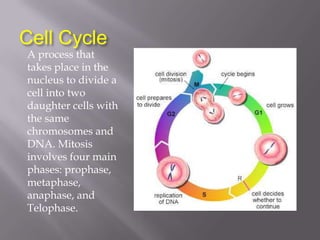
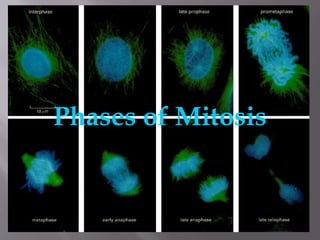
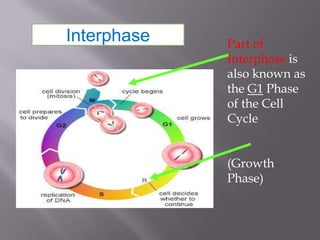
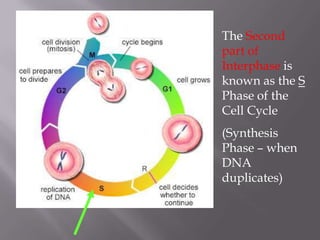
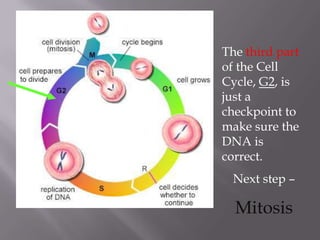
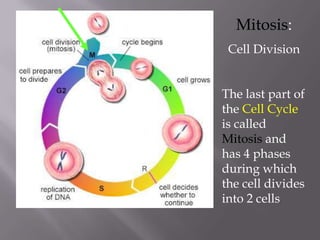
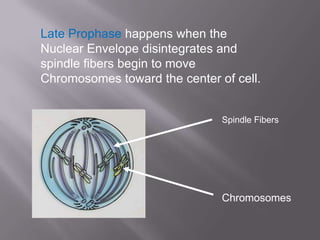
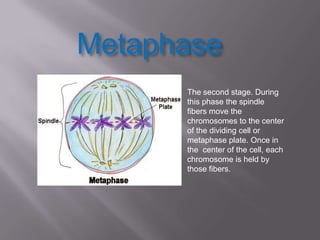
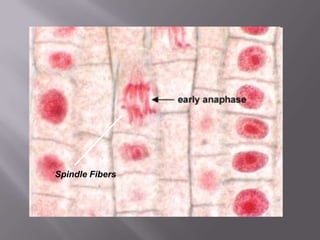
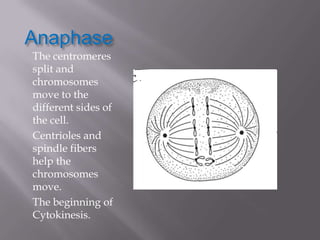
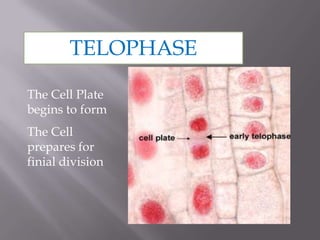
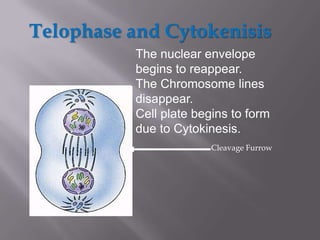
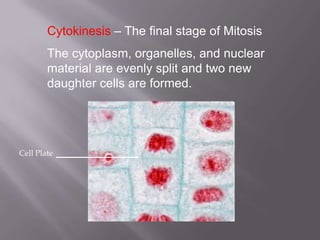
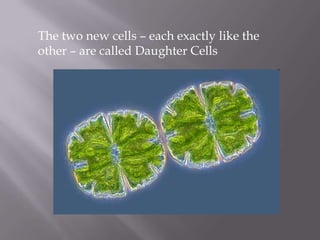
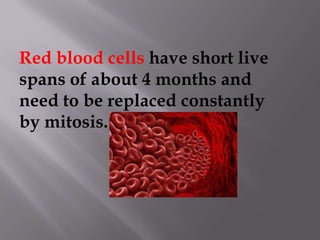
Mitosis is a process of cell division that produces two daughter cells with identical chromosomes and DNA. It involves four main phases - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. During interphase, the cell grows and duplicates its DNA in preparation for division. Mitosis then begins with prophase where the chromosomes condense and spindle fibers form. In metaphase, chromosomes align at the center. In anaphase, chromosomes separate and move to opposite sides. Finally in telophase, the nuclear envelope reforms and cytokinesis completes the division of cytoplasm. Mitosis plays an important role in growth, cell replacement and regeneration.