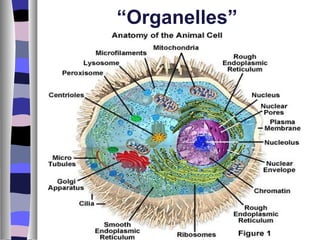
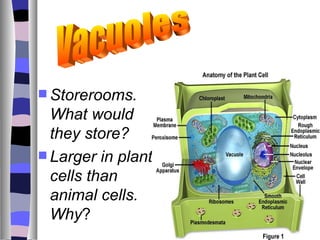
This document provides information about cells and their organelles. It states that Robert Hooke first observed cells in cork in 1665 and described them as compartments like jail cells. It then discusses that cells are the basic functional units of living things, are made of organelles that perform different functions, and that all cells come from pre-existing cells. It provides details about the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells as well as the functions of major cell organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, chloroplasts, cytoskeleton, and cilia and flagella.