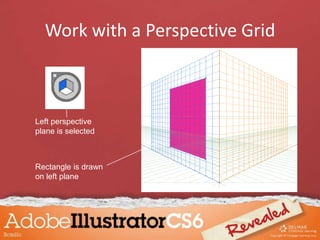
This document discusses how to create and manipulate 3D objects in Adobe Illustrator. It covers extruding and revolving 2D objects, adjusting surface shading and lighting, mapping artwork onto 3D objects, and working with a perspective grid. Key topics include using the Extrude and Revolve effects, manipulating lighting settings, choosing different surface shadings, mapping symbols onto 3D surfaces, and drawing in perspective using the perspective grid tool.