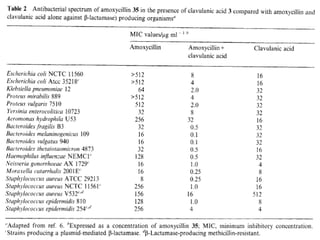
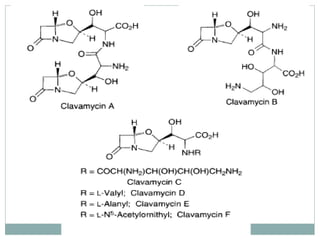
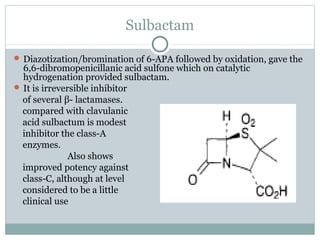
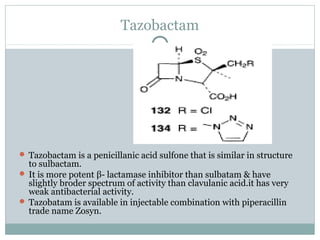
Clavulanic acid is a β-lactamase inhibitor discovered from Streptomyces clavuligerus. It is used in combination with β-lactam antibiotics like amoxicillin to restore their effectiveness against β-lactamase producing bacteria. Clavulanic acid inactivates β-lactamases non-competitively but has weak antibacterial activity itself. Other β-lactamase inhibitors discussed are sulbactam, tazobactam, which have different spectrums of activity and inhibition profiles against various classes of β-lactamases. The development of β-lactamase inhibitors was an important strategy to overcome resistance arising







![Clavulanic Acid
Systematic (IUPAC) name: (2R,5R,Z)-3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-
7-oxo-4-oxa-1-aza-bicyclo[3.2.0] heptane-2-carboxylic acid
Clavulanic acid can be considered as the most important & representive
among the inhibitors of β- lactamases.
It is first clinically useful β- lactamase inhibitor was identified as a natural
product from a strain of Streptomyces clavuligerus.
Structurally it is a 1-oxopenam lacking the 6-acyl amino side chain of
penicillins but possessing a 2-hydroxy ethylidene moiety at C-2
Clavulanic AcidClavulanate Potassium](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calvulanicacidandanaloug-130629065842-phpapp01/85/Calvulanic-acid-and-analoug-9-320.jpg)


![Marketed Combinations
Most commonly, the potassium salt potassium
clavulanate is combined with amoxicillin (co-
amoxiclav) [brand name Augmentin]
Timetin (potassium clavulanate plus ticarcillin)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/calvulanicacidandanaloug-130629065842-phpapp01/85/Calvulanic-acid-and-analoug-12-320.jpg)