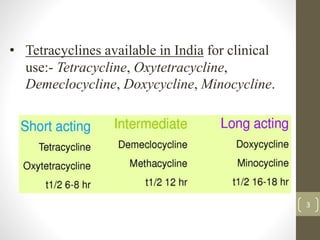
Tetracyclines, introduced in 1948, are broad-spectrum antibiotics effective against a variety of pathogens but not fungi or viruses. They work by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria and are primarily excreted in urine, with absorption affected by food and certain metals. Tetracyclines have several side effects, contraindications during pregnancy and lactation, and are used in treating infections like pneumonia and cholera.