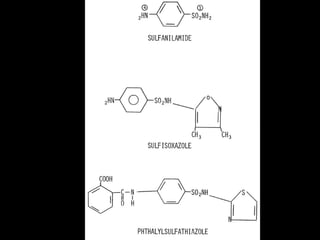
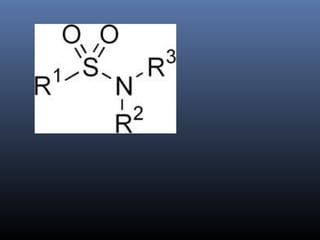
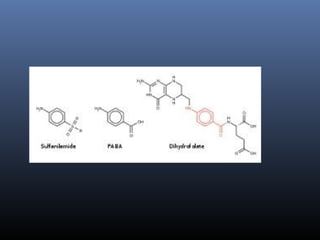
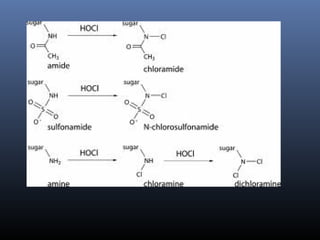
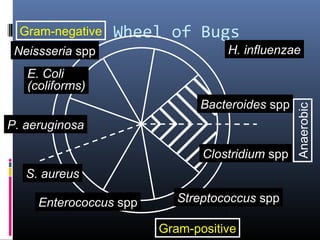
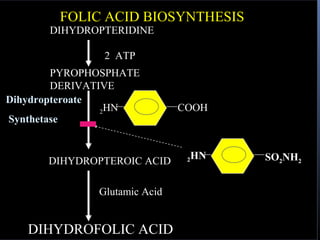
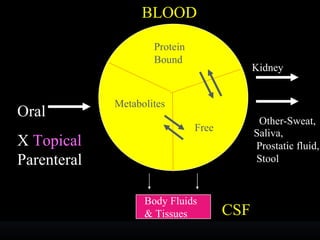
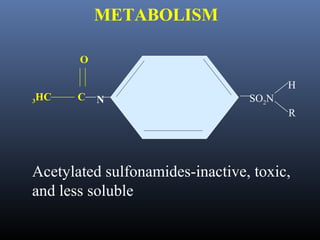
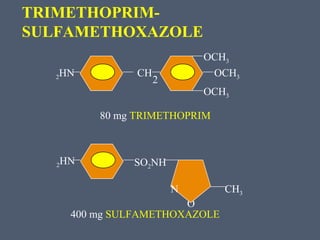
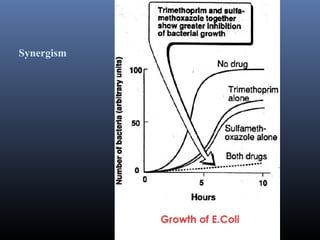
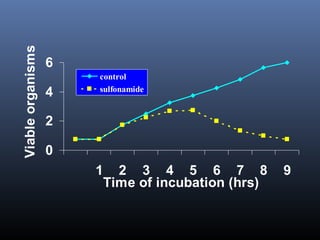
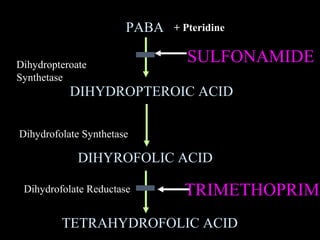
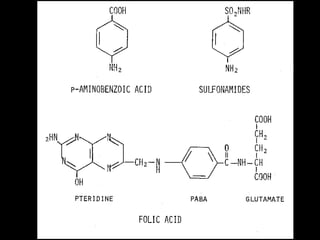
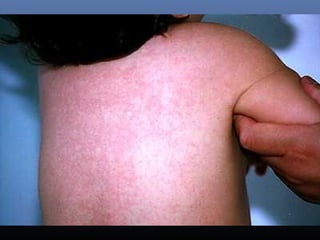
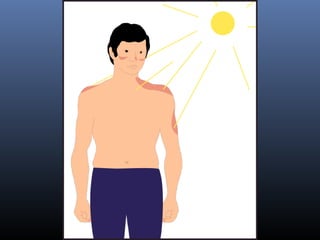
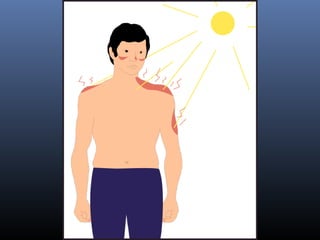
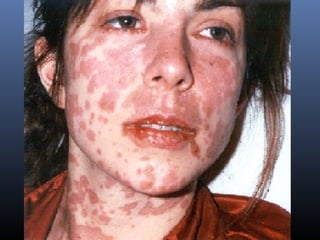
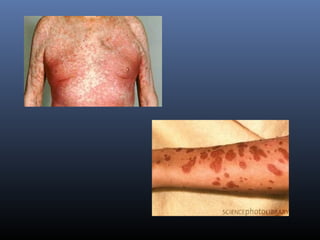
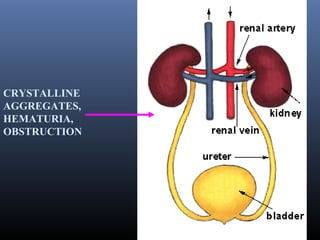
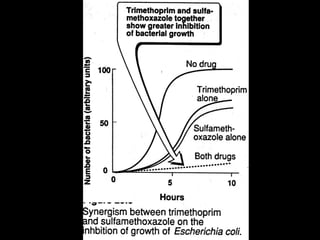
Sulfonamides were the first effective antibacterial agents discovered in the 1930s and were widely used before the development of penicillin. While now largely replaced by other antibiotics, they continue to have therapeutic uses. Key points include: sulfonamides work by inhibiting folic acid biosynthesis; they are excreted renally so dosage should be adjusted for renal impairment; and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is a commonly used combination that is synergistic and has expanded antimicrobial activity. Adverse effects can include allergic reactions and hematological effects like anemia.