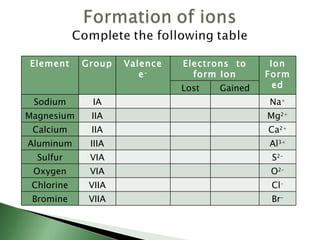
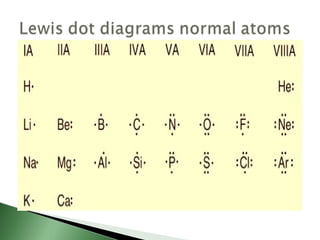
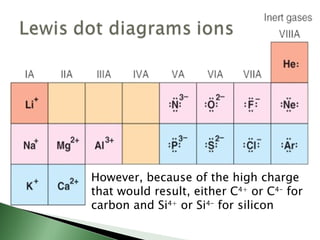
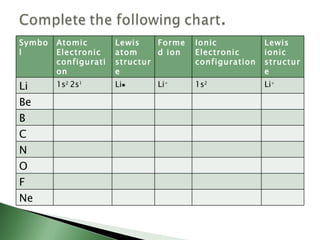
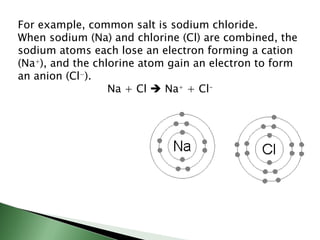
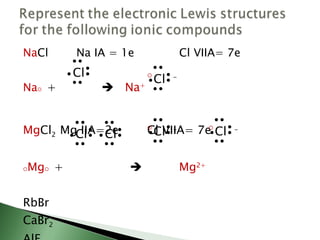
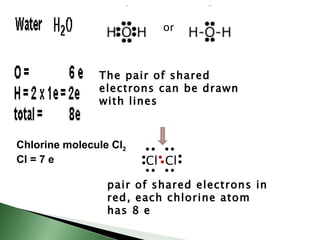
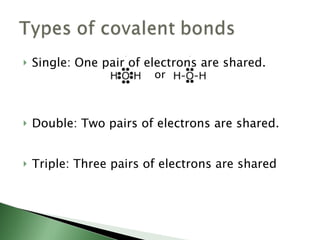
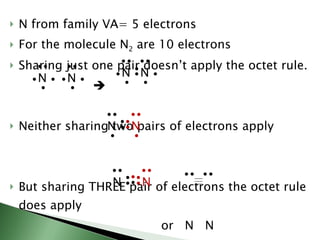
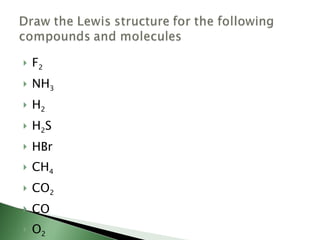
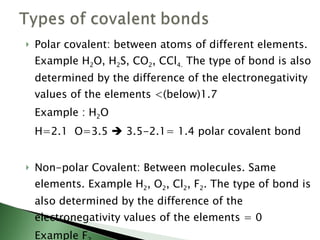
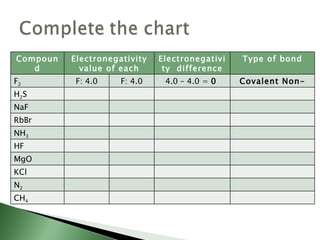
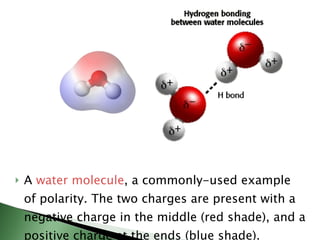
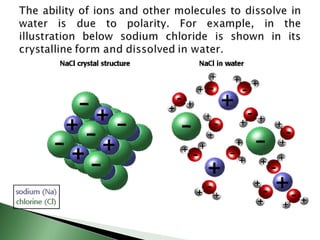
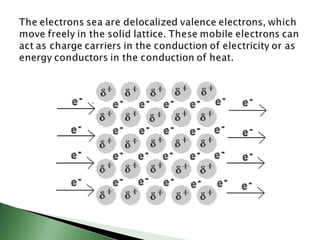
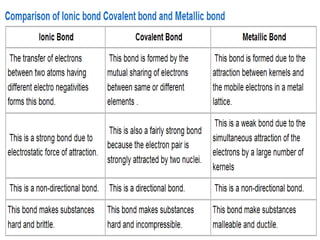
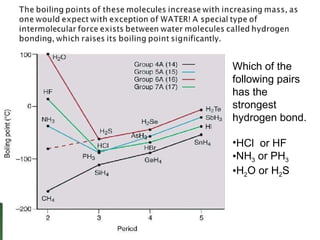
Chemical bonding involves atoms forming stable electronic configurations through gaining, losing or sharing electrons. Ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals when electrons are transferred, while covalent bonds involve sharing electron pairs between nonmetals to achieve stable octets. Different bond types including ionic, covalent and metallic bonding can be identified based on the participating elements and electron configurations involved.