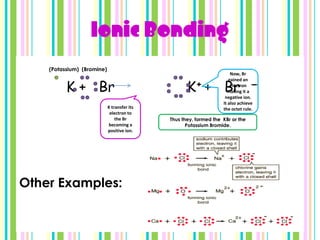
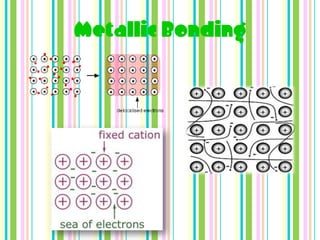
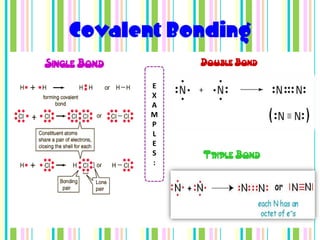
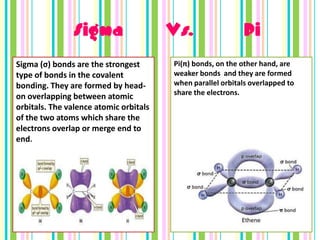
Chemical bonds form when atoms attract each other and bind together. There are three main types of bonds: ionic bonds form when a metal transfers electrons to a non-metal, metallic bonds involve delocalized electrons that move freely between metal atoms, and covalent bonds occur when two non-metals share pairs of electrons. Ionic bonds are strong but brittle, metallic bonds allow metals to conduct heat and electricity, and covalent bonds can be single, double or triple depending on how many electron pairs are shared.