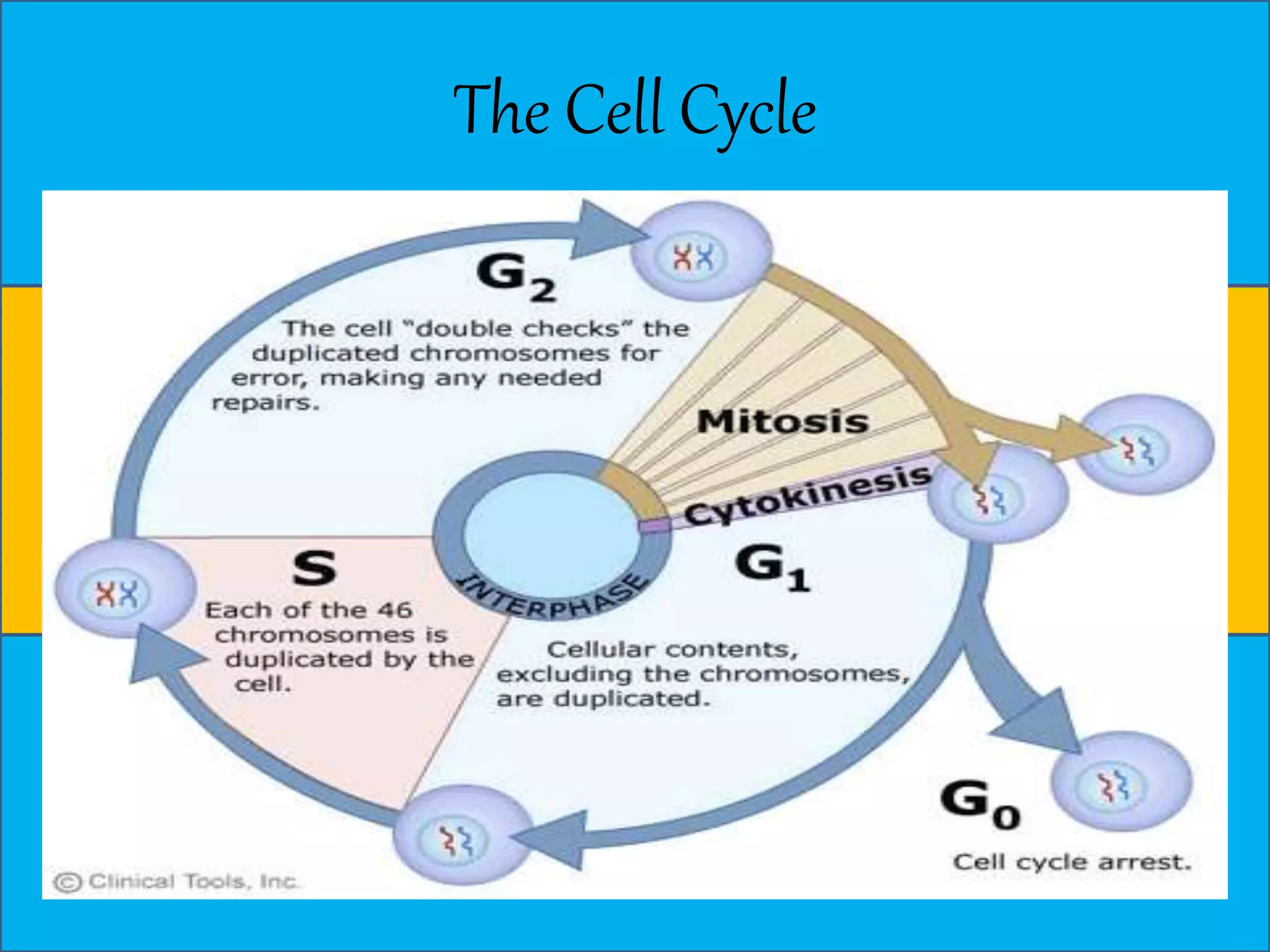
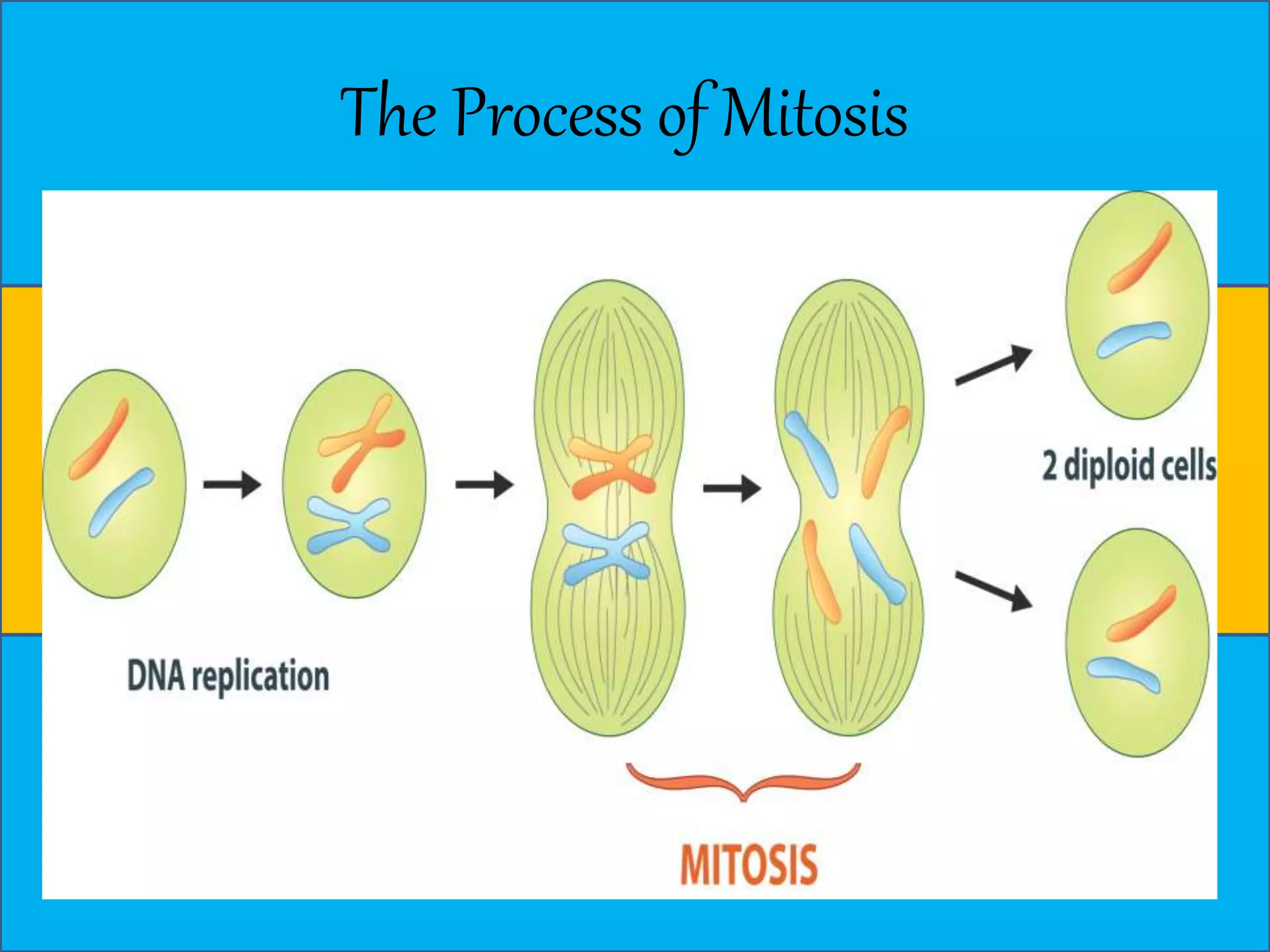
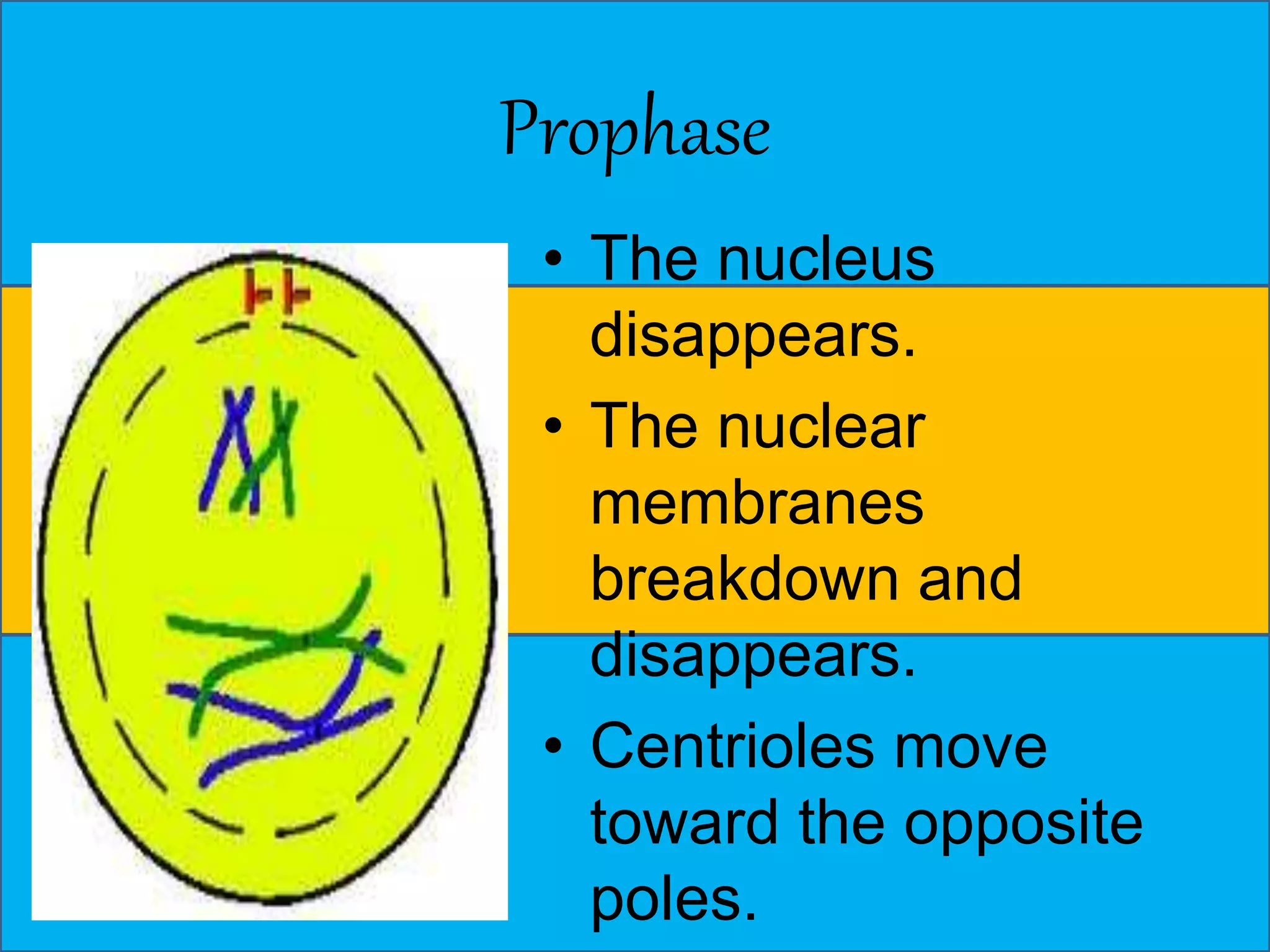
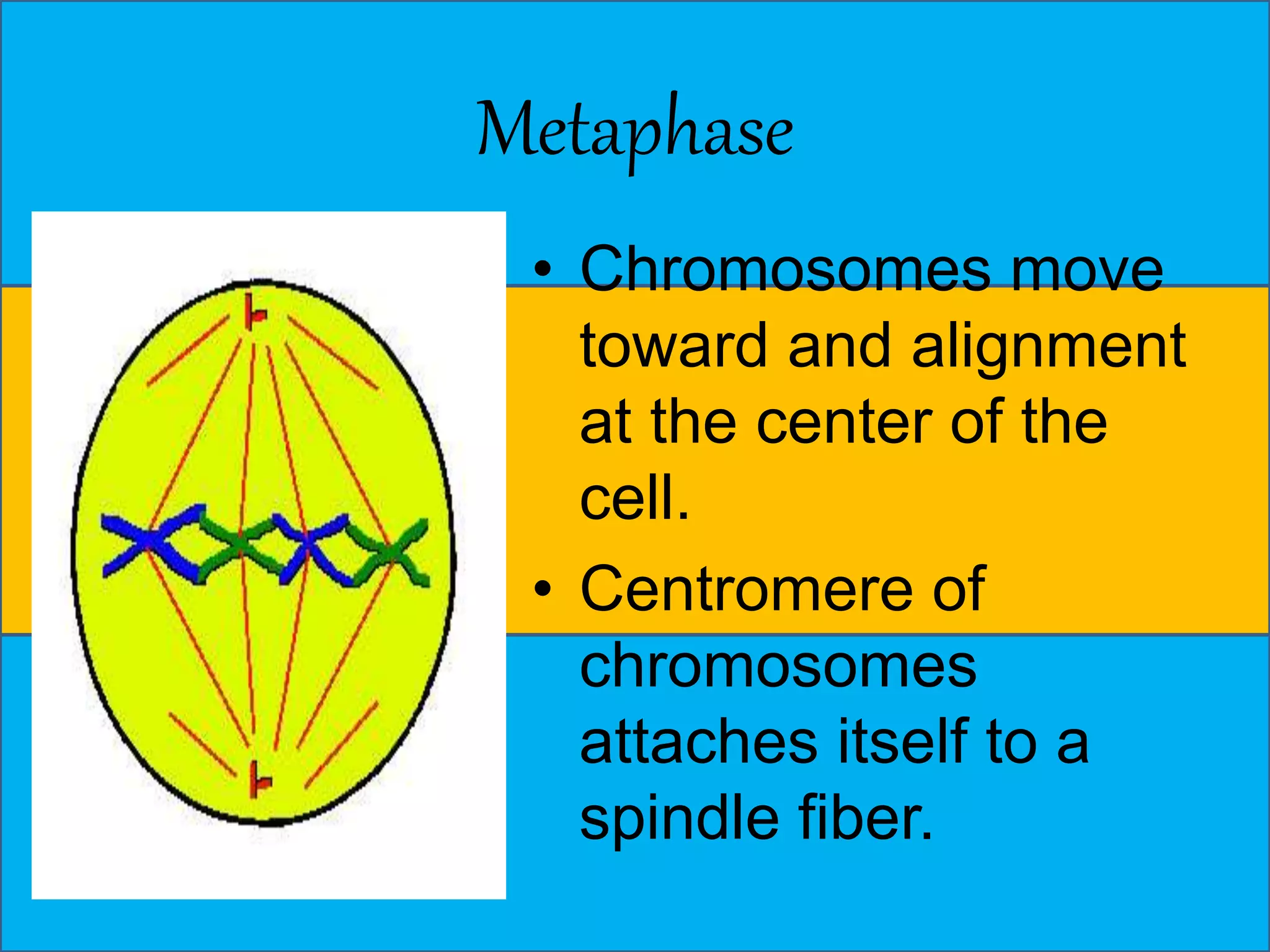
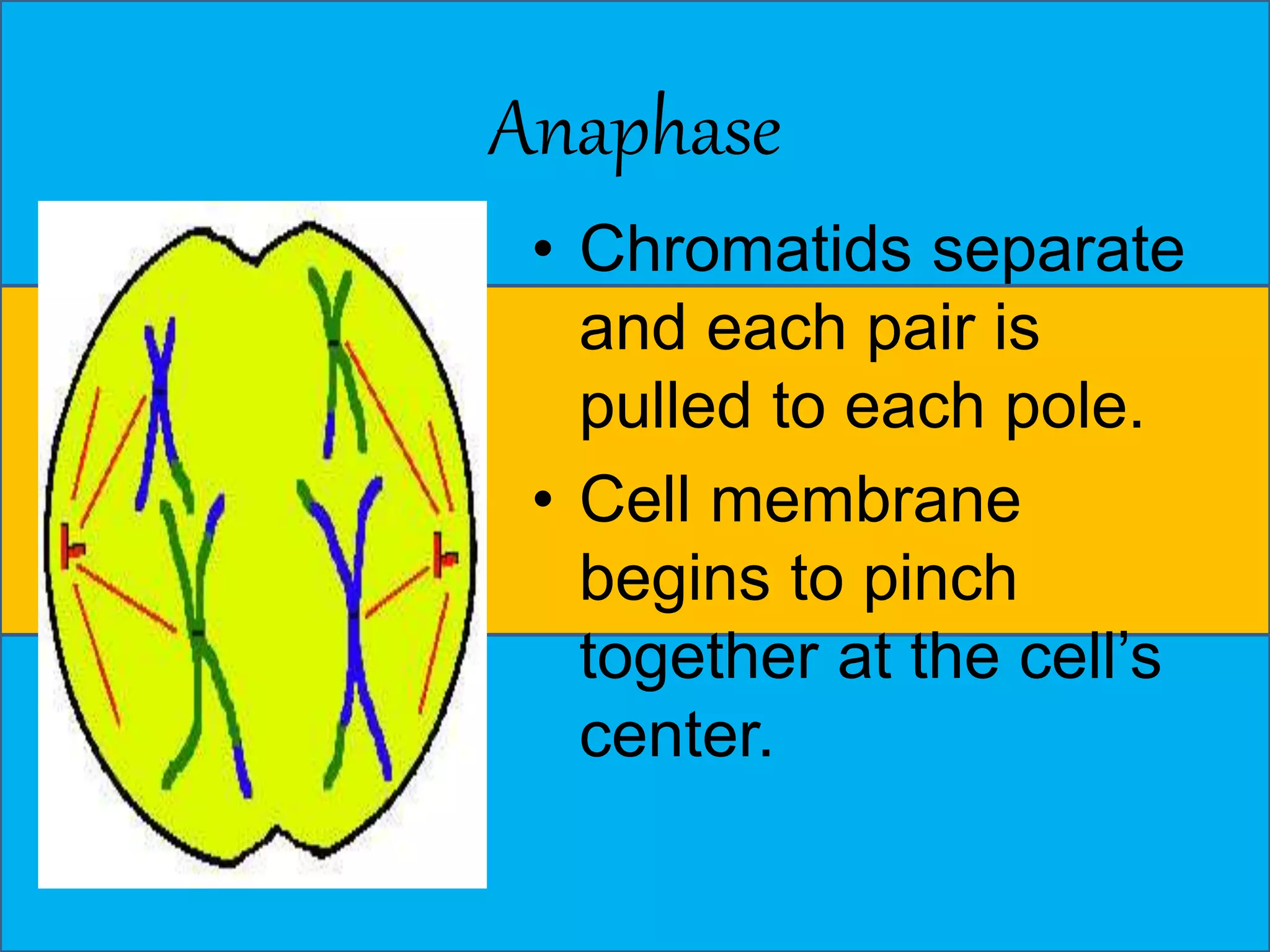
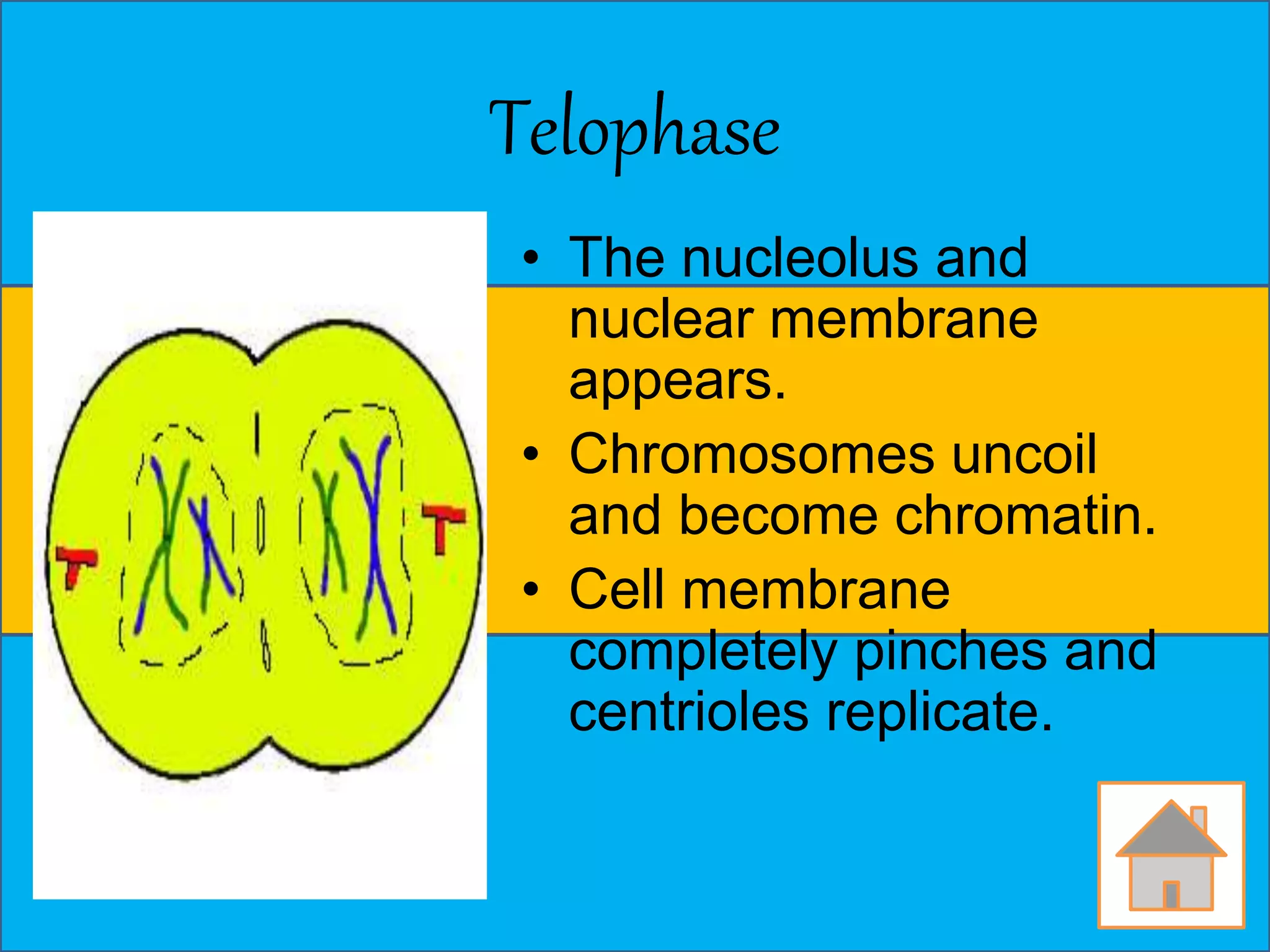
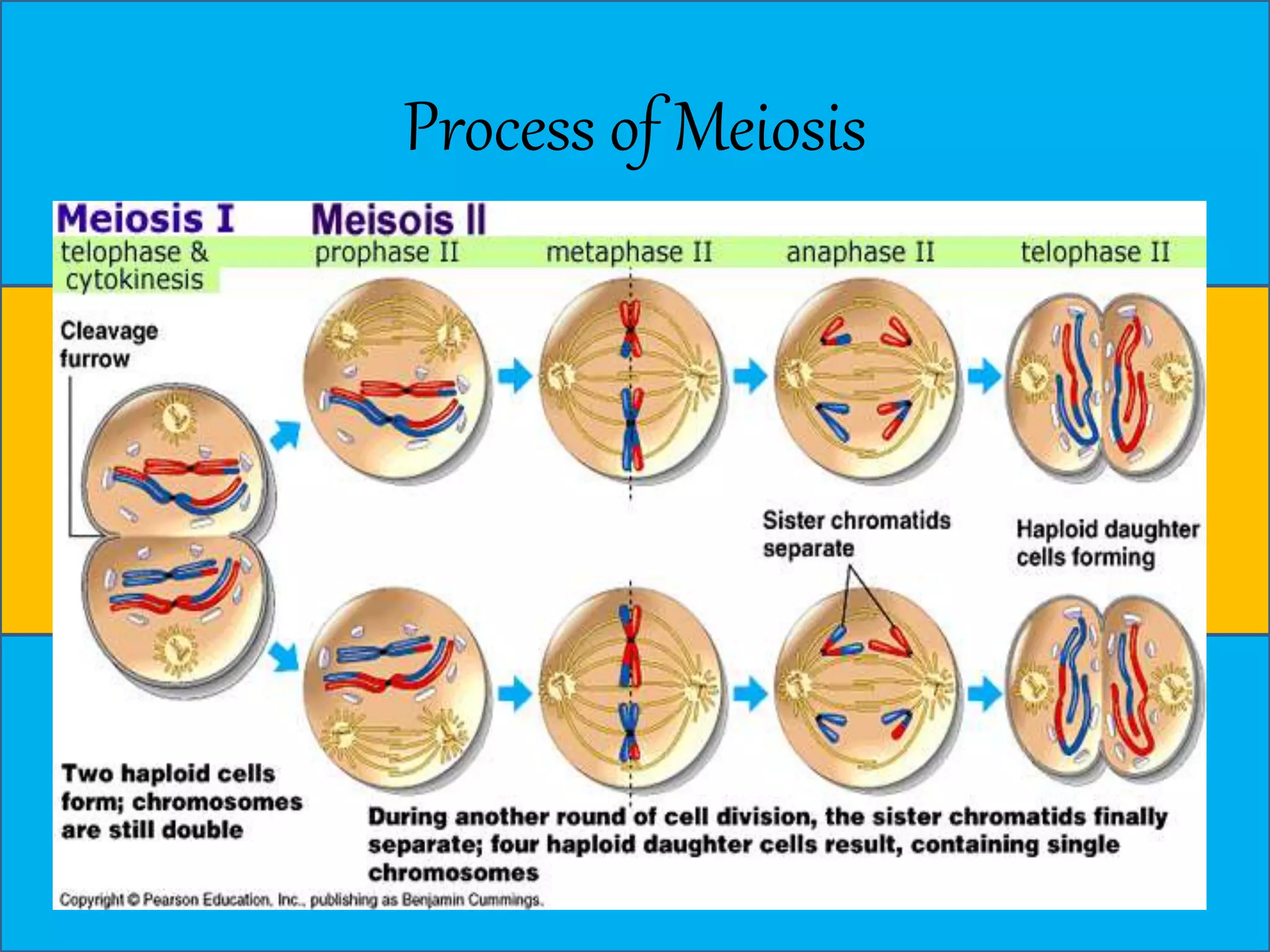
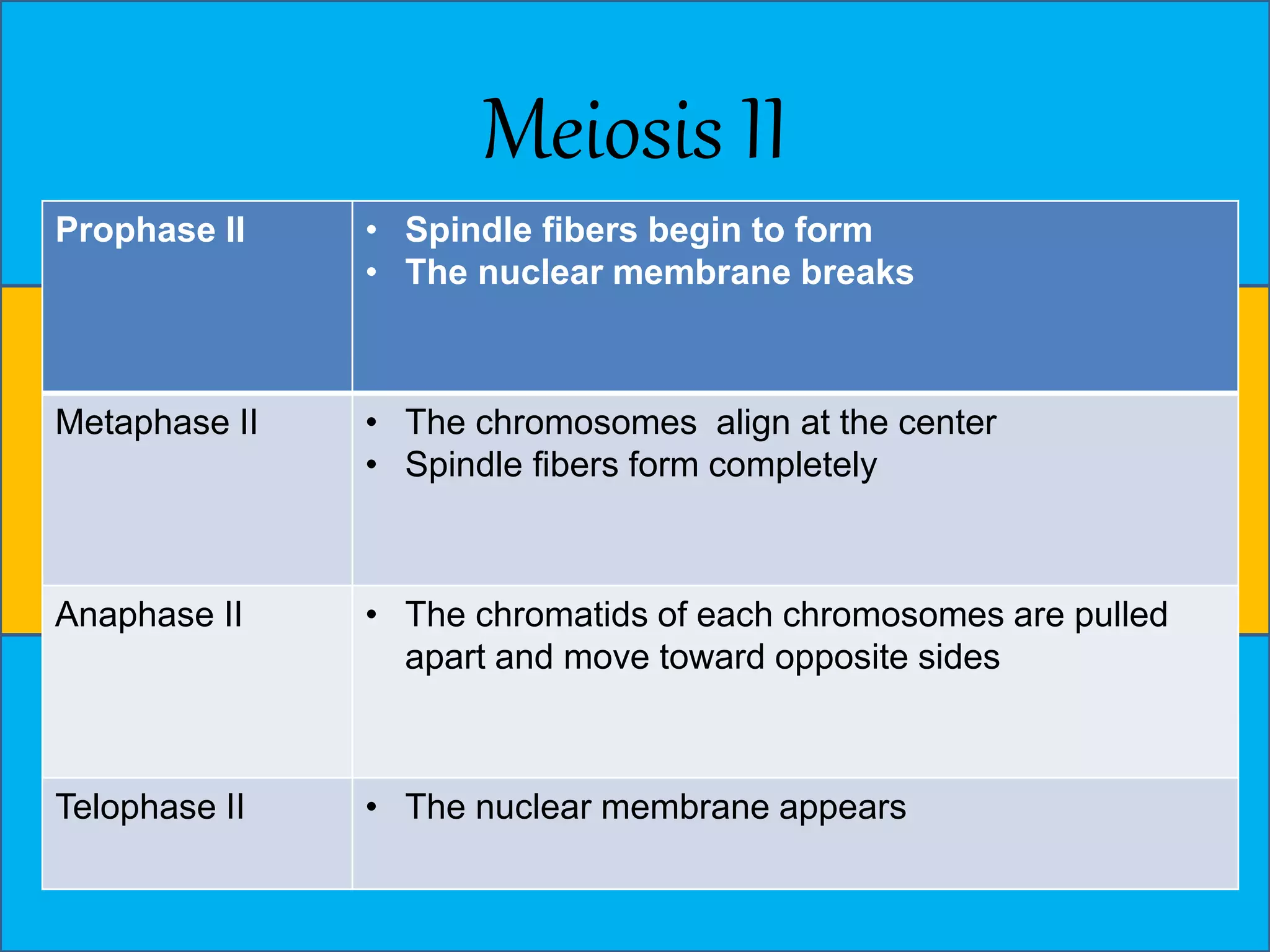
The document discusses cell division through the cell cycle, mitosis, and meiosis. The cell cycle consists of interphase (G1, S, and G2 phases) and mitosis, which produces two daughter cells with identical chromosomes to the parent cell. Mitosis involves four stages - prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Meiosis produces haploid cells through two nuclear divisions and involves prophase I, metaphase I, anaphase I, telophase I, prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II and telophase II.