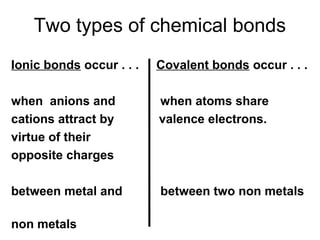
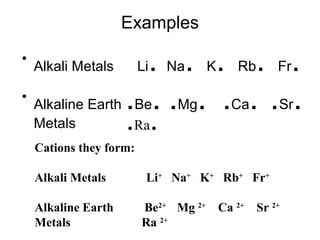
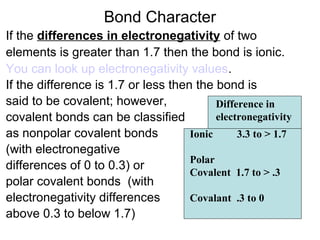
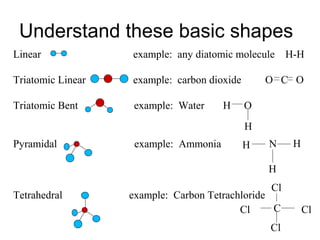
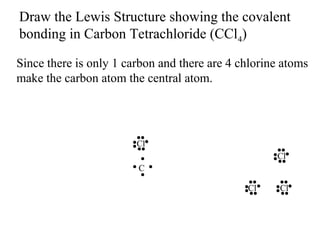
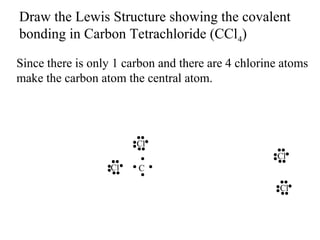
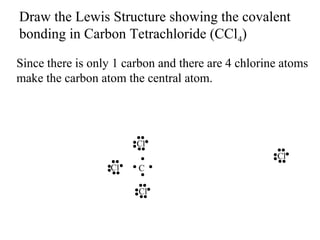
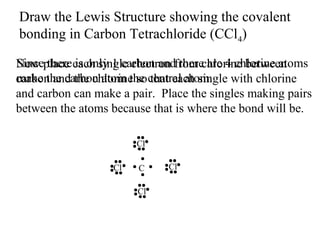
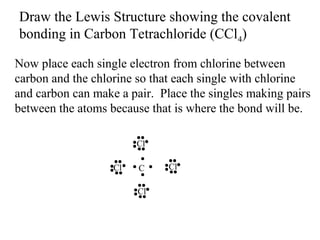
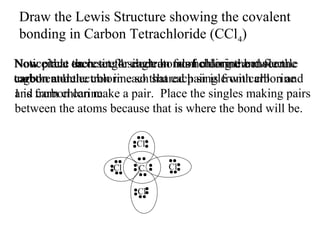
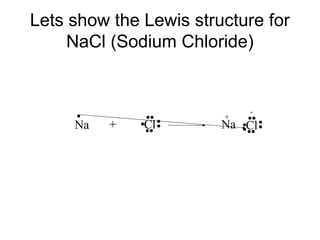
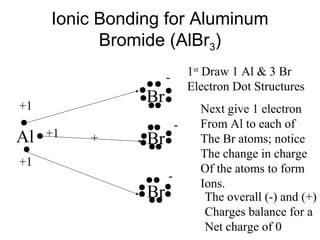
Atoms form bonds to attain a lower potential energy state. They do this through ionic bonds, where oppositely charged ions attract, or covalent bonds, where atoms share valence electrons. Whether a bond is ionic or covalent depends on the electronegativity difference between the atoms. Ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals, while covalent bonds form between two nonmetals. Lewis structures use dots to represent valence electrons and show how atoms share electrons to achieve stable configurations like noble gases. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory explains molecular shapes based on electron pair positioning.