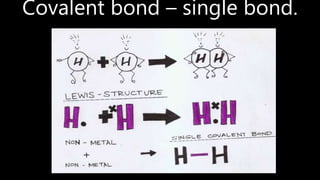
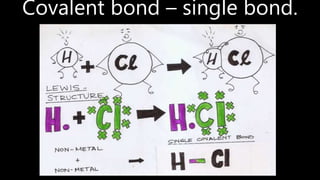
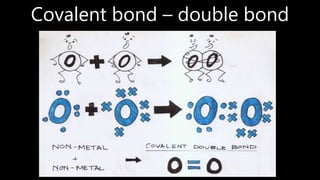
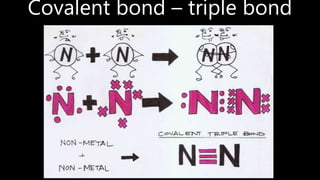
This document discusses different types of chemical bonds including ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. Ionic bonds form when a metal transfers electrons to a non-metal. Covalent bonds form when two non-metals share electrons. Metallic bonds form through electrostatic attraction between positively charged metal ions and delocalized electrons. Examples of different bonds are also provided such as lithium fluoride forming an ionic bond through Li+ and F- ions and metallic bonding in metals occurring through interaction of positively charged atomic residues and free-flowing electrons.




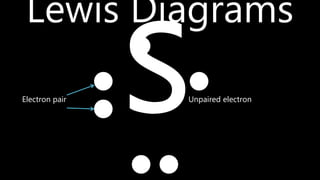



![Metals give off electrons to form cations in order to
obtain a noble gas electron structure.
Li Li+ + e-
[He]2s1 [He]
[Ar]4s2 [Ar]
Ca Ca2++2e-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalbondingandthelewisstructure-160412103402/85/Chemical-bonding-and-the-lewis-structure-14-320.jpg)
![Non-metals gain electrons to form anions in order to
obtain a noble gas electron structure.
N + 3e- [ N ]3-
[He]2s2p3
S + 2e- [ S ]2-
[Ne]3s23p4
[He]2s22p6 = [Ne]
[Ne]3s23p6 = [Ar]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalbondingandthelewisstructure-160412103402/85/Chemical-bonding-and-the-lewis-structure-15-320.jpg)

![Ca Ca2+ + 2e-
2x: F + e- [ F ]-
Ca2+ + 2[ F ]- Ca2+2[ F ]- CaF2
Positive ion:
Negative ion:
Crystal lattice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemicalbondingandthelewisstructure-160412103402/85/Chemical-bonding-and-the-lewis-structure-17-320.jpg)