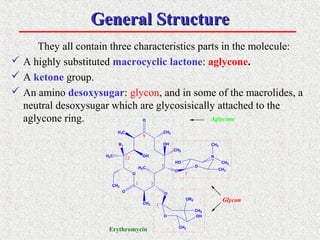
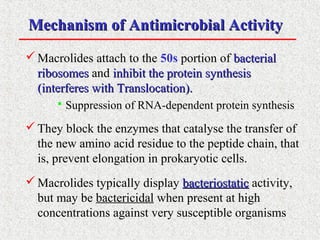
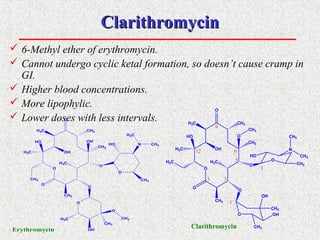
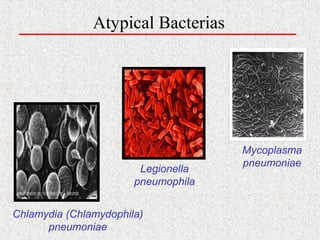
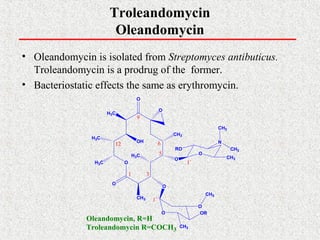
This document covers macrolide antibiotics, detailing their structure, mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, therapeutic applications, and adverse effects. Key macrolides like erythromycin, clarithromycin, and azithromycin are discussed, highlighting their effectiveness against various bacterial infections along with their stability and side effects. Additionally, chemical instability, spectrum of activity, and drug interactions are also addressed.