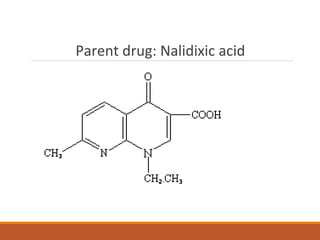
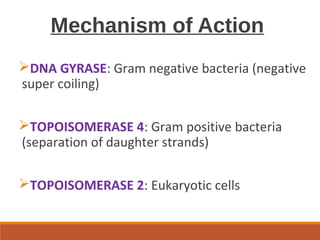
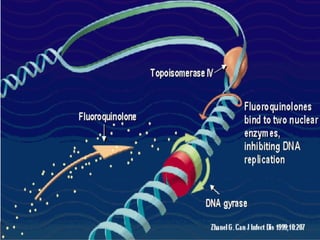
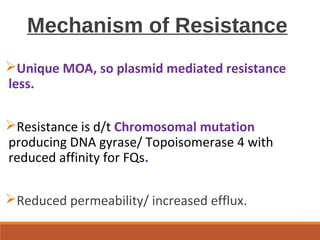
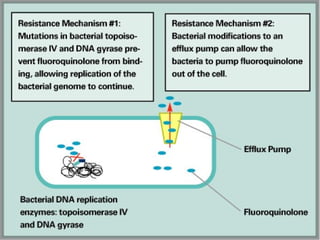
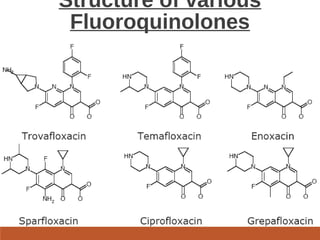
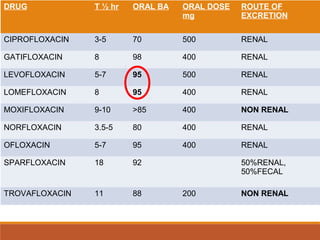
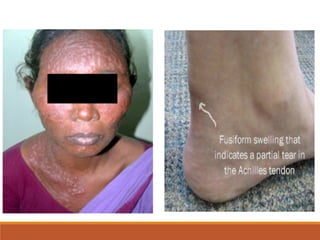
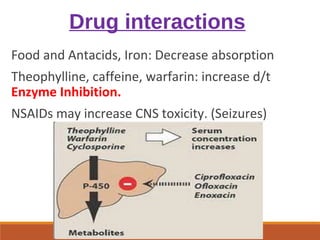
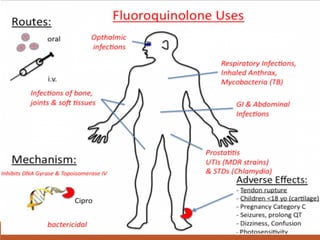
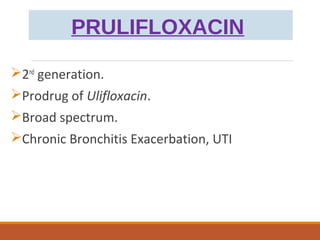
This document discusses fluoroquinolone antibiotics, including their parent drug nalidixic acid, mechanisms of action, classifications, and individual drug profiles. It notes that fluoroquinolones act by inhibiting DNA gyrase and topoisomerase enzymes in bacteria. Common adverse effects include gastrointestinal upset and neurological toxicity. Resistance can develop through chromosomal mutations in bacterial targets or reduced drug permeability. First-generation fluoroquinolones like ciprofloxacin are often used to treat urinary tract infections and respiratory infections.