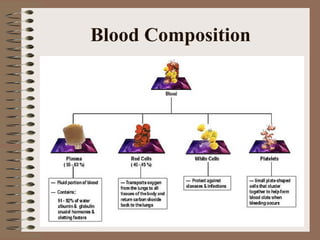
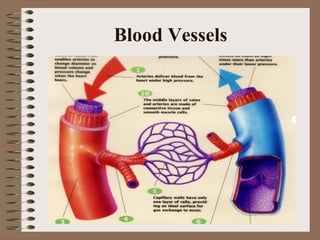
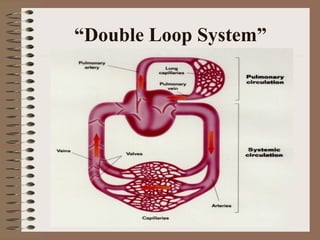
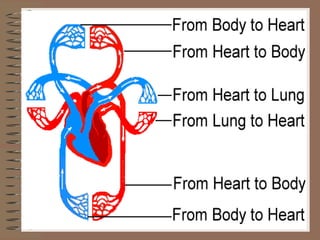
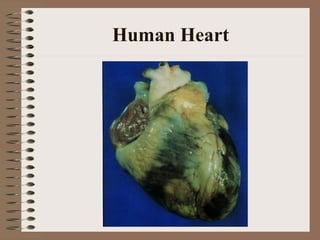
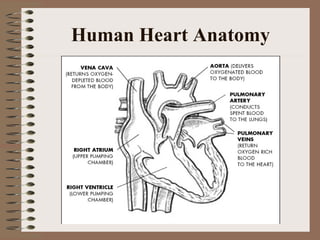
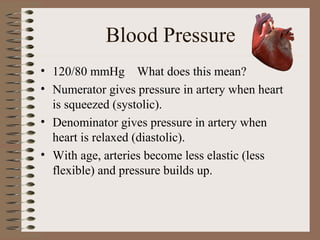
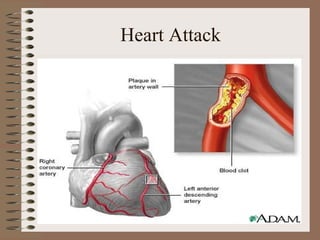
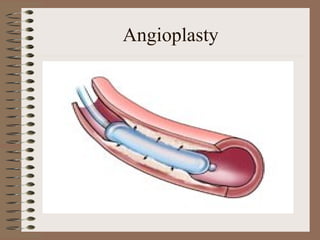
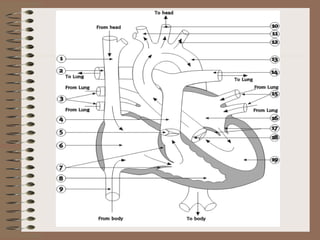
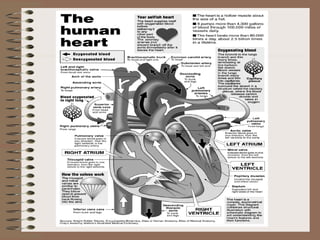
The human circulatory system transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other materials throughout the body via blood flow in blood vessels. Blood is pumped from the heart through arteries and returns to the heart via veins. The circulatory system transports these materials to all cells in the body and picks up waste products, maintaining homeostasis. Diseases of the heart and blood vessels like atherosclerosis, hypertension, and heart attacks are leading causes of death in the US.