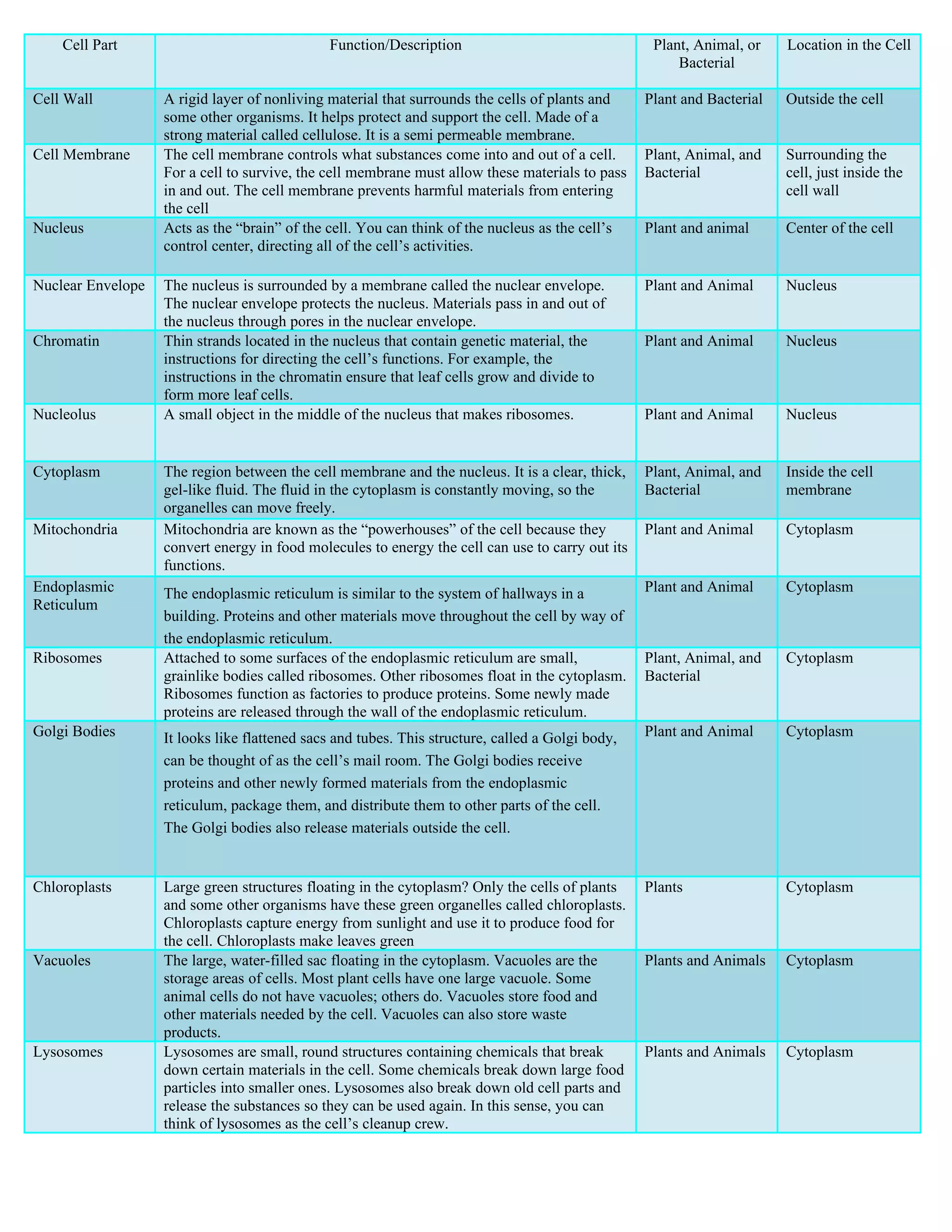
The document describes the major organelles and structures found within plant, animal, and bacterial cells and their locations and functions. It provides a table with the following columns: cell part, function/description, whether it is found in plant, animal, or bacterial cells, and its location within the cell. The key cellular components it outlines include the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, nuclear envelope, chromatin, nucleolus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi bodies, chloroplasts, vacuoles, and lysosomes.