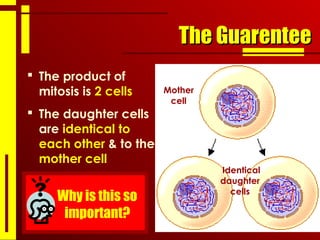
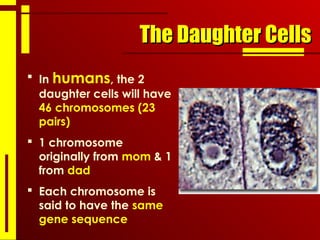
- Cells divide through the process of mitosis in order to grow, repair, or replace damaged cells. Mitosis results in two identical daughter cells that each receive a complete set of chromosomes.
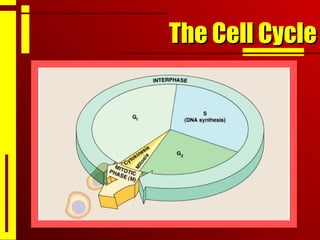
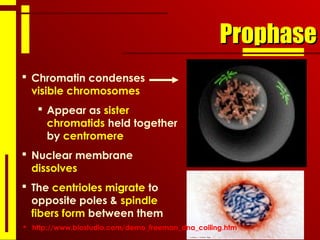
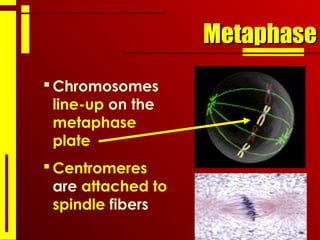
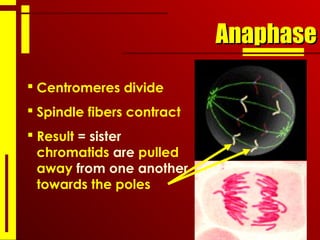
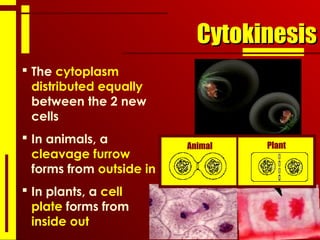
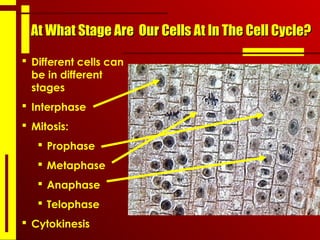
- The cell cycle consists of interphase, where the cell grows and duplicates its DNA, and the mitotic phase, where the cell divides into two daughter cells through the stages of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase, followed by cytokinesis.
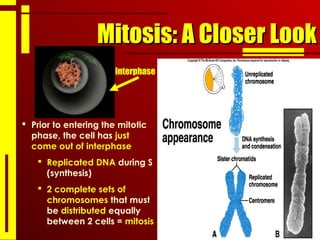
- Mitosis ensures that each daughter cell receives the full complement of genetic material from the parent cell, allowing organisms to grow and maintain healthy tissues through cell replacement.