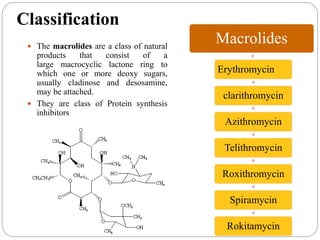
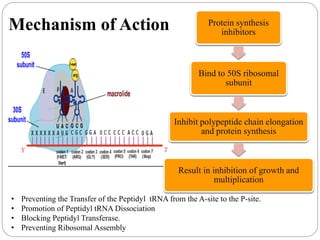
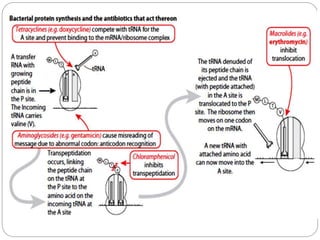
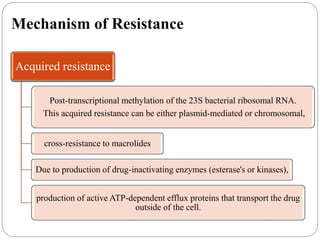
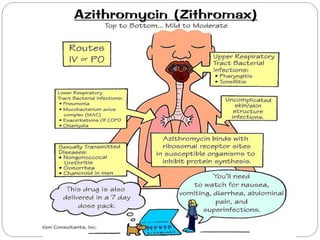
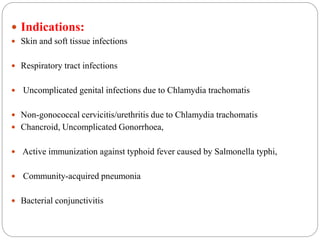
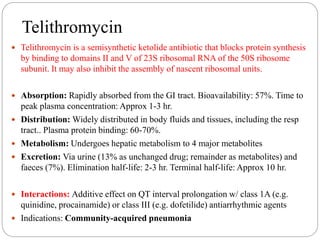
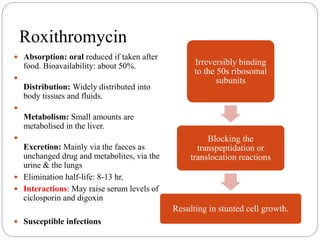
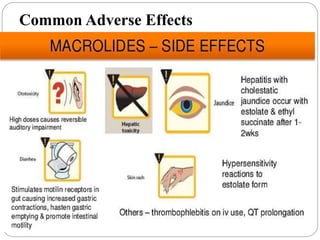
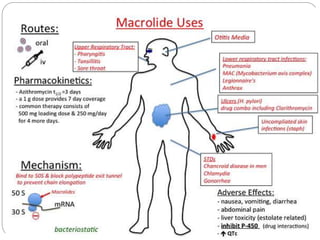
This document discusses macrolide antibiotics, including their classification, mechanism of action, mechanisms of resistance, and examples like erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin, and telithromycin. Macrolides are a class of natural products consisting of a large macrocyclic lactone ring with attached deoxy sugars. They inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and blocking polypeptide chain elongation. Resistance can develop via ribosomal methylation, drug-inactivating enzymes, or efflux pumps. The macrolides discussed have similar spectra but differ in absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and indications.