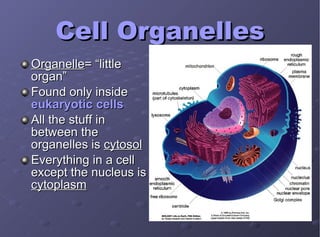
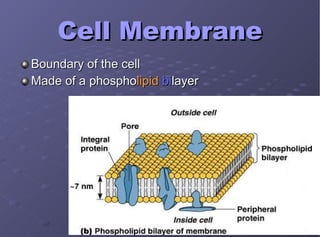
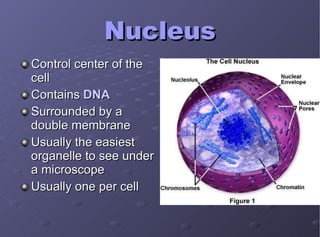
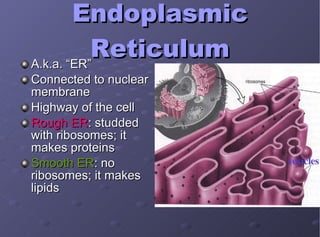
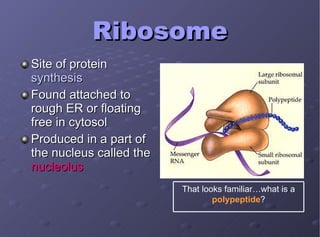
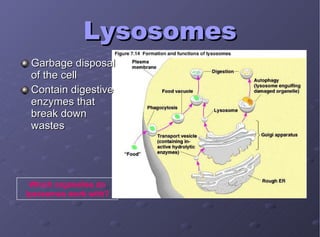
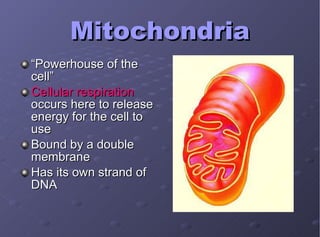
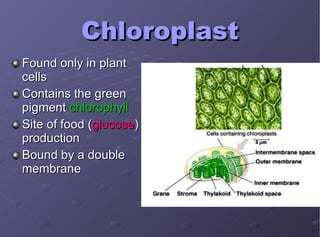
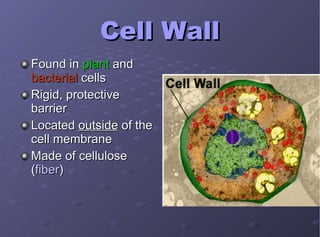
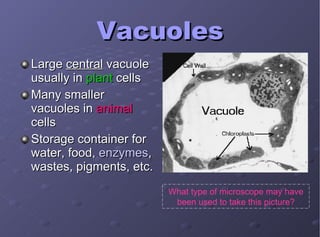
The document describes the main cell organelles found in eukaryotic cells, including their structures and functions. It notes that the nucleus is the control center that contains DNA, the cell membrane forms the boundary, and the endoplasmic reticulum transports proteins and lipids. Other organelles mentioned are ribosomes for protein synthesis, Golgi apparatus for packaging molecules, mitochondria for energy production, chloroplasts for photosynthesis in plants, vacuoles for storage, and centrioles aiding cell division.