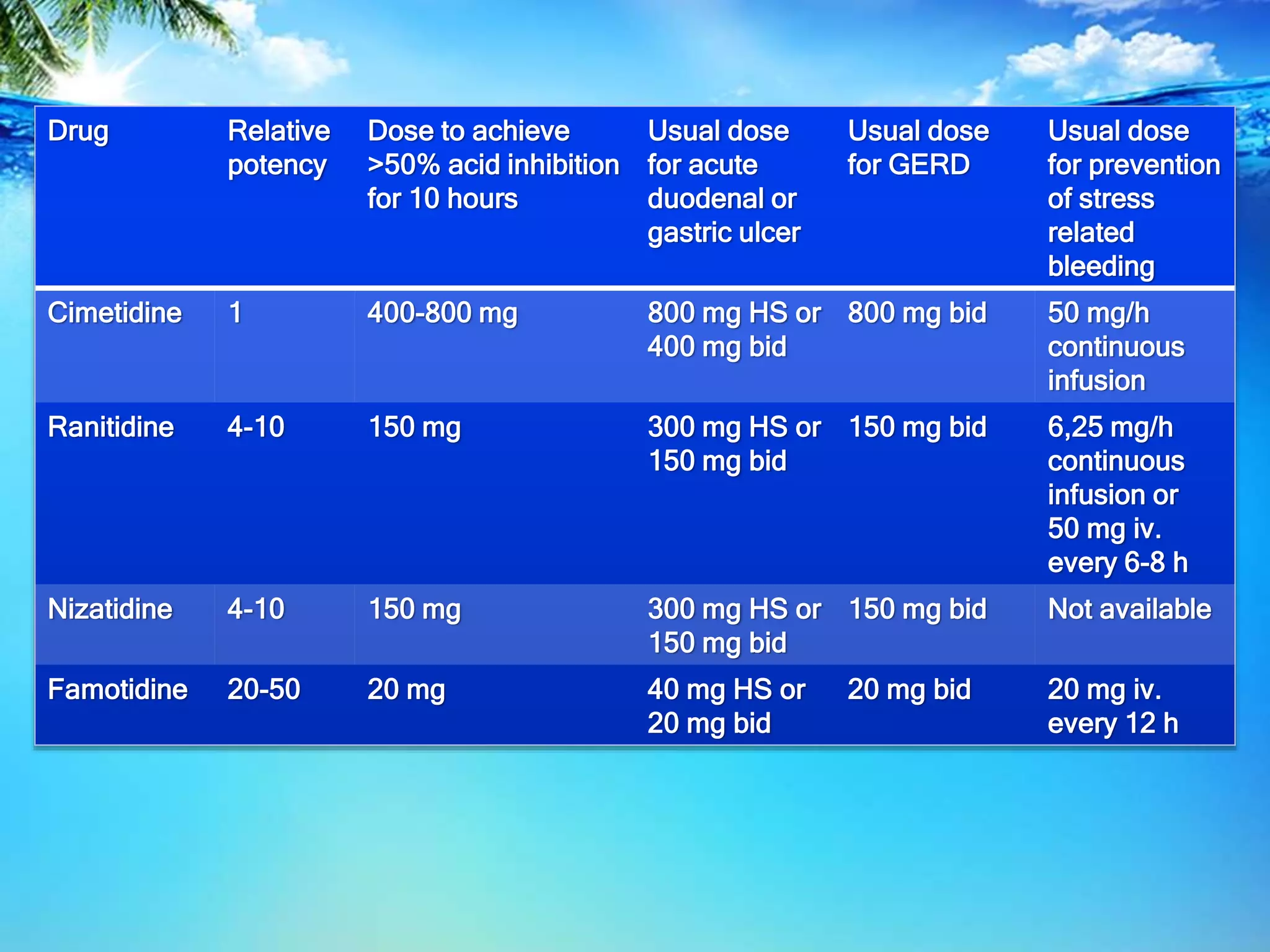
H2-receptor antagonists like cimetidine, ranitidine, famotidine, and nizatidine are rapidly absorbed from the intestine and undergo hepatic metabolism, reducing their bioavailability. They exhibit competitive inhibition at the H2 receptor on parietal cells, suppressing both basal and meal-stimulated acid secretion in a dose-dependent manner. H2 antagonists are effective for conditions like GERD, peptic ulcer disease, and stress-related bleeding by increasing gastric pH and inhibiting acid secretion. However, they can cause adverse effects like diarrhea, headaches, and drug interactions by inhibiting hepatic cytochrome P450 pathways.