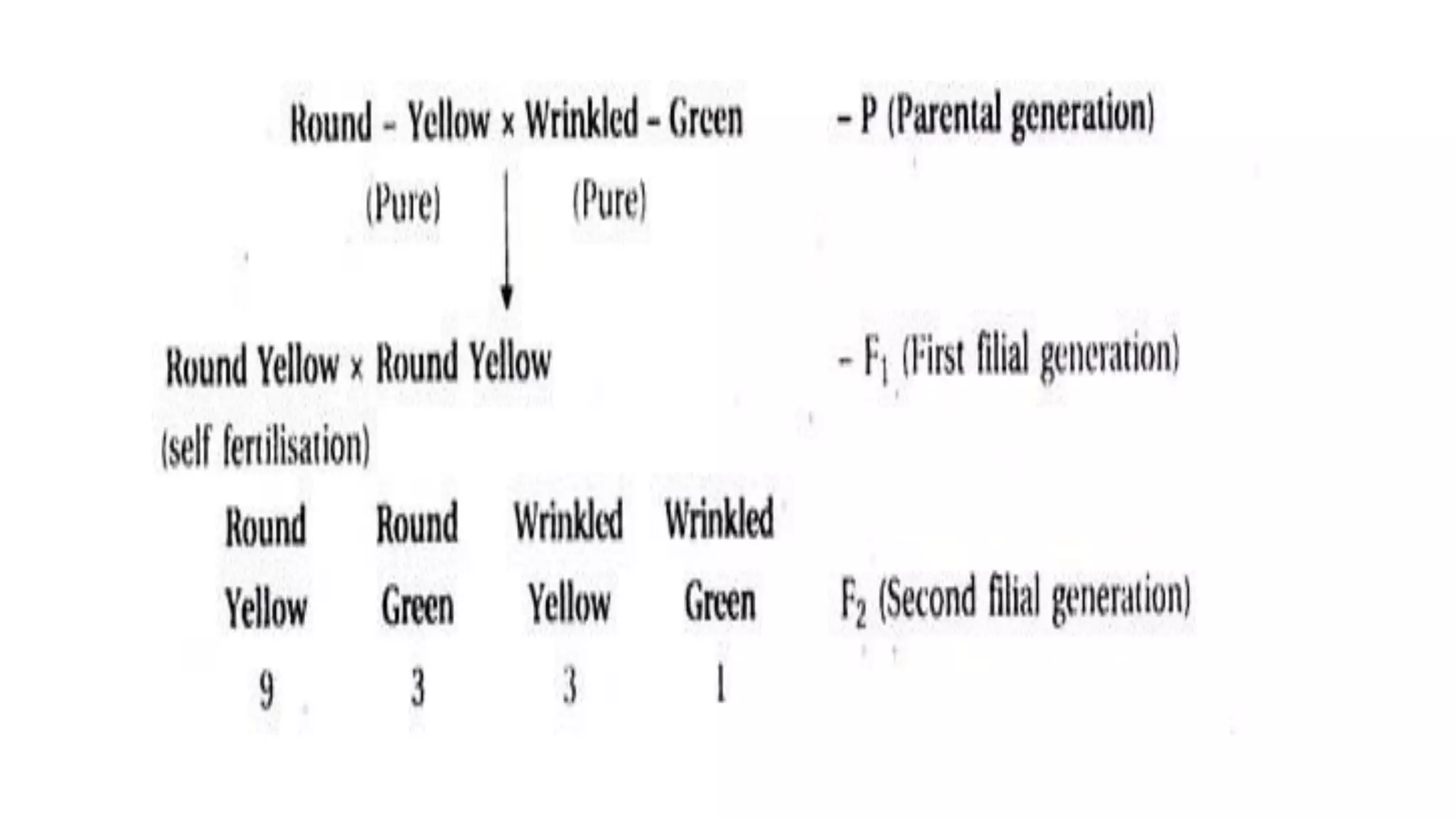
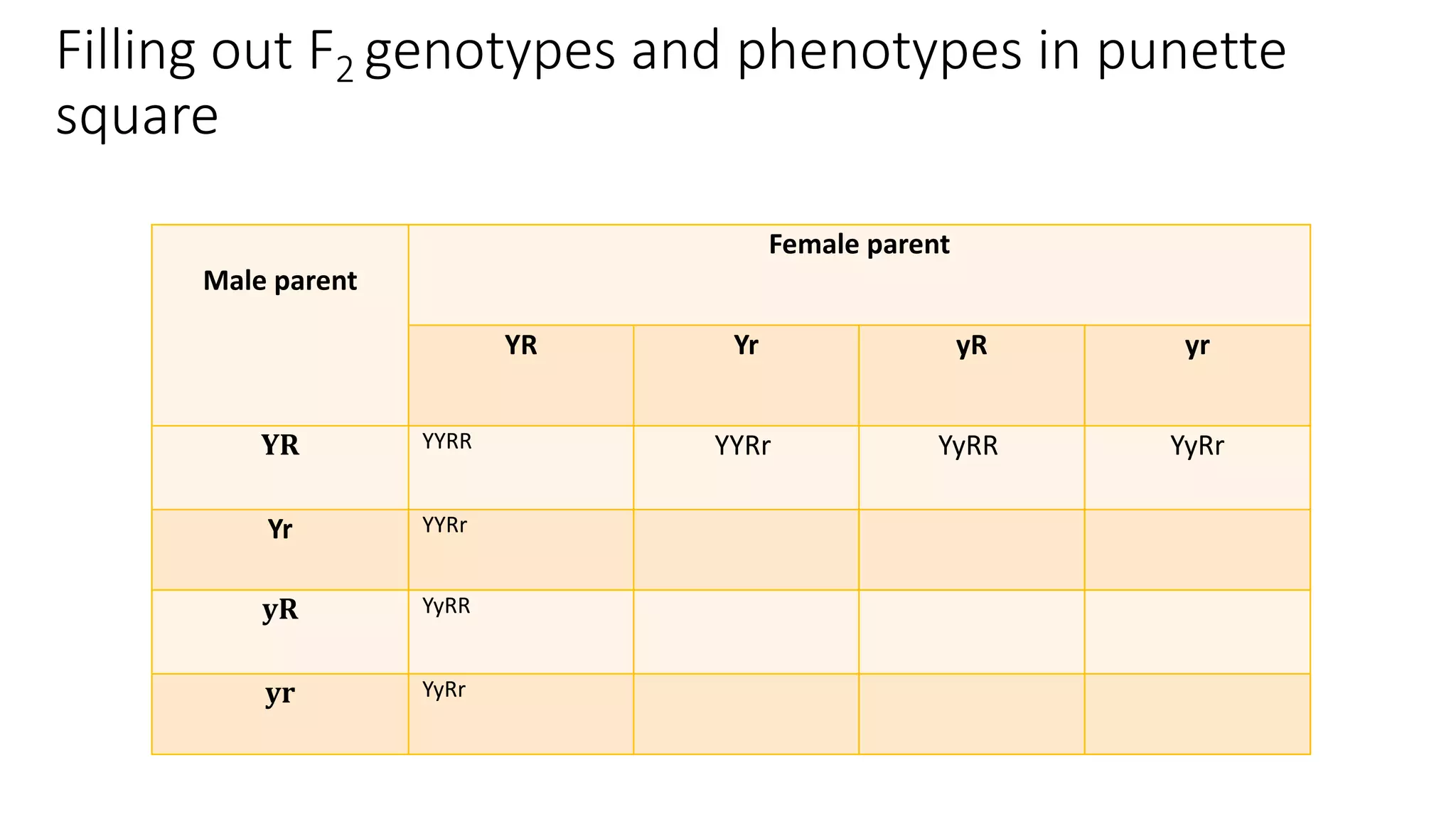
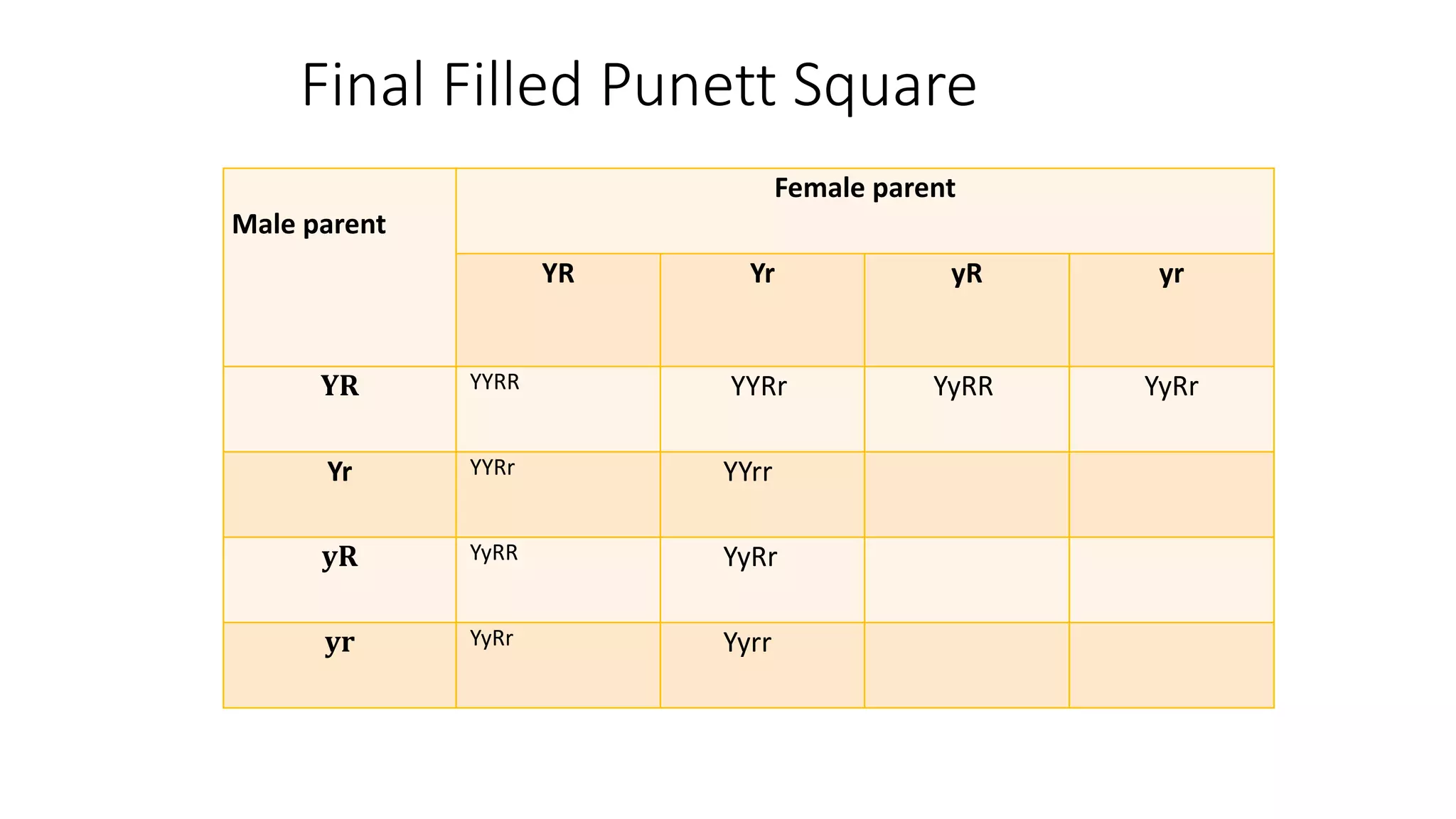
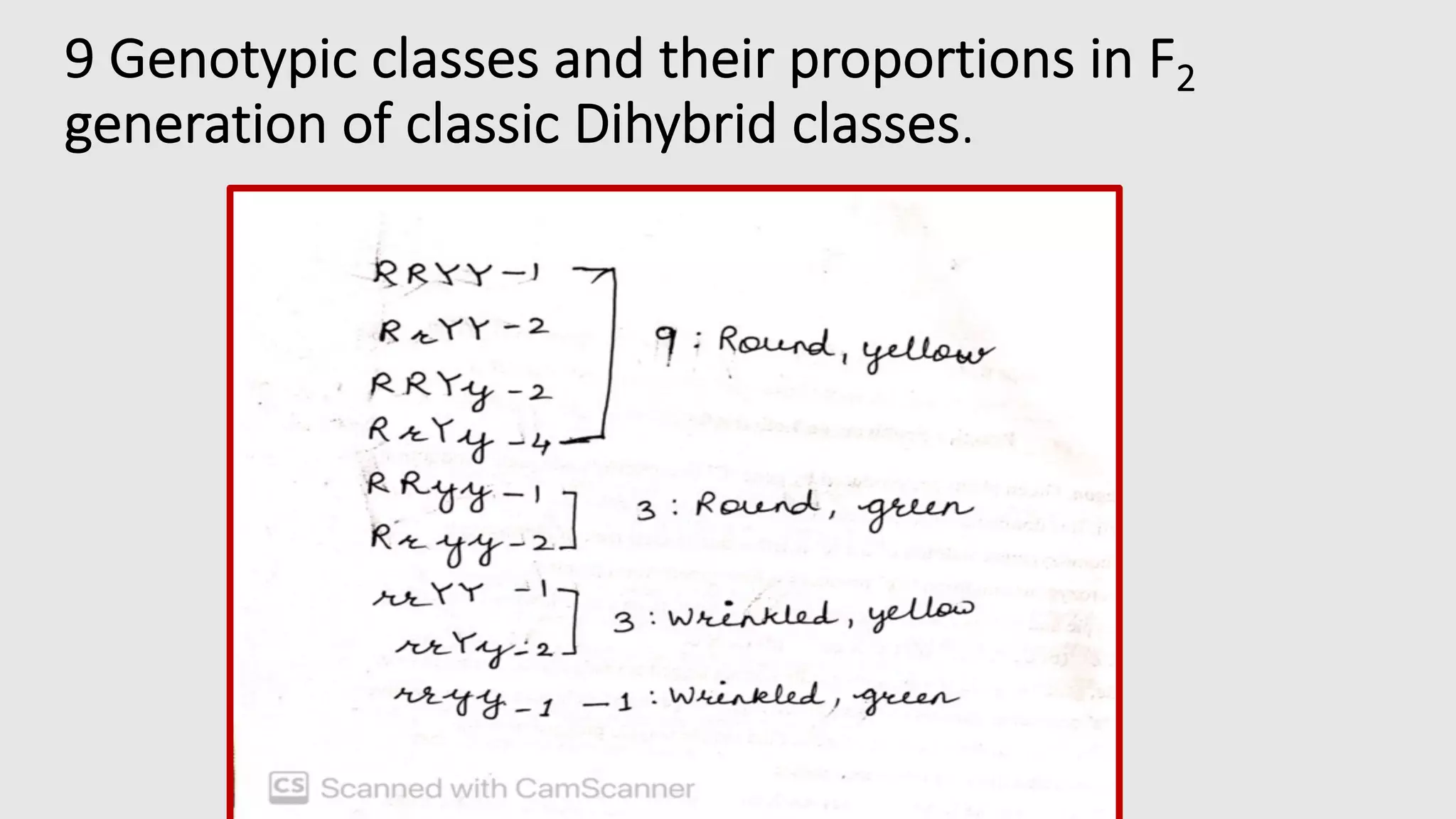
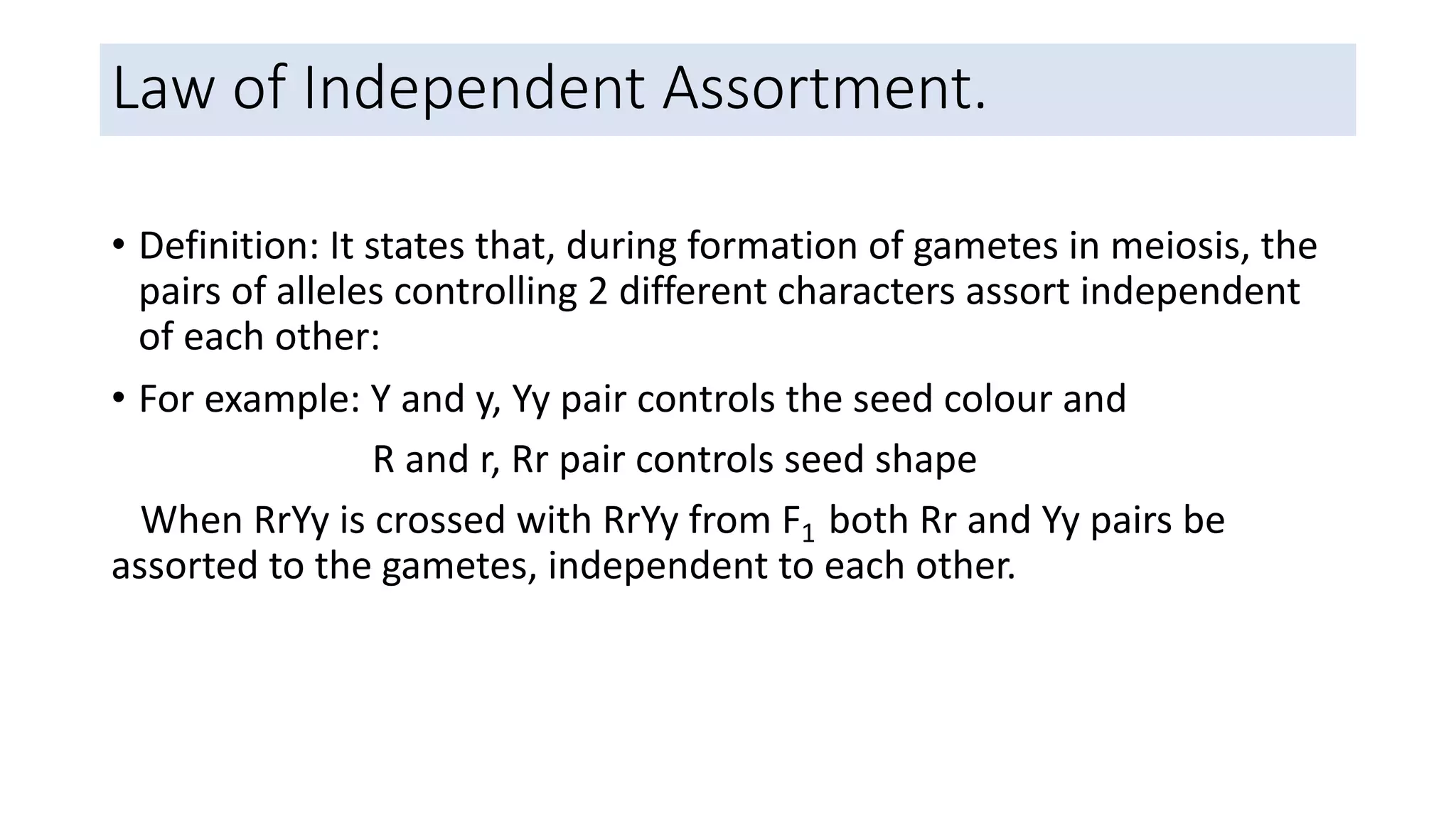
The document outlines the principles of Mendelian genetics through a dihybrid cross involving pea plants with two contrasting traits: seed shape and seed color. It provides details on genotypes, gamete production, and results, culminating in a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 in the F2 generation. Moreover, it includes practice problems to reinforce understanding of genetic crosses and inheritance patterns.