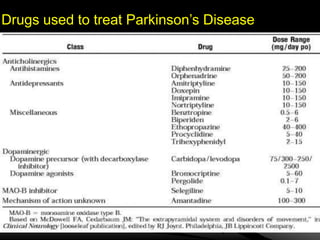
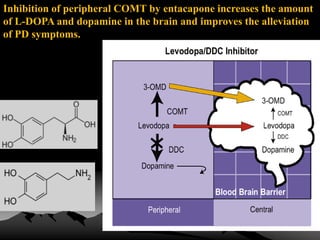
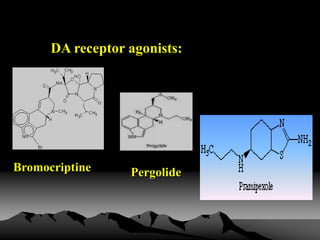
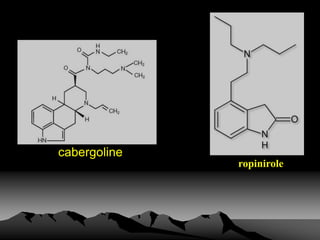
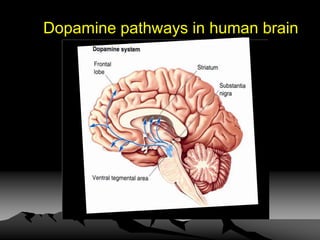
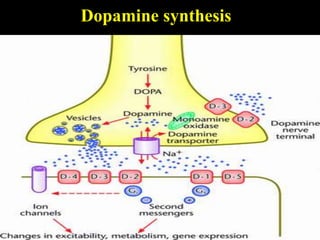
Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder caused by the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain. It is the second most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer's and mainly affects people over 65. The three main motor symptoms are tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia. Levodopa is the most effective treatment for the motor symptoms of Parkinson's but its efficacy decreases over time and is associated with motor complications. Other treatments include dopamine agonists, anticholinergics, COMT inhibitors, and deep brain stimulation. However, no treatment can slow or stop the progression of neuronal degeneration in Parkinson's.






![Causes of Parkinsonism
• Impaired release of dopamine- Idiopathic
parkinsonism.
• Drug depleting dopamine store-reserpine,
tetrabenzine.
• Toxin damaging dopaminergic neuron.
• Viral infection- Encephalitis ,Japanese encephalitis
• Trauma-repeated head injury[punch drunk syndrome]
• Miscellaneus-wilson disease,huntingtion,s disease](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parkinsondiseases-130701060255-phpapp01/85/Parkinson-diseases-7-320.jpg)

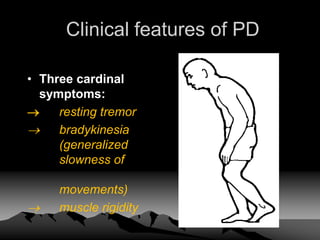
![CLINICAL FEATURE
• TREMORS(4-6hz):
• tremors[pill rolling] at rest, decreases on action.
Usually first in finger/thumb.
• Coarse flexion/extension of finger[pill rolling &
drum beating]
• RIGIDITY-
• Cog wheel type especially in upper limb
{stiffness in all direction of movement}.
• Plastic type {lead type} mostly appreciated in
legs. In trunk rigidity manifest by flexed& stooped
posture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parkinsondiseases-130701060255-phpapp01/85/Parkinson-diseases-12-320.jpg)