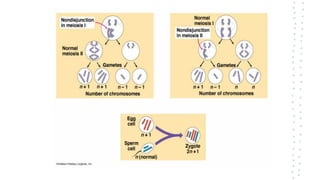
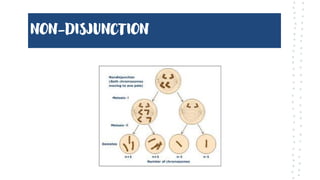
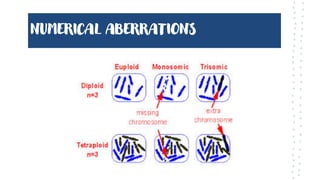
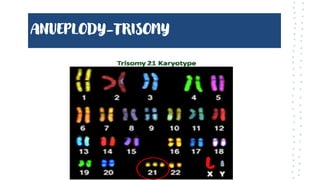
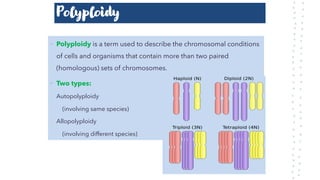
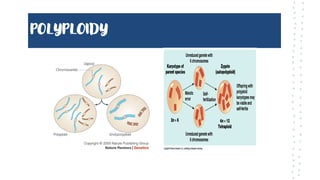
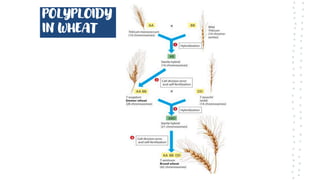
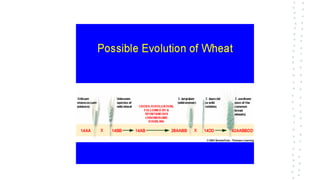
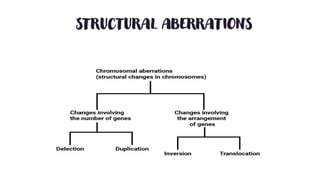
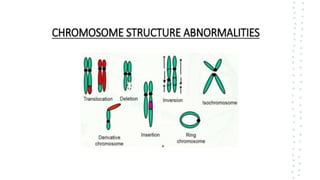
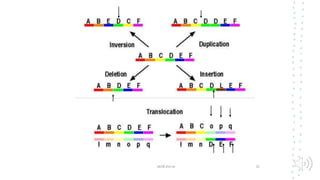
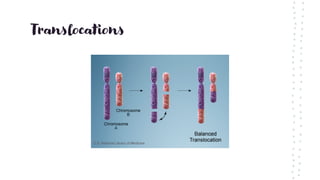
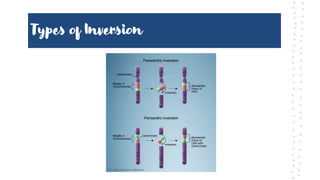
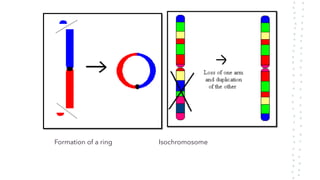
Chromosomal aberrations refer to disruptions in the normal chromosomal content of a cell and are major causes of genetic conditions in humans. There are two main types of chromosomal aberrations: numerical abnormalities which involve an atypical number of chromosomes, and structural abnormalities which alter the structure of chromosomes. Examples of numerical abnormalities include aneuploidy, such as trisomy which is the presence of three copies of a chromosome instead of the normal two copies. Structural abnormalities include deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations which involve portions of chromosomes being removed, duplicated, inverted, or transferred between chromosomes. Common genetic disorders associated with chromosomal aberrations include Down syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome