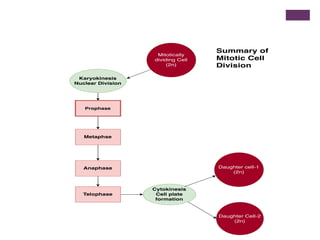
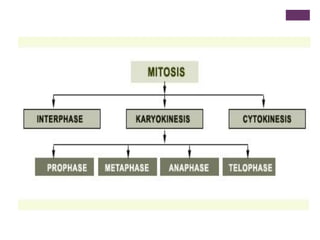
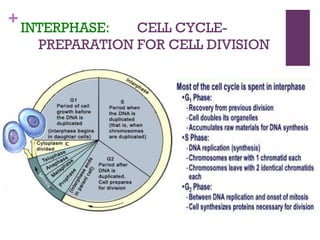
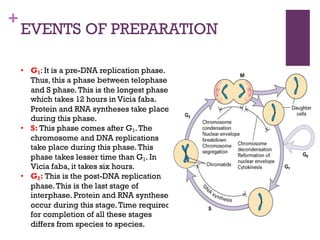
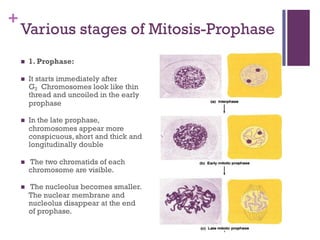
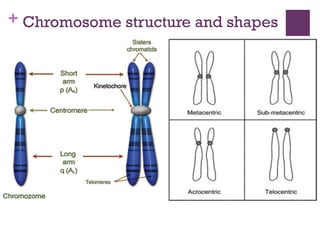
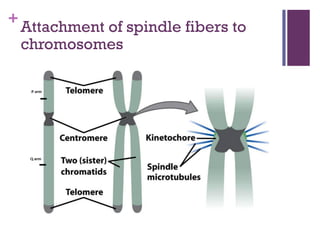
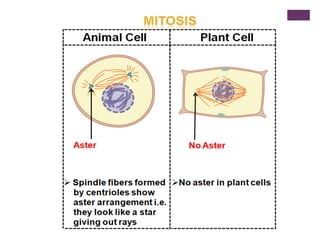
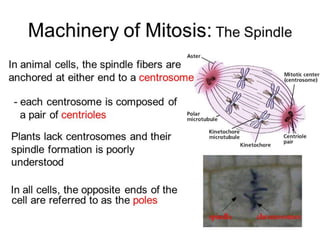
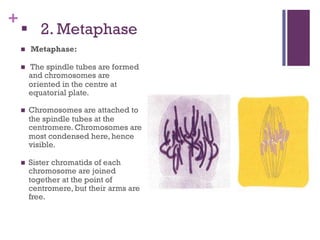
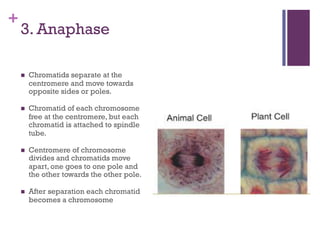
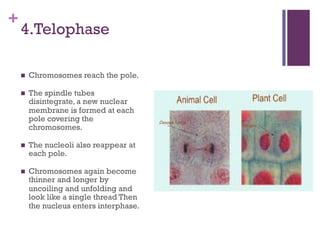
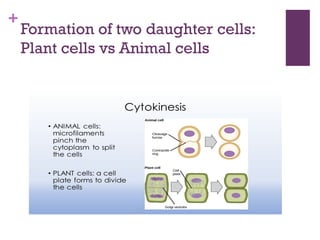
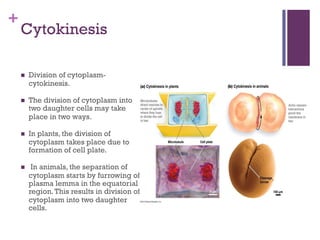
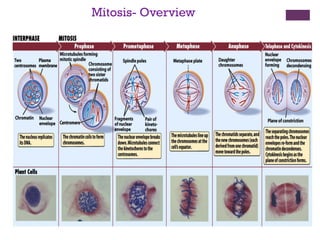
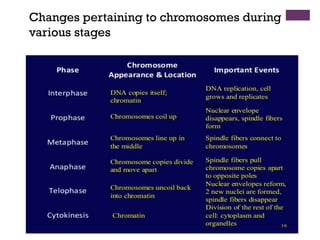
This document provides an overview of mitosis and its stages. Mitosis is the process of nuclear division that produces two identical daughter nuclei from a parent nucleus. It occurs during interphase, which consists of G1, S, and G2 phases that prepare the cell for division. The key stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. During prophase, chromosomes condense and the nuclear envelope breaks down. In metaphase, chromosomes align at the center. Anaphase involves the separation of chromatids to opposite poles. Telophase concludes with the formation of two daughter nuclei. Cytokinesis then divides the cytoplasm to form two daughter cells.