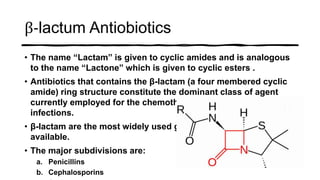
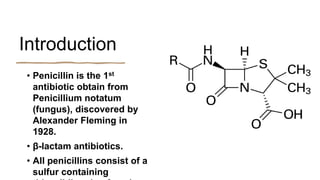
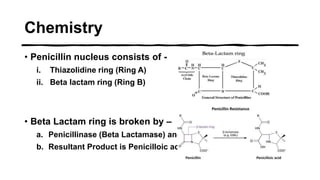
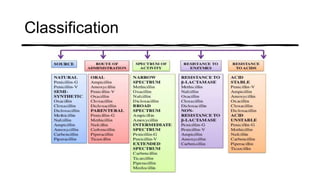
This document provides information on penicillin, including its history, chemistry, mechanisms of action, classifications, and resistance. It was discovered in 1928 by Alexander Fleming and was the first widely used antibiotic. It works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. There are natural, semi-synthetic, and extended-spectrum penicillins that show varied spectra and resistance profiles. Beta-lactamase inhibitors like clavulanic acid are often combined with penicillins to overcome resistance from these enzymes.