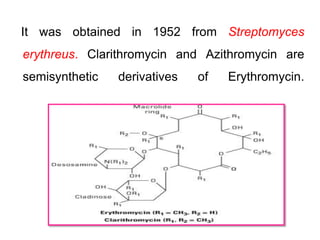
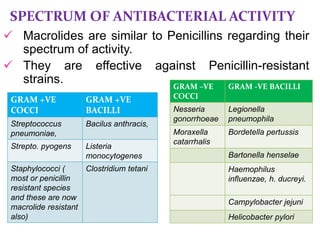
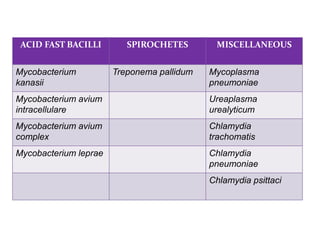
This document discusses macrolide antibiotics. It begins by introducing macrolides as a class of antibiotics characterized by a macrocyclic lactone ring to which sugars are attached. It then focuses on individual macrolides including erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin, roxithromycin, and spiramycin. The document discusses the mechanism of action, spectrum of activity, resistance, pharmacokinetics, uses, interactions, and adverse effects of macrolide antibiotics.