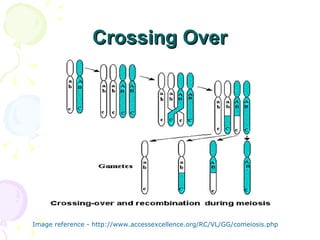
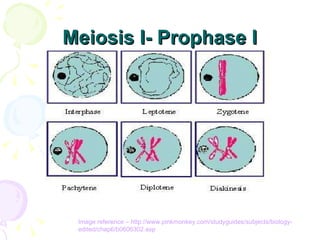
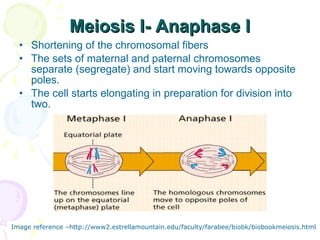
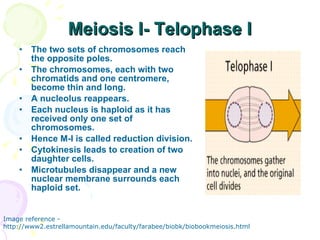
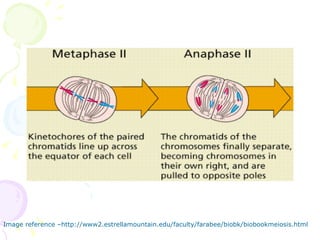
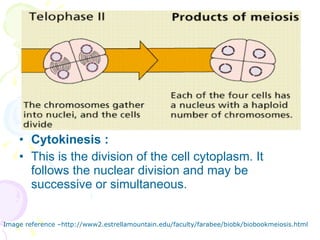
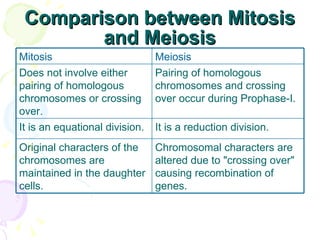
Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division in eukaryotes that facilitates sexual reproduction by reducing the chromosome number by half, leading to the formation of four haploid cells from one diploid cell. This process includes two main divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II, the former involving the pairing and crossing over of homologous chromosomes, which increases genetic diversity. Ultimately, meiosis ensures stable sexual reproduction and generates variation in offspring, distinguishing it from mitosis, which produces genetically identical daughter cells.