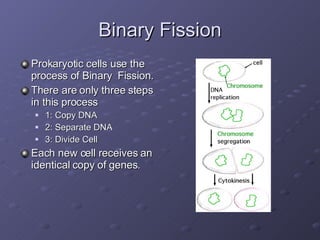
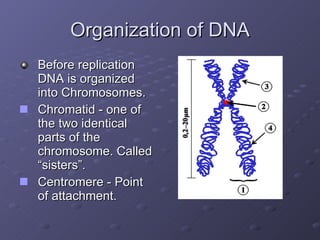
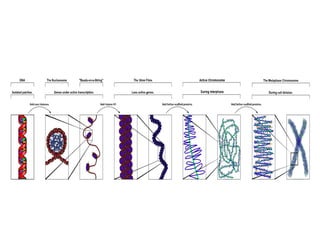
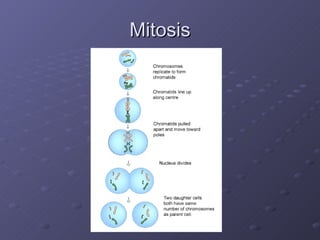
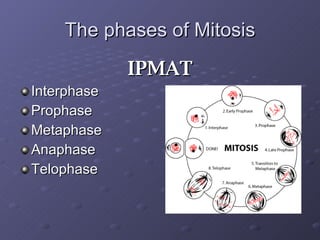
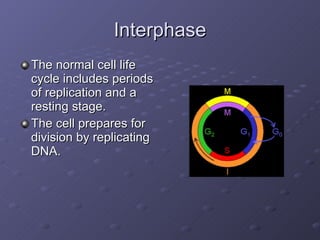
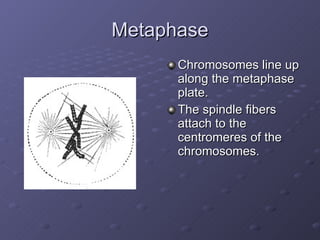
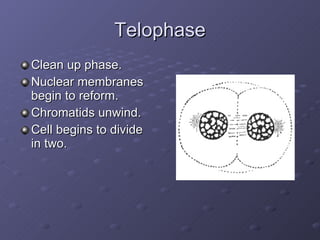
Cell division is the process where a cell divides into two daughter cells. There are two main types of cell division: binary fission in prokaryotes and mitosis in eukaryotes. Mitosis involves copying the cell's DNA during interphase, condensing and aligning chromosomes during prophase and metaphase, separating sister chromatids during anaphase, and dividing the cell into two daughter cells during telophase and cytokinesis. The goal of cell division is to replace old or damaged cells and allow for growth.