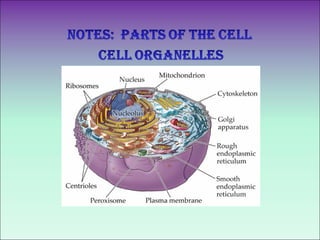
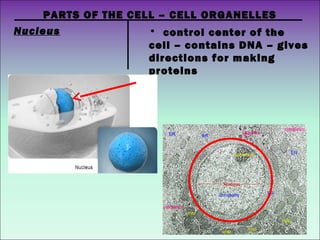
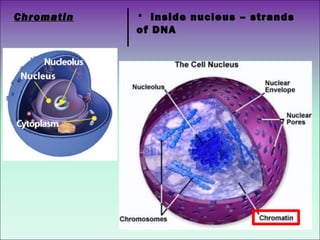
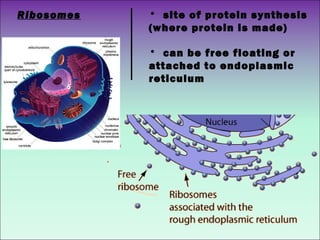
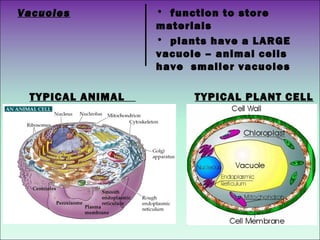
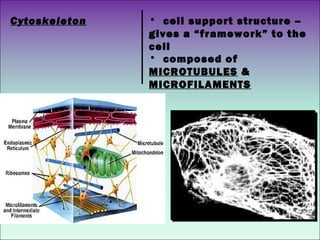
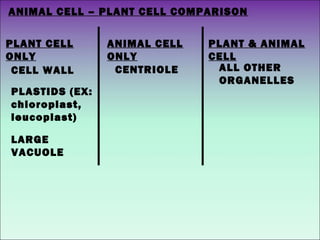
The document describes the main organelles found within cells and their functions. The nucleus contains DNA and directs protein production. The cytoplasm holds organelles and gives the cell shape. Ribosomes produce proteins and the endoplasmic reticulum is a workspace for protein synthesis. Organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts generate energy for the cell.