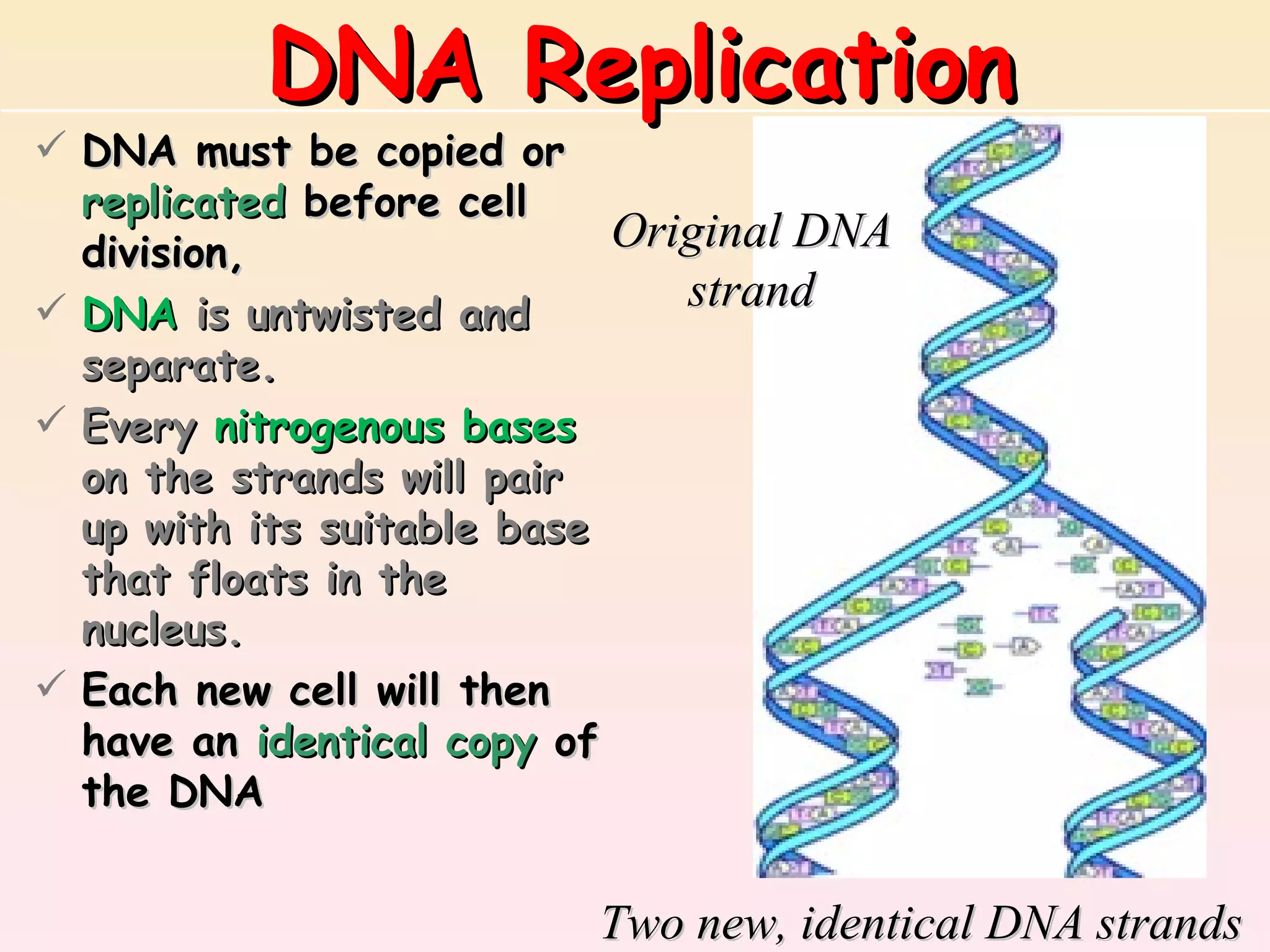
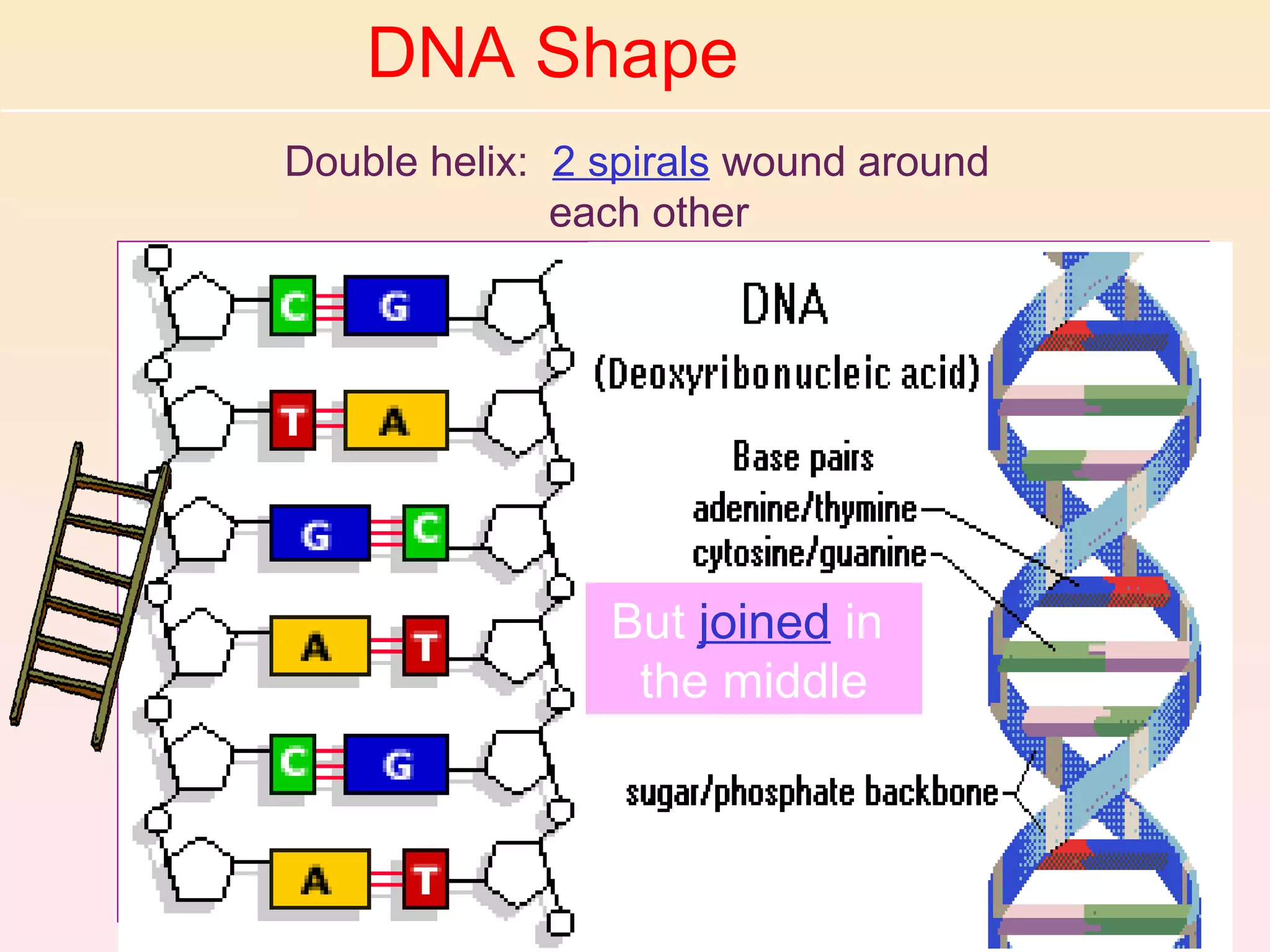
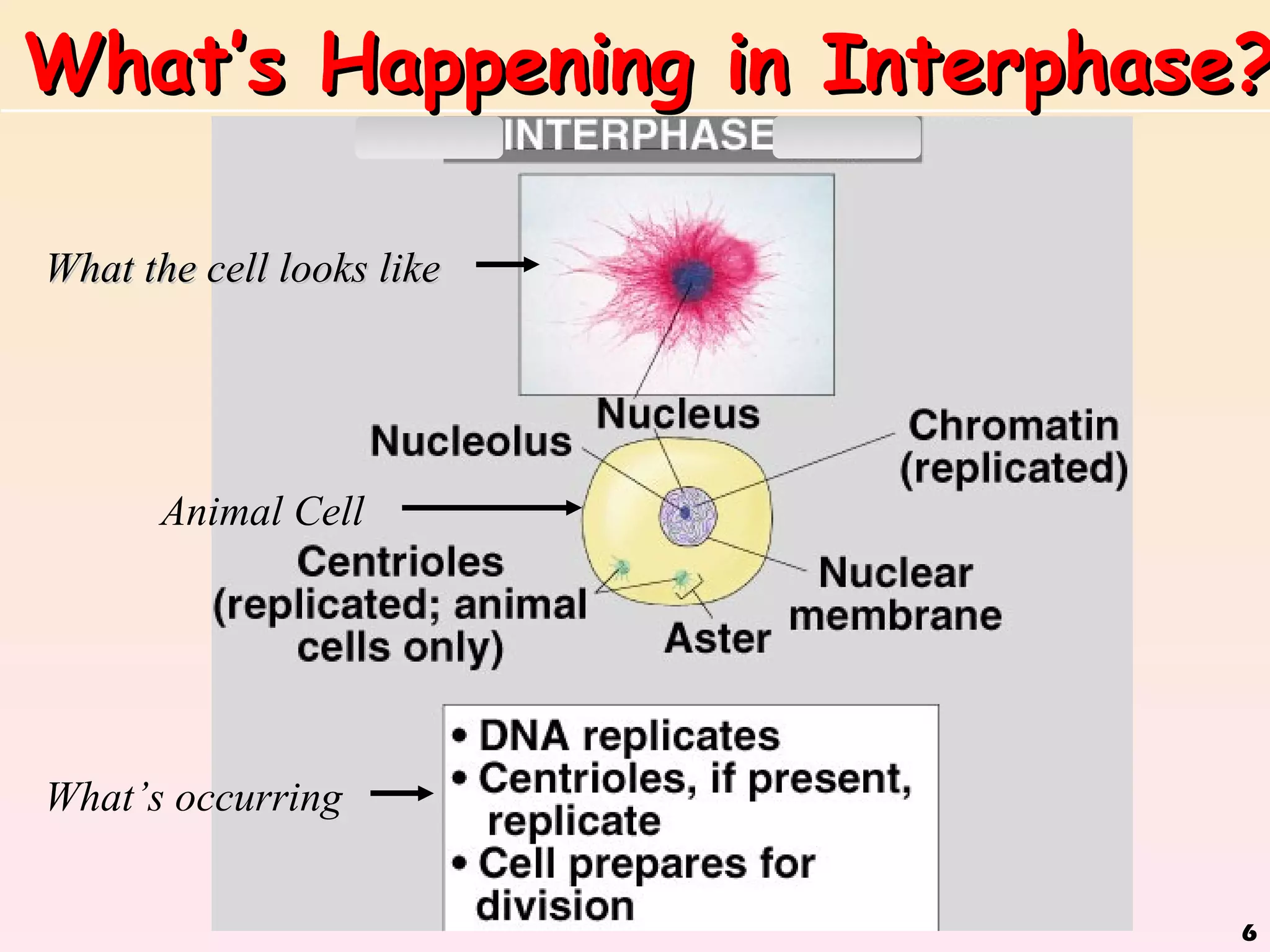
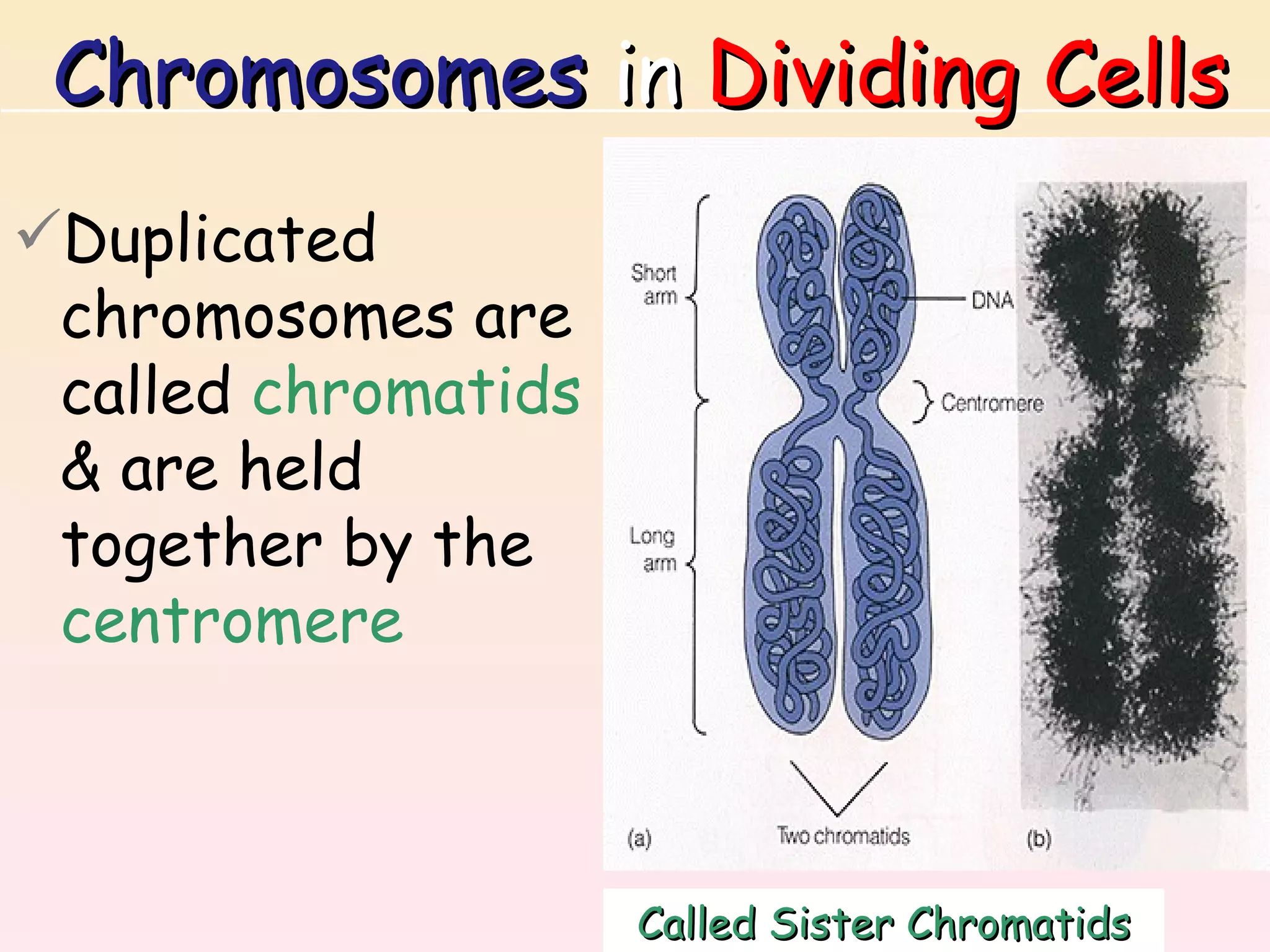
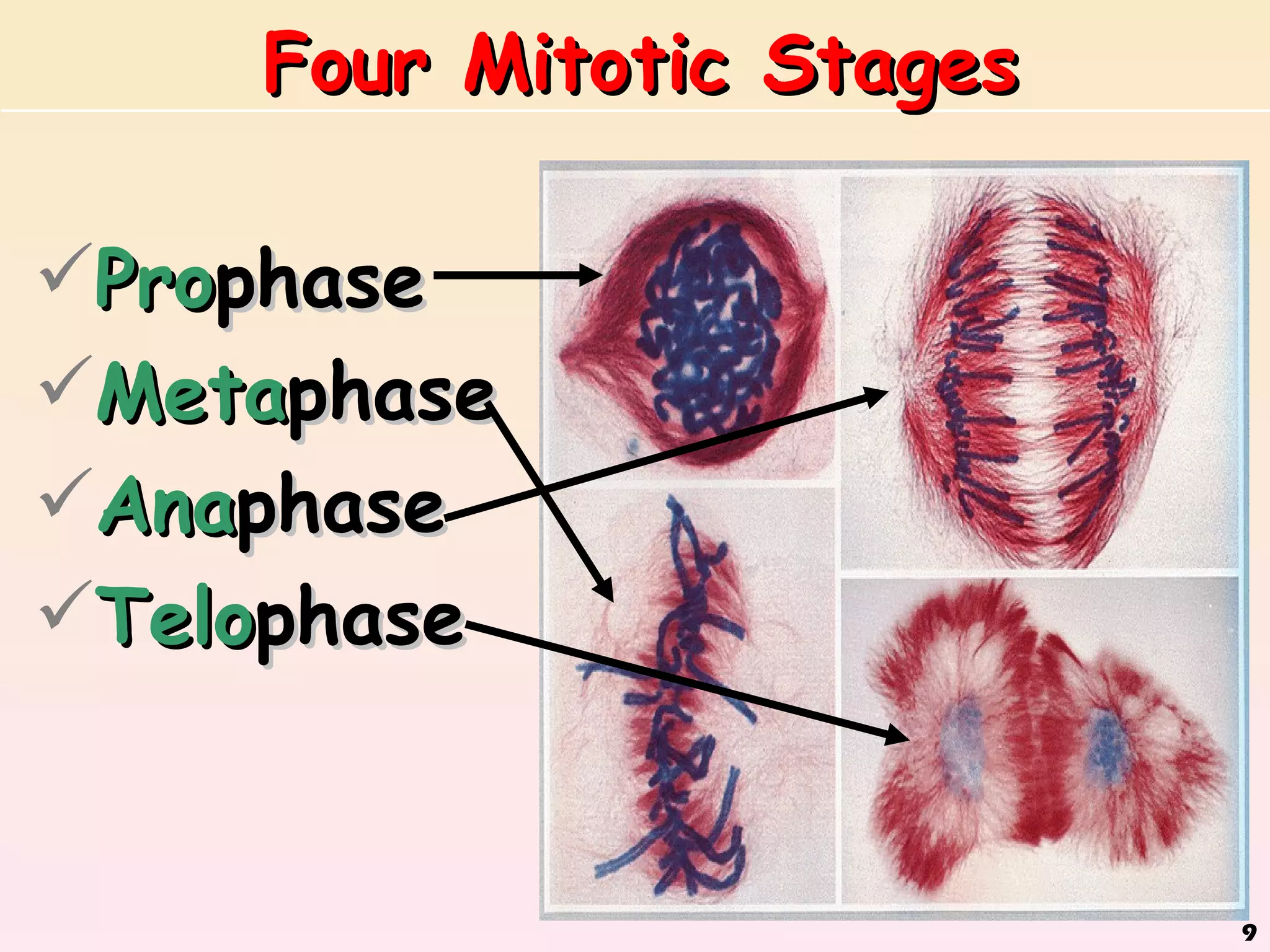
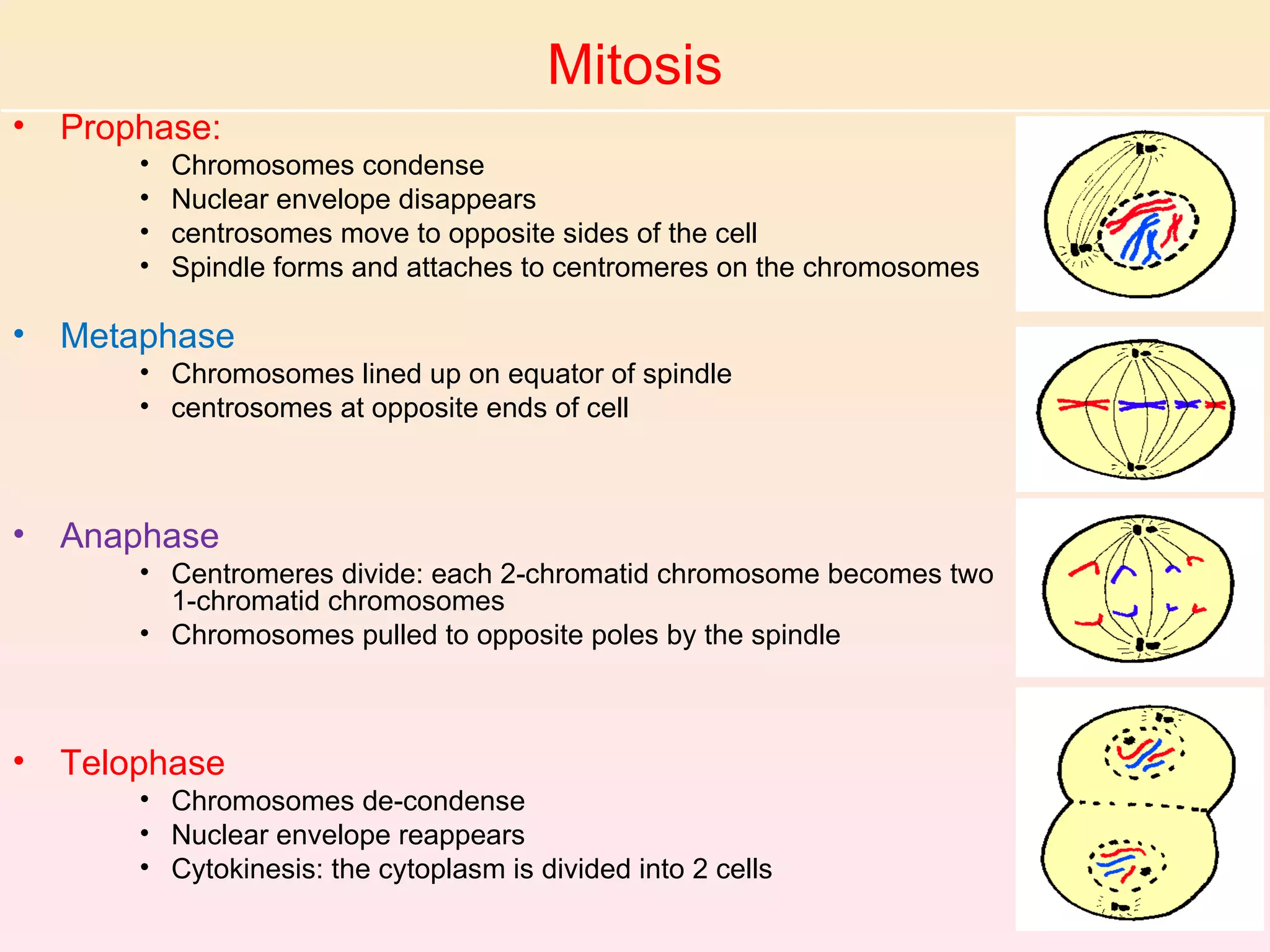
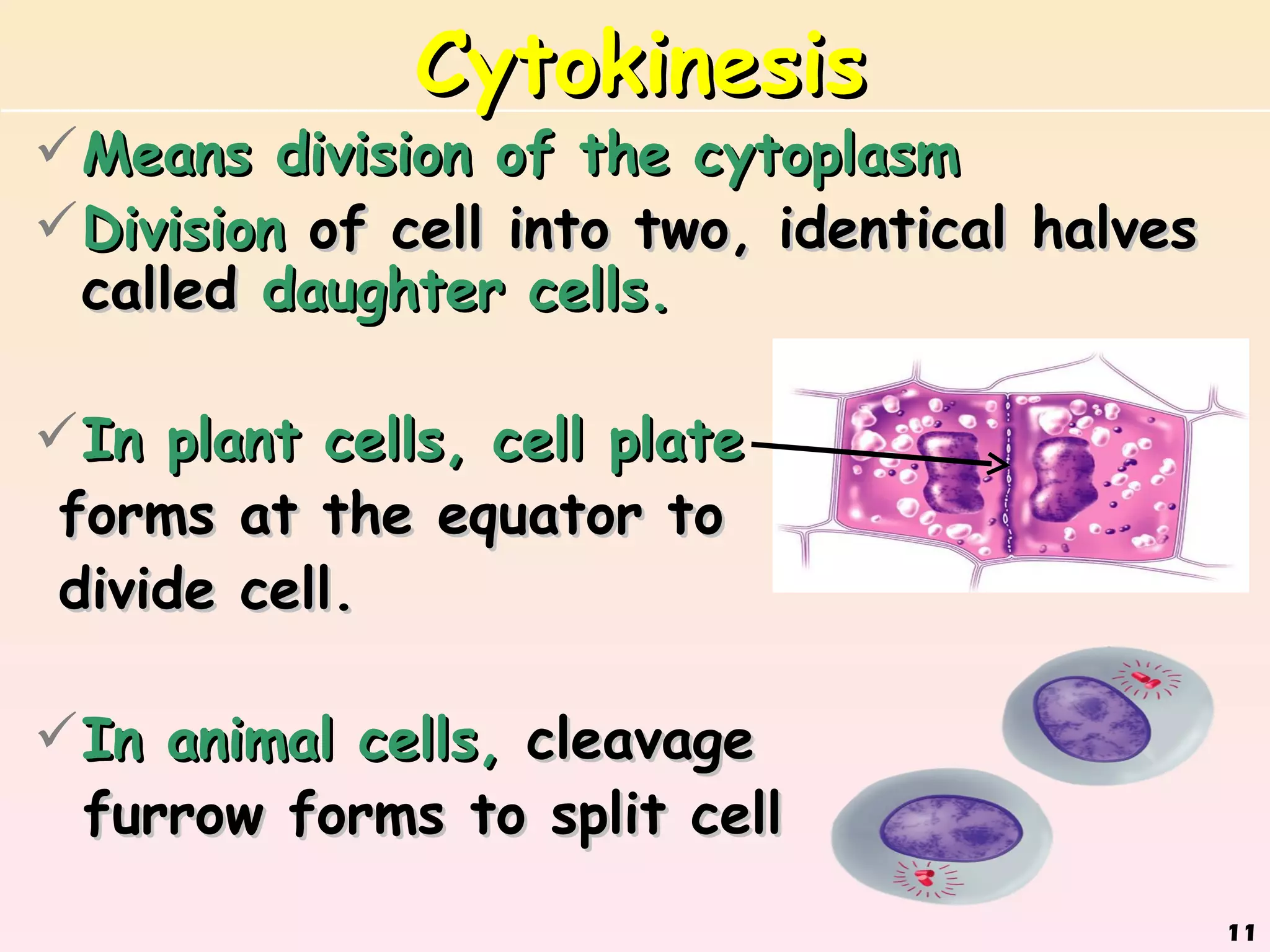
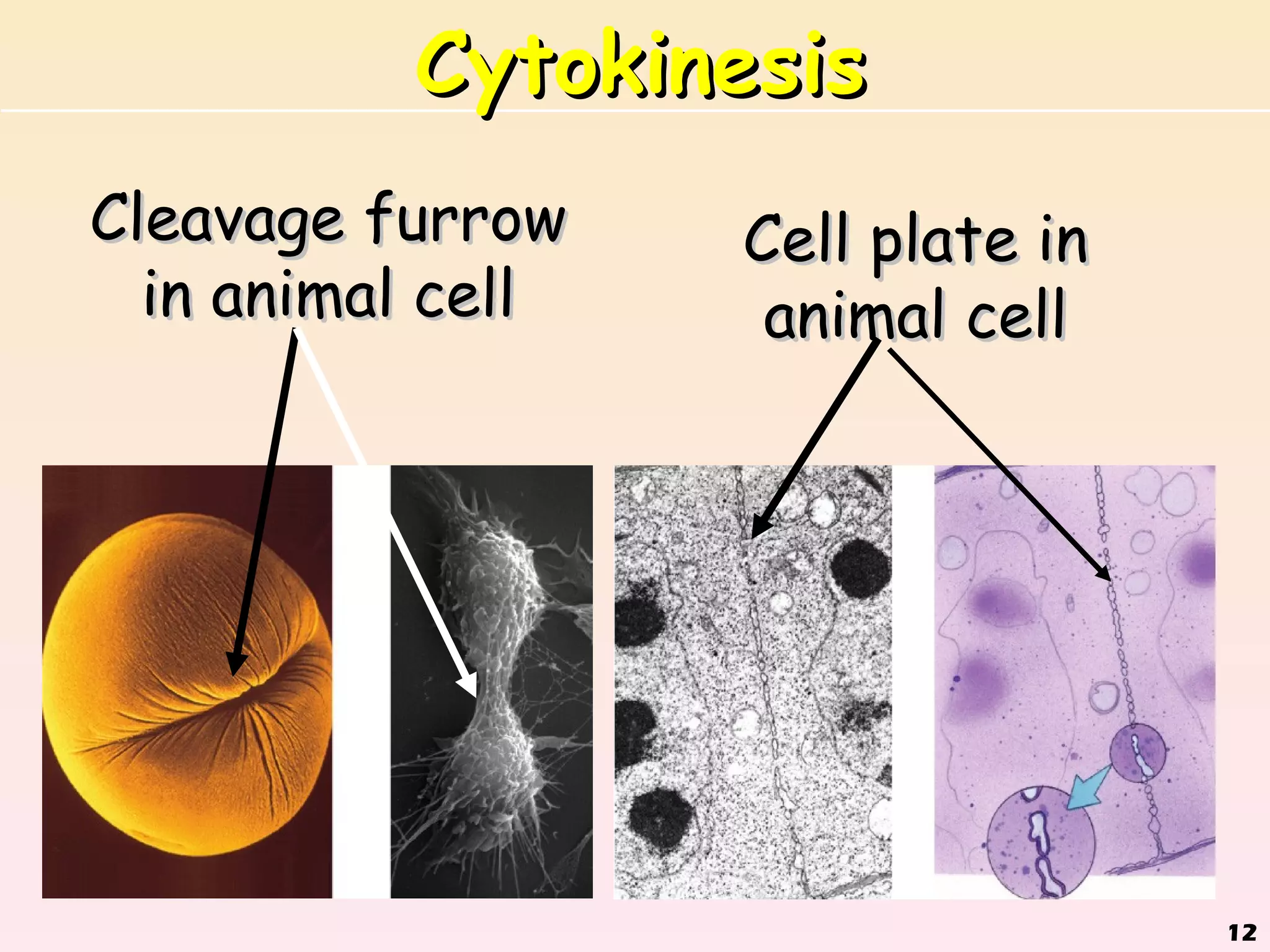
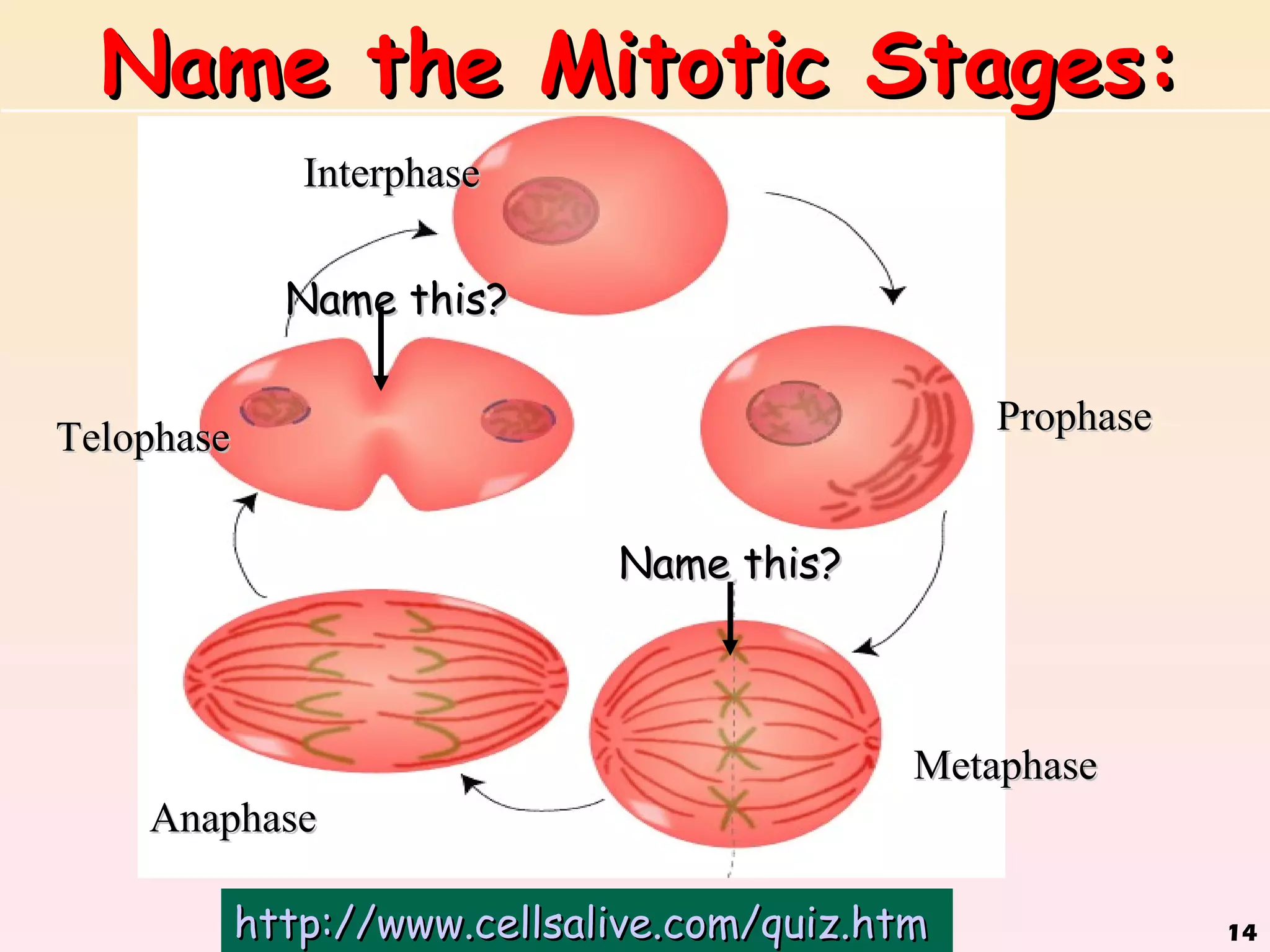
The document discusses cell division, emphasizing that all cells originate from pre-existing cells and that DNA must be replicated prior to division to ensure each new cell receives an identical set. It details the four stages of mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) and the process of cytokinesis, which divides the cytoplasm into two identical daughter cells. Additionally, it contrasts the processes in plant and animal cells during cytokinesis.