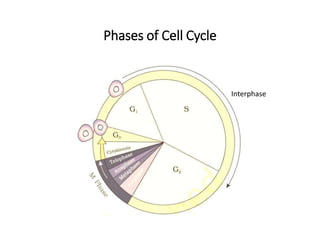
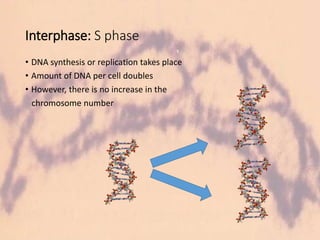
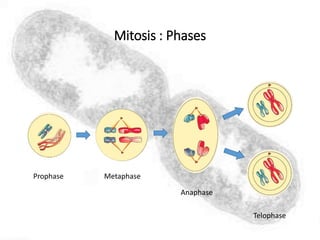
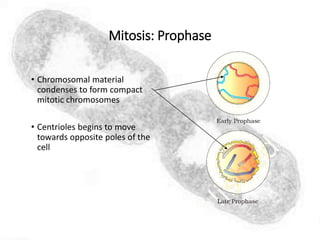
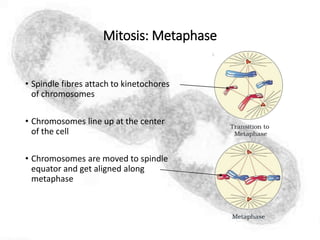
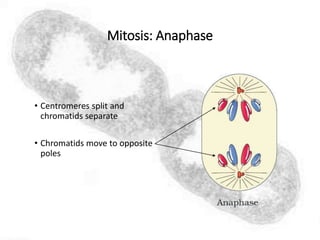
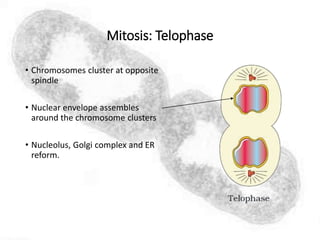
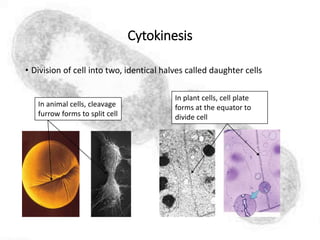
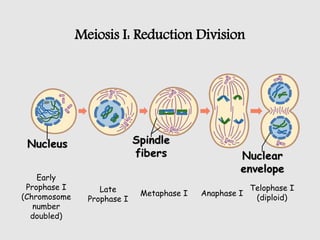
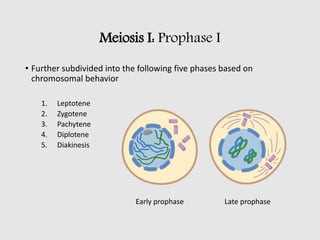
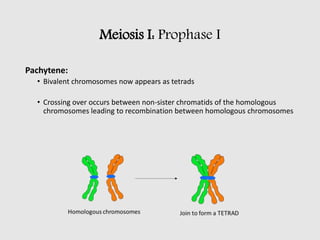
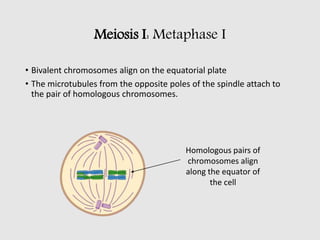
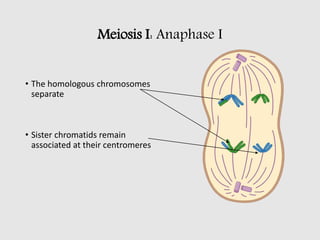
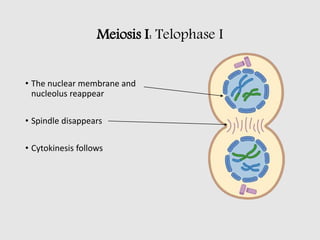
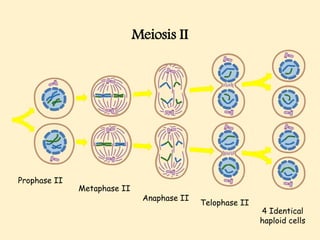
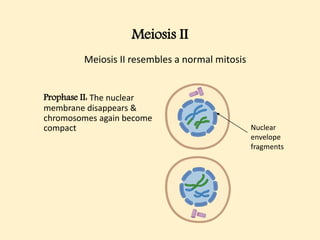
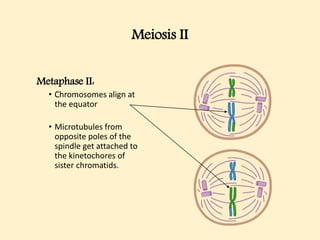
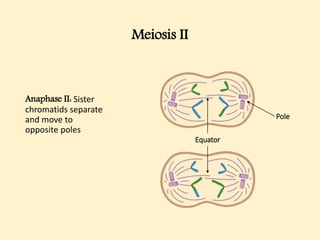
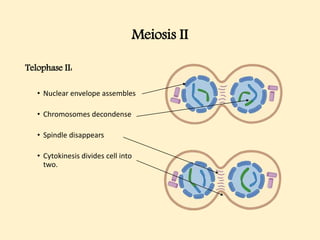
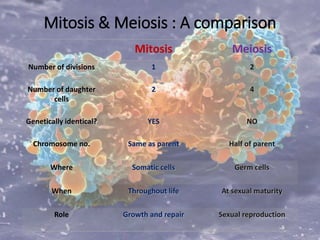
The cell cycle comprises the processes of DNA replication, cell growth, and division into two daughter cells, divided into interphase and mitosis. Interphase includes G1, S, and G2 phases, while mitosis consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, ensuring the generation of genetically identical cells. Meiosis, a specialized division for producing haploid cells, involves two rounds of division and recombination, promoting genetic diversity while reducing the chromosome number by half.